How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have
News Leon
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
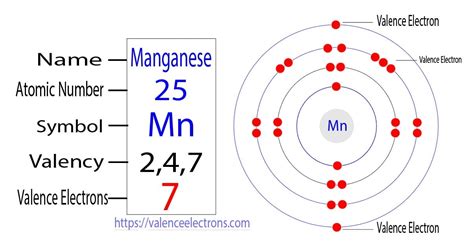
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have? A Deep Dive into Manganese's Electronic Structure
Manganese (Mn), a fascinating transition metal, plays a crucial role in various biological and industrial processes. Understanding its electronic structure, particularly the number of valence electrons, is key to comprehending its diverse chemical behavior. This article will delve deep into the electronic configuration of manganese, explaining how to determine its valence electrons and exploring the implications of this number on its reactivity and properties.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Before we focus on manganese, let's establish a foundational understanding of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom. These are the electrons that participate in chemical bonding, determining an element's reactivity and the types of chemical bonds it can form (ionic, covalent, metallic). The number of valence electrons significantly influences an element's chemical properties, such as its electronegativity, ionization energy, and oxidation states.
Determining Manganese's Electronic Configuration
To determine the number of valence electrons in manganese, we need to first establish its electronic configuration. Manganese's atomic number is 25, meaning it has 25 protons and 25 electrons in a neutral atom. Following the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule, the electronic configuration of manganese is:
1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d⁵
This configuration tells us the distribution of electrons across different energy levels (shells) and sub-shells within the atom.
- 1s², 2s², 2p⁶, 3s², 3p⁶: These represent the inner core electrons, which are tightly bound to the nucleus and do not typically participate in chemical bonding.
- 4s²3d⁵: These are the outermost electrons and are considered the valence electrons. The 4s subshell fills before the 3d subshell according to the Aufbau principle, but the 4s and 3d electrons have similar energies and often participate equally in chemical bonding for transition metals.
How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have? The Answer
Based on the electronic configuration, manganese possesses seven valence electrons. These seven electrons (two from the 4s orbital and five from the 3d orbital) are responsible for manganese's diverse chemical behavior and ability to form a wide range of compounds with varying oxidation states.
The Significance of Seven Valence Electrons
The presence of seven valence electrons has profound implications for manganese's properties:
1. Variable Oxidation States:
The seven valence electrons allow manganese to exhibit a wide range of oxidation states, from +2 to +7. This versatility is a hallmark of transition metals and is directly related to the relatively similar energies of the 4s and 3d electrons. The ability to lose varying numbers of electrons leads to the formation of numerous compounds with diverse properties. For instance, Mn²⁺ (in manganese(II) chloride) is quite different from Mn⁷⁺ (in potassium permanganate).
2. Complex Formation:
Manganese's d-orbital electrons contribute to its ability to form complex ions. The partially filled d-orbitals can accept electron pairs from ligands (molecules or ions that bond to a central metal ion), creating stable coordination complexes. These complexes play critical roles in biological systems and catalysis.
3. Catalytic Activity:
Manganese's variable oxidation states and ability to form complexes contribute to its catalytic activity in numerous reactions. Manganese-containing enzymes are essential in biological systems, playing critical roles in photosynthesis and other metabolic processes. Industrially, manganese catalysts find applications in various chemical transformations.
4. Magnetic Properties:
The unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals contribute to manganese's paramagnetic properties. This means manganese is attracted to external magnetic fields. The magnitude of paramagnetism is dependent on the oxidation state and the number of unpaired electrons.
5. Color in Compounds:
The d-d electronic transitions in manganese complexes result in the characteristic colors observed in many manganese compounds. The specific color depends on the oxidation state, the surrounding ligands, and the geometry of the complex.
Manganese in Different Oxidation States: A Closer Look
Let's briefly examine manganese in a few of its common oxidation states:
-
Mn²⁺ (Manganese(II)): This is a relatively stable oxidation state, often found in simple salts like MnCl₂ (manganese(II) chloride). It has a pale pink color in aqueous solutions.
-
Mn³⁺ (Manganese(III)): This oxidation state is less stable than Mn²⁺ and often found in complexes. It's known for its relatively strong oxidizing power.
-
Mn⁴⁺ (Manganese(IV)): This oxidation state is usually found in oxides like MnO₂ (manganese dioxide), a crucial component in batteries and catalysts.
-
Mn⁷⁺ (Manganese(VII)): This is the highest common oxidation state for manganese and is found in permanganate ions (MnO₄⁻), which are potent oxidizing agents with a characteristic deep purple color. Potassium permanganate (KMnO₄) is a common example.
Manganese's Importance in Biology and Industry
Manganese's unique properties, stemming directly from its seven valence electrons, contribute to its significance in various biological and industrial processes.
Biological Roles:
- Enzyme Cofactor: Manganese acts as an essential cofactor in several enzymes, including superoxide dismutase, which protects cells from damage by free radicals.
- Photosynthesis: Manganese plays a critical role in the oxygen-evolving complex in plants, facilitating the crucial process of photosynthesis.
- Bone Formation: Manganese contributes to bone formation and overall skeletal health.
Industrial Applications:
- Steel Production: Manganese is added to steel to enhance its strength, hardness, and toughness.
- Batteries: Manganese dioxide (MnO₂) is a key component in many dry-cell batteries.
- Pigments: Manganese compounds are used as pigments in paints and ceramics.
- Catalysis: Manganese catalysts are employed in various industrial chemical processes.
Conclusion: The Valence Electrons and the Versatile Nature of Manganese
The seven valence electrons of manganese are the key to understanding its diverse and significant roles in both biological and industrial settings. This number dictates its variable oxidation states, complex formation abilities, catalytic activity, magnetic properties, and the colors observed in its compounds. By appreciating the fundamental relationship between electron configuration and chemical properties, we can fully grasp the importance of this fascinating transition metal. The exploration of manganese's electronic structure highlights the power of understanding atomic structure in predicting and interpreting the behavior of elements and their compounds. Further research into manganese's unique properties continues to reveal new applications and expand our understanding of its critical roles in the world around us. The seemingly simple question, "How many valence electrons does Mn have?" opens the door to a rich understanding of the complexities of chemistry and the vital role of this element in our lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Make A Magnet At Home
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Decrease In Demand And An Increase In Supply Will
Mar 19, 2025
-
Prove The Square Root Of 5 Is Irrational
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Figure Shown Is A Rectangle With A Semicircle
Mar 19, 2025
-
Letter To A Principal From Parent
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
