A Decrease In Demand And An Increase In Supply Will
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
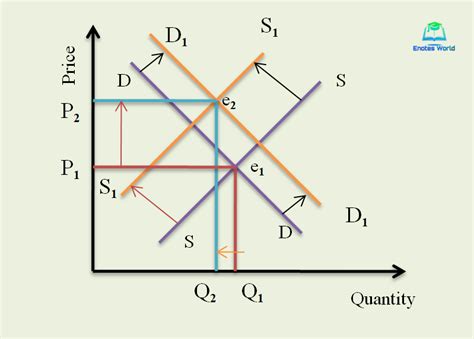
Table of Contents
A Decrease in Demand and an Increase in Supply Will… Lead to a Lower Price
The fundamental principles of supply and demand are cornerstones of economic theory. They dictate the price and quantity of goods and services in a market. Understanding how changes in these forces interact is crucial for businesses, consumers, and policymakers alike. This article delves into the consequences of a simultaneous decrease in demand and an increase in supply, exploring the mechanics, implications, and real-world examples of this economic scenario.
Understanding the Basics: Supply and Demand
Before exploring the combined effect of decreased demand and increased supply, it's important to revisit the individual concepts:
Demand: The Consumer's Desire
Demand represents the consumer's willingness and ability to purchase a good or service at various price points. Several factors influence demand, including:
- Price of the good: A higher price generally leads to lower demand (the law of demand).
- Consumer income: Higher incomes often translate to higher demand for normal goods, while demand for inferior goods might decrease.
- Prices of related goods: The demand for substitutes (e.g., butter and margarine) moves inversely, while the demand for complements (e.g., cars and gasoline) moves in the same direction.
- Consumer tastes and preferences: Changes in fashion, trends, or consumer perception can significantly impact demand.
- Consumer expectations: Anticipated future price changes or shortages can influence current demand.
A decrease in demand signifies a shift to the left of the demand curve, indicating consumers are willing to buy less at every price point. This might be due to a change in consumer tastes, a decrease in income, the rise of a substitute good, or negative publicity surrounding the product.
Supply: The Producer's Offering
Supply represents the producer's willingness and ability to offer a good or service at various price points. Factors affecting supply include:
- Price of the good: Higher prices incentivize producers to supply more (the law of supply).
- Input costs: Increases in the cost of raw materials, labor, or energy will reduce supply.
- Technology: Technological advancements can lead to increased efficiency and higher supply.
- Government policies: Taxes, subsidies, and regulations can influence supply.
- Producer expectations: Anticipations of future price changes or market conditions can affect current supply.
An increase in supply signifies a rightward shift of the supply curve, indicating producers are willing to offer more at every price point. This might result from technological improvements, lower input costs, government subsidies, or an influx of new producers into the market.
The Combined Effect: Decrease in Demand and Increase in Supply
When a decrease in demand occurs simultaneously with an increase in supply, the market equilibrium – the point where supply and demand intersect – shifts dramatically. The most significant consequence is a substantial decrease in the equilibrium price.
The Price Drop Explained
The decrease in demand reduces the quantity demanded at every price level. Simultaneously, the increase in supply increases the quantity supplied at every price level. This creates a surplus in the market – the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded. This surplus puts downward pressure on prices as producers compete to sell their goods. To clear the surplus, prices must fall until the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied at a new, lower equilibrium point.
Graphical Representation
Imagine a standard supply and demand graph. A decrease in demand shifts the demand curve to the left. An increase in supply shifts the supply curve to the right. The intersection of these two new curves represents the new equilibrium point, characterized by a significantly lower price and potentially a lower quantity than the original equilibrium.
Potential Scenarios and Nuances
While the general outcome is a price decrease, the magnitude of the price drop and the change in the equilibrium quantity depend on the relative magnitudes of the shifts in supply and demand.
- Large decrease in demand, small increase in supply: The price decrease will be significant, and the equilibrium quantity might even decrease.
- Small decrease in demand, large increase in supply: The price decrease will be substantial, and the equilibrium quantity will likely increase, but less than the increase in supply alone would have caused.
- Similar magnitude shifts: The price decrease will be moderate, and the effect on the equilibrium quantity will depend on the specifics of the curves.
Real-World Examples
Numerous real-world examples illustrate this economic principle:
- The Solar Panel Market: Advances in technology have led to a significant increase in the supply of solar panels, lowering their production costs. Simultaneously, decreased consumer demand due to economic downturns or changes in energy policies could further depress prices.
- The Smartphone Market: The relentless innovation in the smartphone industry constantly increases supply. However, saturation in developed markets and slower growth in emerging markets can lead to a decrease in demand, forcing prices downward.
- The Oil Market: Unexpectedly high oil production (increased supply) combined with a global economic slowdown (decreased demand) can cause a dramatic drop in oil prices, as witnessed in 2014-2016.
- The Agricultural Sector: Favorable weather conditions resulting in bumper crops (increased supply) alongside reduced consumer spending (decreased demand) can drive down agricultural product prices, potentially hurting farmers' incomes.
Implications and Considerations
The simultaneous decrease in demand and increase in supply has significant implications for various stakeholders:
- Producers: Producers will likely experience lower revenues and profits. They might need to adjust their production levels, cut costs, or even exit the market.
- Consumers: Consumers benefit from lower prices, allowing them to purchase goods at a more affordable rate. However, this can lead to concerns about quality if producers cut corners to maintain profitability.
- Government: Governments may need to implement policies to support affected industries, such as subsidies or tax breaks. They might also need to address issues related to market stability and potential job losses.
Strategies for Businesses Facing This Scenario
Businesses facing a decrease in demand and an increase in supply must adapt to survive:
- Cost Reduction: Streamlining operations and reducing production costs becomes crucial to maintain profitability at lower prices.
- Innovation and Differentiation: Developing new features, improving product quality, or focusing on niche markets can help businesses stand out and command better prices.
- Marketing and Promotion: Effective marketing campaigns can stimulate demand and create a stronger brand presence.
- Diversification: Expanding product lines or exploring new markets can mitigate the impact of a decline in a specific sector.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with other businesses can create synergies and improve market competitiveness.
Conclusion: Navigating the Shifting Sands of Supply and Demand
A simultaneous decrease in demand and increase in supply invariably leads to a lower price. Understanding this fundamental economic principle is essential for navigating the complexities of the market. Businesses must adapt to changing conditions through strategic planning, cost management, and innovative approaches. Consumers benefit from lower prices, although quality concerns might arise. Policymakers play a critical role in ensuring market stability and supporting industries affected by such shifts. The dynamic interplay of supply and demand continues to shape economic landscapes, making it a critical area of ongoing study and analysis. By understanding the intricacies of these forces, businesses and consumers can make informed decisions and navigate the market more effectively.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Calculate Boiling Point Of A Solution
Mar 19, 2025
-
Oxidation Number Of Cr In Cr2o72
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are The Importance Of Political Parties
Mar 19, 2025
-
Convert 59 Degrees Fahrenheit To Celsius
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is 120 Hours In Days
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Decrease In Demand And An Increase In Supply Will . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
