Hcl Is A Compound Or Element
News Leon
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
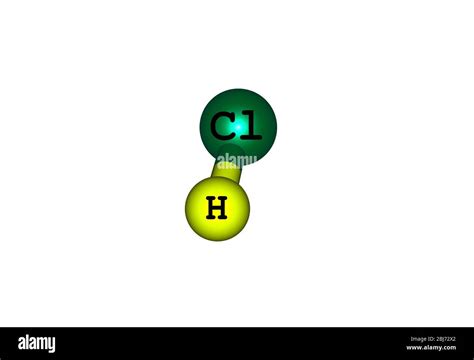
Table of Contents
HCL: Is it a Compound or an Element? A Deep Dive into Chemical Composition
Understanding the fundamental building blocks of matter is crucial in chemistry. This article delves into the classification of hydrogen chloride (HCl), clarifying whether it's an element or a compound. We'll explore the definitions of elements and compounds, examine the molecular structure of HCl, and discuss its properties to definitively answer this question. We'll also touch upon related concepts like ionic compounds, acids, and the difference between molecules and compounds.
Elements vs. Compounds: A Foundational Distinction
Before we classify HCl, let's establish a clear understanding of the terms "element" and "compound."
What is an Element?
An element is a pure substance consisting entirely of one type of atom. Atoms are the fundamental units of matter, characterized by their atomic number, which represents the number of protons in their nucleus. The periodic table organizes all known elements based on their atomic number and chemical properties. Examples of elements include hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), carbon (C), and iron (Fe). Elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
What is a Compound?
A compound, on the other hand, is a substance formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio. This chemical bonding involves the sharing or transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in a new substance with distinct properties from its constituent elements. The properties of a compound are different from the properties of the elements that make it up. For example, water (H₂O) is a compound formed from hydrogen and oxygen. It's a liquid at room temperature, while its constituent elements—hydrogen and oxygen—are gases. Compounds can be broken down into simpler substances (their constituent elements) through chemical reactions.
The Case of Hydrogen Chloride (HCl)
Now, let's focus on hydrogen chloride (HCl). To determine whether it's an element or a compound, we need to examine its composition and structure.
The Molecular Structure of HCl
HCl is composed of two different elements: hydrogen (H) and chlorine (Cl). These atoms are bonded together covalently, meaning they share a pair of electrons to form a stable molecule. This shared electron pair creates a strong bond between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms. The resulting molecule, HCl, is a distinct chemical entity with its own unique properties.
Evidence Supporting HCl as a Compound
Several pieces of evidence definitively classify HCl as a compound:
- Presence of Multiple Elements: HCl contains two different elements, hydrogen and chlorine. This is the fundamental defining characteristic of a compound.
- Fixed Ratio: The atoms in HCl are always present in a 1:1 ratio. One hydrogen atom is bonded to one chlorine atom. This fixed ratio distinguishes compounds from mixtures, where the ratio of components can vary.
- Distinct Properties: HCl possesses properties that are different from those of hydrogen and chlorine. For instance, hydrogen and chlorine are both gases at room temperature, while HCl is a gas but readily dissolves in water to form hydrochloric acid, a strong acid. This difference in properties strongly suggests the formation of a new substance—a compound.
- Chemical Reactions: HCl can participate in various chemical reactions, resulting in the formation of other compounds. This reactivity further highlights its distinct chemical identity as a compound.
HCl: Beyond the Compound Classification
While definitively classifying HCl as a compound is straightforward, exploring its further properties deepens our understanding.
HCl as an Acid
Hydrochloric acid (HCl(aq)), formed when hydrogen chloride gas dissolves in water, is a strong acid. Acids are substances that donate protons (H⁺ ions) in aqueous solutions. HCl readily donates its proton, resulting in a high concentration of H⁺ ions in the solution. This high concentration of H⁺ ions is what gives hydrochloric acid its acidic properties, such as its ability to react with bases, change the color of indicators (like litmus paper), and corrode metals.
HCl as an Ionic Compound (in Solution)
In aqueous solutions, HCl behaves as an ionic compound. Although the HCl molecule is covalently bonded, the interaction with water molecules causes the hydrogen-chlorine bond to break heterolytically. This means the electrons from the covalent bond are unevenly distributed. Consequently, H+ and Cl- ions exist independently in the solution. This dissociation is crucial to understanding HCl's behavior as a strong acid and its various applications.
Molecules vs. Compounds: An Important Clarification
It's essential to distinguish between molecules and compounds. All compounds are made up of molecules, but not all molecules are compounds. A molecule is simply a group of two or more atoms bonded together. This group of atoms can be of the same element (like O₂ - oxygen gas), or of different elements (like H₂O - water). Compounds are a subset of molecules, specifically those containing two or more different elements. Therefore, while HCl is both a molecule and a compound, oxygen gas (O₂) is a molecule but not a compound.
Real-World Applications of Hydrogen Chloride
HCl finds numerous applications across various industries:
- Industrial Production: HCl is used extensively in the production of various chemicals, including PVC (polyvinyl chloride) plastics, and other organic compounds.
- Metal Cleaning: Its acidic nature makes it useful for cleaning metals, removing rust, and etching surfaces.
- Food Processing: In controlled amounts, HCl is sometimes used as a food additive and is a component of stomach acid.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: It’s used in the synthesis of certain pharmaceuticals.
- Laboratory Use: HCl is a common reagent in chemical laboratories, used in various analytical and synthetic procedures.
Conclusion: Understanding HCL's Chemical Nature
In conclusion, hydrogen chloride (HCl) is unequivocally a compound. It comprises two different elements, hydrogen and chlorine, chemically bonded together in a fixed 1:1 ratio. Its unique properties, distinct from those of its constituent elements, its behavior as a strong acid in solution, and its numerous applications further solidify its classification as a compound. Understanding the fundamental distinctions between elements and compounds is crucial for grasping the basics of chemistry and appreciating the diverse roles these substances play in our world. The complexities of HCl, such as its behavior as an ionic compound in solution, demonstrate the intricate nature of chemical bonding and reactivity, highlighting the rich tapestry of chemical interactions. Further exploration of this compound can lead to a deeper understanding of chemical principles and their applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Equivalent Capacitance Of The Four Capacitors
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Primary Air Pollutant
Apr 03, 2025
-
Hydrogen Peroxide Is Exposed To Sunlight
Apr 03, 2025
-
Is Nh2 Electron Donating Or Withdrawing
Apr 03, 2025
-
In Two Sentences Describe Your Favorite Meal
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Hcl Is A Compound Or Element . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
