How Does An Aneroid Barometer Work
News Leon
Mar 26, 2025 · 7 min read
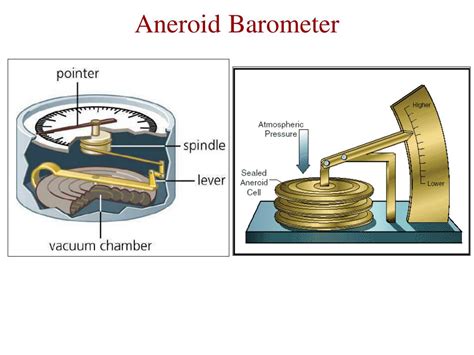
Table of Contents
How Does an Aneroid Barometer Work? A Deep Dive into Atmospheric Pressure Measurement
The seemingly simple aneroid barometer, a staple in weather forecasting and aviation for over a century, holds a fascinating mechanism within its compact casing. Understanding how this device accurately measures atmospheric pressure, a crucial factor in weather prediction and altitude determination, requires a look into its intricate design and the principles of physics it employs. This comprehensive guide will demystify the inner workings of an aneroid barometer, exploring its components, functionality, and applications.
Understanding Atmospheric Pressure: The Foundation of Barometric Measurement
Before delving into the specifics of the aneroid barometer, it's crucial to grasp the concept of atmospheric pressure. Atmospheric pressure is the force exerted by the weight of the air column above a given point on the Earth's surface. This pressure varies depending on several factors:
-
Altitude: Pressure decreases with increasing altitude because there's less air above to exert force. This is a fundamental principle in aviation, where altitude is often determined using barometric pressure.
-
Temperature: Warmer air is less dense than colder air, resulting in lower pressure at higher temperatures.
-
Weather Systems: High-pressure systems generally indicate fair weather, while low-pressure systems often precede storms and precipitation. Changes in pressure are key indicators in weather forecasting.
-
Humidity: Moist air is less dense than dry air, leading to slightly lower pressure in humid conditions.
The Anatomy of an Aneroid Barometer: Dissecting the Components
The aneroid barometer doesn't rely on a column of liquid like a mercury barometer. Instead, its core component is a sealed, evacuated metal cell known as an aneroid capsule (also sometimes referred to as a vacuum capsule or simply a capsule). This is where the magic happens. Let's break down the key parts:
1. The Aneroid Capsule: The Heart of the Barometer
The aneroid capsule is a flexible, hermetically sealed metal container from which most of the air has been evacuated. It's typically made of a corrugated, thin-walled metal alloy, often phosphor bronze or beryllium copper, allowing it to expand and contract easily. The near-vacuum within creates a flexible, responsive membrane to external air pressure changes.
How does it respond to pressure changes? When atmospheric pressure increases, it compresses the capsule, making it slightly smaller. Conversely, when atmospheric pressure decreases, the capsule expands. This minuscule expansion and contraction is the fundamental principle behind the barometer's operation.
2. The Linkage System: Translating Movement into Readable Data
The minute movements of the aneroid capsule are too small to be directly read. Therefore, a sophisticated linkage system amplifies these changes into larger, more easily observable movements. This system usually consists of a series of levers and gears connected to the capsule.
This linkage system magnifies the capsule's tiny changes, transforming them into a much larger rotational movement. This rotational movement is precisely calibrated to ensure accurate pressure readings.
3. The Pointer and Dial: Visualizing Atmospheric Pressure
The amplified movement from the linkage system is transferred to a pointer that rotates across a calibrated dial. This dial is marked in units of pressure, typically millibars (mb), hectopascals (hPa), inches of mercury (inHg), or even millimeters of mercury (mmHg). The pointer's position directly indicates the current atmospheric pressure.
The dial itself often includes additional markings for weather interpretation. These might include labeled zones indicating "Fair," "Change," or "Stormy" based on the pressure reading. These are guidelines and should be interpreted in conjunction with other weather data.
4. The Adjustment Mechanism: Ensuring Accuracy
Most aneroid barometers include a small screw or lever that allows for calibration adjustment. This is crucial because the capsule's sensitivity can change over time due to factors like temperature and aging. Regular calibration ensures the barometer provides accurate readings. This is often accomplished by referencing a known accurate pressure reading from another source, or by making minor adjustments for local altitude.
5. The Casing: Protection and Aesthetics
The entire mechanism is enclosed in a protective casing, usually made of metal or plastic. This casing protects the sensitive internal components from damage and environmental factors while also providing a suitable platform for the dial and pointer. The casing also often incorporates features such as a protective glass cover over the dial and a hanging hook for easy mounting.
How the Aneroid Barometer Works: A Step-by-Step Explanation
-
Atmospheric Pressure Acts on the Capsule: The evacuated aneroid capsule is highly sensitive to changes in external atmospheric pressure. When atmospheric pressure rises, it compresses the capsule. When atmospheric pressure falls, the capsule expands.
-
Capsule Movement is Amplified: The tiny movements of the capsule are amplified by the linkage system, magnifying the changes to a visible degree.
-
Amplified Movement Rotates the Pointer: The magnified movement is transferred to the pointer, causing it to rotate across the calibrated dial.
-
The Dial Displays the Pressure: The position of the pointer on the dial directly corresponds to the current atmospheric pressure, providing a clear visual indication of the atmospheric conditions.
-
Calibration Ensures Accuracy: The small adjustment mechanism allows users to calibrate the barometer, maintaining its accuracy over time.
Applications of Aneroid Barometers: Beyond Weather Forecasting
While widely known for weather forecasting, aneroid barometers have diverse applications:
-
Aviation: Aircraft altimeters use aneroid barometers to measure altitude. By knowing the pressure at sea level and comparing it to the pressure at the aircraft's current altitude, the altimeter calculates the height above sea level.
-
Hiking and Mountaineering: Hikers and mountaineers use aneroid barometers (or altimeters) to determine their altitude, aid navigation, and gauge weather changes in mountainous areas.
-
Scientific Research: Aneroid barometers are employed in meteorological research and various scientific studies where precise pressure measurement is required.
-
Home Weather Monitoring: Many households utilize aneroid barometers as an aesthetically pleasing and functional way to monitor local weather trends.
-
Industrial Applications: Some industrial processes require precise pressure monitoring, and aneroid barometers can fulfill this need in various scenarios.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Aneroid Barometers
Advantages:
-
Portability and Durability: Aneroid barometers are relatively compact and robust, making them ideal for portable applications.
-
Simplicity and Ease of Use: They are easy to read and require minimal maintenance.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to other types of barometers, aneroid barometers are generally more affordable.
-
Aesthetic Appeal: Their classic design makes them attractive additions to any home or office.
Disadvantages:
-
Sensitivity to Temperature and Altitude: Temperature changes can affect the accuracy of the readings, and they need to be adjusted for altitude.
-
Limited Precision: Aneroid barometers generally offer less precision compared to digital or mercury barometers.
-
Potential for Mechanical Wear: Over time, the mechanical parts can wear down, reducing accuracy. Regular calibration is essential.
-
Dependence on Calibration: The accuracy of an aneroid barometer relies heavily on proper calibration and adjustment, which requires some level of user knowledge.
Maintaining and Calibrating Your Aneroid Barometer
To maintain the accuracy of your aneroid barometer, follow these guidelines:
-
Avoid Shocks and Vibrations: Protect the barometer from impacts or excessive vibrations to prevent damage to the internal mechanism.
-
Regular Cleaning: Gently wipe the casing with a soft cloth to remove dust and debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals.
-
Periodic Calibration: While not a frequent necessity, periodic calibration using a known pressure source or professional calibration services will ensure the continued accuracy of the readings. This is often recommended annually or if there are any indications of inaccuracy.
-
Consider Environmental Factors: Remember that temperature and altitude variations influence readings; compensate where applicable.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the Aneroid Barometer
The aneroid barometer, despite its seemingly simple design, is a marvel of mechanical engineering. Its ability to accurately measure atmospheric pressure, a key parameter for weather forecasting and altitude determination, has made it an indispensable tool for centuries. While modern technology offers digital alternatives, the classic elegance and functional reliability of the aneroid barometer remain appealing to both professionals and enthusiasts. Understanding its inner workings allows for a deeper appreciation of its enduring legacy in the world of scientific instrumentation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Boiling Water Is A Chemical Change
Mar 29, 2025
-
An Oscillating Block Spring System Has A Mechanical Energy
Mar 29, 2025
-
A Manager Who Maintains A Stakeholder View Will
Mar 29, 2025
-
In Which Organelle Does Cellular Respiration Take Place
Mar 29, 2025
-
A Carbohydrate That Makes Up The Exoskeleton Of Insects
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does An Aneroid Barometer Work . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
