Balance This Equation C2h6 O2 Co2 H2o
News Leon
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
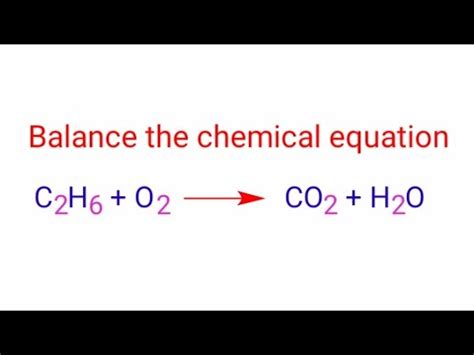
Table of Contents
Balancing the Equation: C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
Balancing chemical equations is a fundamental concept in chemistry. It's crucial for understanding stoichiometry, which governs the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. This article will delve deep into balancing the combustion reaction of ethane (C₂H₆) with oxygen (O₂), resulting in carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O). We'll explore various methods, explain the underlying principles, and touch upon the practical significance of this balanced equation.
Understanding the Combustion of Ethane
Before we jump into the balancing process, let's understand the reaction itself. Ethane (C₂H₆) is a simple alkane, a hydrocarbon containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms. Combustion is a rapid reaction with oxygen (O₂) that releases a significant amount of energy in the form of heat and light. In the case of ethane combustion, the products are carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O). This is a classic example of an exothermic reaction. The unbalanced equation representing this reaction is:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
This equation, in its unbalanced form, simply states the reactants and products involved. However, it doesn't reflect the accurate ratio of molecules involved in the reaction. This is where balancing comes in.
Methods for Balancing Chemical Equations
Several methods can be used to balance chemical equations. We'll explore two common approaches:
1. Balancing by Inspection
This method involves systematically adjusting the coefficients (the numbers in front of the chemical formulas) until the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. It's often a trial-and-error process, particularly for simpler equations.
Let's try this with our ethane combustion equation:
-
Balance Carbon (C): There are two carbon atoms on the left (in C₂H₆), so we need two carbon dioxide molecules on the right:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → 2CO₂ + H₂O
-
Balance Hydrogen (H): There are six hydrogen atoms on the left (in C₂H₆), and each water molecule (H₂O) contains two hydrogen atoms. Therefore, we need three water molecules on the right:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → 2CO₂ + 3H₂O
-
Balance Oxygen (O): Now, let's count the oxygen atoms. On the right side, we have four oxygen atoms from 2CO₂ (2 x 2 = 4) and three oxygen atoms from 3H₂O (3 x 1 = 3), totaling seven oxygen atoms. To balance this, we need ⁷/₂ O₂ molecules on the left:
C₂H₆ + ⁷/₂O₂ → 2CO₂ + 3H₂O
While this balances the equation, it's generally preferred to have whole-number coefficients. To achieve this, we multiply the entire equation by 2:
2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O
This is now the balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of ethane.
2. Algebraic Method
The algebraic method provides a more systematic approach, particularly useful for complex equations. This method involves assigning variables to the coefficients and setting up a system of algebraic equations based on the conservation of atoms.
Let's apply this method to our ethane combustion:
-
Assign variables to the coefficients:
aC₂H₆ + bO₂ → cCO₂ + dH₂O
-
Set up equations based on atom conservation:
- Carbon (C): 2a = c
- Hydrogen (H): 6a = 2d
- Oxygen (O): 2b = 2c + d
-
Solve the system of equations: We can choose a value for one variable and solve for the others. Let's set a = 1:
- c = 2a = 2
- d = 3a = 3
- 2b = 2(2) + 3 = 7 => b = ⁷/₂
-
To obtain whole-number coefficients, multiply all coefficients by 2:
2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O
This confirms the balanced equation obtained using the inspection method.
Significance of the Balanced Equation
The balanced equation, 2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O, carries significant meaning:
-
Stoichiometric Ratios: It shows the precise molar ratios of reactants and products. For every 2 moles of ethane reacted, 7 moles of oxygen are required, producing 4 moles of carbon dioxide and 6 moles of water.
-
Quantitative Calculations: This equation forms the basis for various stoichiometric calculations. For example, we can calculate the mass of carbon dioxide produced from a given mass of ethane, or the volume of oxygen consumed in a reaction.
-
Understanding Reaction Efficiency: The balanced equation helps determine the limiting reactant in a reaction – the reactant that is completely consumed first, thus limiting the amount of product formed.
-
Environmental Implications: The balanced equation is vital in understanding the environmental impact of ethane combustion. It highlights the amount of greenhouse gas (CO₂) produced, enabling assessments of its contribution to climate change.
Incomplete Combustion of Ethane
It's important to note that the equation above represents complete combustion. Under conditions with limited oxygen supply, incomplete combustion can occur, producing carbon monoxide (CO) and/or soot (carbon, C) in addition to carbon dioxide and water. The equations for incomplete combustion are more complex and will vary depending on the oxygen availability. Examples include:
- 2C₂H₆ + 5O₂ → 4CO + 6H₂O (Producing carbon monoxide)
- 2C₂H₆ + 3O₂ → 4C + 6H₂O (Producing soot)
The actual products of combustion depend on factors like the ethane-to-oxygen ratio, temperature, and pressure.
Practical Applications
The balanced equation for ethane combustion has numerous practical applications:
-
Industrial Processes: Ethane is a valuable feedstock in the petrochemical industry. Understanding its combustion is crucial for designing efficient and safe combustion processes in power generation and industrial heating applications.
-
Internal Combustion Engines: The combustion of hydrocarbons, including ethane (although less common than other alkanes like propane and butane), is fundamental to the operation of internal combustion engines. Balancing the equation is essential for engine design and optimization.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Accurate knowledge of the combustion products is vital for monitoring and regulating emissions from various sources, contributing to environmental protection efforts.
-
Energy Calculations: Thermochemical calculations, using the balanced equation, allow us to determine the enthalpy change (heat released) during ethane combustion, which is essential for assessing its energy content.
Conclusion
Balancing the chemical equation for the combustion of ethane, 2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O, is more than just a mathematical exercise. It's a fundamental step in understanding the stoichiometry of the reaction, enabling quantitative calculations, assessing environmental impacts, and optimizing various industrial processes. The ability to balance chemical equations is crucial for anyone working in chemistry, chemical engineering, or related fields. Furthermore, understanding both complete and incomplete combustion scenarios provides a comprehensive view of this important chemical reaction and its real-world implications. By mastering this skill, one gains a deeper appreciation for the quantitative nature of chemical reactions and their impact on our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Determine The Value Of X In The Figure
Mar 28, 2025
-
In The Figure Light Is Incident At Angle
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is It Easier To Swim In Salt Water
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 9 11 As A Decimal
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Square Is Cut Into 4 Identical Rectangles
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Balance This Equation C2h6 O2 Co2 H2o . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
