How Many Neutrons Does Sr Have
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
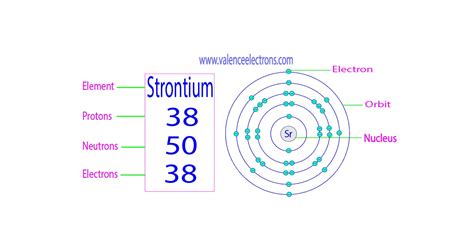
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons Does Strontium (Sr) Have? Isotopes, Abundance, and Applications
Strontium (Sr), a fascinating alkaline earth metal, doesn't have a single answer to the question of how many neutrons it possesses. This is because strontium exists in nature as a mixture of several isotopes. Each isotope of strontium has the same number of protons (38, defining it as strontium), but differs in the number of neutrons. Understanding this variation is key to comprehending strontium's properties and applications. This article will delve deep into the isotopic composition of strontium, exploring the number of neutrons in each isotope, their abundance, and the broader implications for scientific applications.
Understanding Isotopes and Atomic Structure
Before diving into strontium's specifics, let's briefly review the fundamentals of atomic structure. An atom consists of a nucleus containing protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral charge), surrounded by a cloud of electrons (negatively charged). The number of protons determines the element's atomic number and its place on the periodic table. The number of neutrons, however, can vary, leading to different isotopes of the same element.
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. This difference in neutron number affects the atom's mass but not its chemical properties significantly. The mass number of an isotope is the sum of its protons and neutrons. For example, an isotope denoted as ¹⁰⁷Ag has 47 protons (atomic number of silver) and 60 neutrons (107 - 47 = 60).
Strontium Isotopes: A Detailed Look
Strontium (Sr) has four stable isotopes found naturally:
- ⁸⁴Sr: This isotope contains 38 protons and 46 neutrons (84 - 38 = 46).
- ⁸⁶Sr: This isotope has 38 protons and 48 neutrons (86 - 38 = 48).
- ⁸⁷Sr: This isotope possesses 38 protons and 49 neutrons (87 - 38 = 49).
- ⁸⁸Sr: This is the most abundant isotope of strontium, containing 38 protons and 50 neutrons (88 - 38 = 50).
In addition to these stable isotopes, several radioactive isotopes of strontium exist, including:
- ⁹⁰Sr: This radioactive isotope is a significant byproduct of nuclear fission and is particularly concerning due to its long half-life and potential for bioaccumulation. It has 38 protons and 52 neutrons (90 - 38 = 52).
The number of neutrons directly impacts the isotope's mass and stability. Isotopes with an unstable neutron-proton ratio tend to be radioactive, undergoing decay to achieve a more stable configuration. This decay process often involves the emission of particles like alpha, beta, or gamma radiation.
Isotopic Abundance and Average Atomic Mass
The abundance of each strontium isotope varies in different geological samples. The average atomic mass of strontium, listed on the periodic table (approximately 87.62 amu), is a weighted average reflecting the abundance of each isotope. ⁸⁸Sr is the most abundant isotope, contributing significantly to the average atomic mass. The relative abundance of each isotope is crucial in various scientific applications, especially in geochemistry and archaeology.
Variations in strontium isotopic ratios in different geological formations provide valuable information for dating rocks and understanding geological processes. This is because the relative abundance of strontium isotopes can change over geological time scales due to radioactive decay of certain isotopes. Analyzing these variations helps scientists trace the origin of rocks and minerals, reconstruct past geological events, and even investigate the formation of planetary bodies.
Applications of Strontium and its Isotopes
Strontium and its isotopes find applications in diverse fields, capitalizing on their unique properties:
1. Geochronology and Geochemistry:
As mentioned earlier, the varying ratios of strontium isotopes are fundamental tools in geochronology. Scientists use ⁸⁷Sr/⁸⁶Sr ratios to date rocks and minerals, providing insights into geological timelines and Earth's history. The variations in strontium isotopic ratios are also used to trace the origin of rocks and minerals, helping to understand geological processes like magmatism, metamorphism, and weathering.
2. Archaeology and Anthropology:
Strontium isotope analysis is a powerful tool in archaeology and anthropology. By analyzing the strontium isotope ratios in human remains (teeth and bones), researchers can determine the geographical origin of individuals. This technique helps reconstruct migration patterns, trace ancient trade routes, and provide insights into human movement and settlement patterns throughout history.
3. Medical Applications:
Certain strontium isotopes have medical applications. For example, ⁸⁹Sr is used in radiotherapy to treat bone cancer. It targets bone tissue, delivering radiation directly to cancerous cells, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. However, careful handling is necessary due to its radioactivity.
4. Materials Science:
Strontium compounds are used in various materials science applications. Strontium titanate (SrTiO₃), for example, is a versatile material with applications in electronics and optics due to its high dielectric constant and refractive index. Strontium ferrite is a crucial component in high-frequency magnetic devices.
5. Pyrotechnics:
Strontium salts are employed in pyrotechnics to produce a vibrant red color in fireworks and flares. The excitation of strontium atoms during combustion emits characteristic red light, creating the dazzling spectacle we associate with fireworks.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Strontium's Isotopic Composition
The question of how many neutrons strontium has isn't straightforward. It highlights the importance of understanding isotopes and their variations. The different isotopes of strontium, with their varying neutron numbers, play crucial roles in diverse fields. From dating rocks and tracing human migration to medical applications and materials science, strontium's isotopic composition holds immense scientific and practical value. Continued research into strontium isotopes will undoubtedly lead to further advancements and discoveries in various scientific disciplines. The detailed understanding of its isotopic abundance and properties enhances our ability to interpret geological processes, trace historical events, and develop new technologies. The versatility of strontium and its isotopes showcases the remarkable impact of nuclear structure on the properties and applications of elements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 6 25 As A Fraction
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Compounds Is Ionic
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Characteristic Is Common To All Chordates
Mar 28, 2025
-
Give The Major Product For The Following Reaction
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is India In The Northern Or Southern Hemisphere
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Does Sr Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
