How Many Valence Electrons Are In Cesium
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
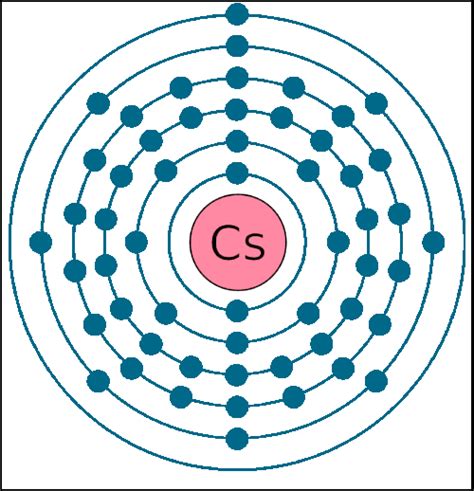
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Are in Cesium? A Deep Dive into Alkali Metals
Cesium, a fascinating element with a silvery-gold hue and a plethora of applications, sits proudly in Group 1 of the periodic table – the alkali metals. Understanding its electronic structure, particularly the number of valence electrons, is crucial to comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. This article will delve into the specifics of cesium's valence electrons, exploring its atomic structure, its place within the periodic table, and its resulting chemical properties. We’ll also touch upon some of its intriguing applications.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Reactivity
Before we zero in on cesium, let's establish a firm grasp on the concept of valence electrons. These are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom, also known as the valence shell. These electrons are the primary players in chemical bonding, determining how an atom interacts with other atoms to form molecules and compounds. The number of valence electrons dictates an element's reactivity, oxidation state, and the types of bonds it can form (ionic, covalent, metallic). Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share valence electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, often resembling that of a noble gas (a full outer shell).
Cesium's Position in the Periodic Table: A Telltale Sign
Cesium (Cs), with an atomic number of 55, resides in Group 1, Period 6 of the periodic table. This placement provides a crucial clue to its electronic structure. Group 1 elements, also known as alkali metals, are characterized by having one valence electron in their outermost shell. This single valence electron is easily lost, leading to the formation of a +1 cation (Cs⁺).
The Electronic Configuration of Cesium: Unraveling the Mystery
The electronic configuration of an atom dictates the arrangement of electrons in its various energy levels and subshells. Cesium's electronic configuration is [Xe] 6s¹. This notation tells us several key things:
- [Xe]: This represents the core electrons, which have the same electron configuration as Xenon (a noble gas). These core electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus and generally don't participate in chemical bonding.
- 6s¹: This indicates that there's one electron in the 6s subshell. The 6s subshell is the outermost shell, making this single electron the valence electron.
This clearly shows that cesium possesses only one valence electron.
The Chemical Behavior of Cesium: A Consequence of its Single Valence Electron
The presence of just one loosely held valence electron is the driving force behind cesium's chemical behavior. It readily loses this electron to achieve a stable octet (a full outer shell like the noble gases), resulting in the formation of a stable +1 ion (Cs⁺). This explains why cesium is highly reactive, especially with water and other oxidizing agents. The reaction with water is exceptionally vigorous, often resulting in a fiery explosion due to the rapid release of hydrogen gas.
Cesium's Reactions: A Closer Look
-
Reaction with Water: Cesium reacts violently with water, producing cesium hydroxide (CsOH) and hydrogen gas (H₂). The reaction is highly exothermic, releasing significant heat.
-
Reaction with Halogens: Cesium reacts readily with halogens (Group 17 elements like chlorine, bromine, and iodine) to form ionic compounds called cesium halides (e.g., CsCl, CsBr, CsI). These reactions are also highly exothermic.
-
Reaction with Oxygen: Cesium reacts with oxygen to form cesium oxides, including the superoxide (CsO₂) and peroxide (Cs₂O₂).
-
Reaction with Acids: Cesium reacts vigorously with acids, displacing hydrogen gas and forming cesium salts.
Applications of Cesium: Harnessing its Unique Properties
Cesium's unique properties, stemming directly from its single valence electron and resulting reactivity, have led to several important applications:
-
Atomic Clocks: Cesium's highly precise atomic transitions are exploited in atomic clocks, which are among the most accurate timekeeping devices ever developed. These clocks are critical for various applications, including GPS systems and scientific research.
-
Oil and Gas Exploration: Cesium formate is used in drilling fluids for oil and gas exploration. Its high density helps increase the efficiency of the drilling process.
-
Medical Applications: While not as widespread as other elements, cesium has some niche medical applications, though these often involve its radioactive isotopes rather than its chemical properties.
-
Photoelectric Cells: Cesium is used in photoelectric cells due to its low ionization energy; it readily emits electrons when exposed to light.
Beyond the Basics: Delving Deeper into Cesium's Electronic Structure
While we've established that cesium has one valence electron, a more nuanced understanding requires examining the quantum mechanical description of its electron orbitals. The single valence electron occupies the 6s orbital, which is a relatively high energy level compared to the core electrons. This higher energy level contributes to cesium's low ionization energy and high reactivity. The larger size of the cesium atom, also a consequence of its position in the periodic table, further contributes to the ease with which it loses its valence electron.
Comparing Cesium to Other Alkali Metals: Identifying Similarities and Differences
Cesium shares many similarities with other alkali metals, primarily due to their commonality of having a single valence electron. However, there are also differences, particularly in reactivity. Cesium is the most reactive of all the alkali metals due to its low ionization energy and large atomic size. This high reactivity necessitates careful handling and storage of cesium to prevent hazardous reactions.
Conclusion: The Significance of Cesium's Single Valence Electron
In conclusion, cesium possesses one valence electron, a characteristic that dictates its chemical properties, reactivity, and a range of applications. Its placement in Group 1 of the periodic table and its electronic configuration ([Xe] 6s¹) clearly demonstrate this. Understanding the significance of this single valence electron is key to appreciating cesium's unique role in chemistry and its diverse applications in various fields, from atomic clocks to oil exploration. This single electron, seemingly insignificant in number, holds the key to cesium's remarkable characteristics and contributions to modern technology and science. Further research and exploration into its properties will undoubtedly unlock even more exciting applications for this remarkable element in the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Homogeneous Mixture Of Two Or More Substances Is A
Mar 26, 2025
-
In Which Stage Of Meiosis Crossing Over Occurs
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Lymphoid Organ
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Reason For Doing A Test Cross
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is The Following Relation A Function
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Are In Cesium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
