Area Of A Circle With A Radius Of 8
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
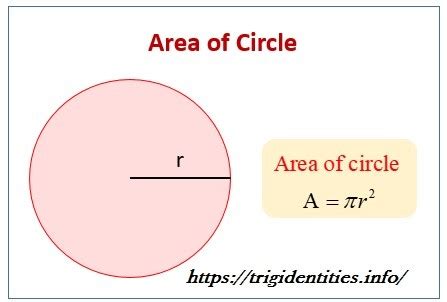
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into the Area of a Circle with an 8-Unit Radius
The seemingly simple question – what is the area of a circle with a radius of 8 units? – opens a door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, mathematical principles, and their practical applications. While the calculation itself is straightforward, understanding the underlying concepts and exploring related topics enhances our mathematical literacy and problem-solving skills. This article will delve deep into this seemingly simple problem, unpacking the formula, exploring its historical context, and demonstrating its relevance in various fields.
Understanding the Formula: πr²
The area of any circle is determined by a single, crucial measurement: its radius. The radius (r) is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. The formula for calculating the area (A) of a circle is famously concise:
A = πr²
Where:
- A represents the area of the circle.
- r represents the radius of the circle.
- π (pi) is a mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159. Pi represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter and is an irrational number, meaning its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating.
Calculating the Area: A Circle with Radius 8
Given a circle with a radius of 8 units (it could be 8 centimeters, 8 meters, 8 inches, or any other unit of length), we can directly apply the formula:
A = π * (8)²
A = π * 64
Using the approximation of π ≈ 3.14159, we get:
A ≈ 3.14159 * 64 ≈ 201.06176 square units
Therefore, the area of a circle with a radius of 8 units is approximately 201.06 square units. Remember that the units for area are always squared because we are measuring a two-dimensional space.
The Significance of Pi (π)
The constant π is central to understanding circles and spheres. Its ubiquity extends far beyond simple area calculations. Pi appears in countless mathematical formulas, spanning diverse fields like:
- Trigonometry: Pi is fundamental to defining angles in radians.
- Calculus: Pi emerges in integration and differentiation problems related to circular shapes.
- Probability and Statistics: Pi appears in various statistical distributions and probability calculations.
- Physics and Engineering: Pi is essential in calculating the circumference of circles, the volume of spheres, and numerous other physical phenomena.
The History and Mystery of Pi
The pursuit of understanding π has captivated mathematicians for millennia. Ancient civilizations, including the Babylonians and Egyptians, made surprisingly accurate estimations of pi. The Greek mathematician Archimedes developed a method of approximating pi using polygons inscribed within and circumscribed around a circle. The ongoing quest to calculate more precise values of pi continues to this day, pushing the boundaries of computational power and mathematical understanding. This enduring fascination highlights the fundamental nature of π in mathematics and its continued relevance in the modern age.
Applications of Circle Area Calculations
The ability to calculate the area of a circle is not just an abstract mathematical exercise; it has practical applications in numerous fields:
Engineering and Construction
- Pipe Sizing: Determining the cross-sectional area of pipes is crucial for calculating fluid flow rates and selecting appropriately sized pipes for various applications.
- Circular Structures: Calculating the area of circular structures like domes, tanks, and foundations is essential for material estimations and structural design.
- Land Surveying: Measuring and calculating the area of circular or irregularly shaped plots of land is necessary for land ownership, development, and resource management.
Science and Research
- Biology: Analyzing cellular structures, studying the growth patterns of organisms, and modeling biological processes often involve the calculation of circular areas.
- Astronomy: Estimating the size of celestial bodies and understanding their surface areas involves circular calculations.
- Physics: In many physics experiments and analyses, the area of a circle or its components is an essential consideration.
Everyday Applications
- Gardening: Calculating the area of a circular garden bed helps determine the amount of soil, plants, and other resources required.
- Cooking: Determining the appropriate size of a pizza or a cake involves understanding circular areas.
- Art and Design: Creating circular designs, logos, and patterns often relies on understanding area calculations.
Beyond the Basic Formula: Exploring Related Concepts
While the formula A = πr² is fundamental, understanding related geometric concepts enhances our comprehension of circles and their properties. This includes:
Diameter and Circumference
The diameter of a circle is twice its radius (d = 2r). The circumference (C) of a circle, its distance around the edge, is given by the formula:
C = 2πr or C = πd
Understanding the relationship between radius, diameter, and circumference is crucial for comprehensive comprehension of circle geometry.
Sectors and Segments
A sector of a circle is a region bounded by two radii and an arc of the circle. The area of a sector is a fraction of the total area of the circle, proportional to the angle subtended at the center. A segment of a circle is a region bounded by a chord and an arc. Calculating the areas of sectors and segments requires additional geometrical considerations beyond the basic area formula.
Annulus
An annulus is the region between two concentric circles (circles sharing the same center). Its area is calculated by subtracting the area of the smaller circle from the area of the larger circle.
Advanced Applications and Extensions
The principles of calculating circular areas extend into more complex mathematical and scientific realms. These include:
Calculus and Integration
Calculus provides powerful tools for calculating areas of more complex shapes, including those with curved boundaries. Integration can be used to precisely determine the area of irregular regions.
Multivariable Calculus
In three-dimensional space, the concept of area extends to surface area calculations for spheres and other curved surfaces. Multivariable calculus provides the framework for dealing with these complex calculations.
Computational Geometry
Computational geometry deals with algorithms and computational techniques for solving geometrical problems, including the efficient calculation of areas of complex shapes.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of Circle Area Calculations
The calculation of the area of a circle with a radius of 8 units, while a seemingly simple problem, underscores the power and elegance of mathematics. From its practical applications in engineering and construction to its significance in scientific research and everyday life, the ability to calculate circular area remains a crucial skill. Understanding the underlying principles, exploring related concepts, and grasping the historical context of this fundamental calculation allows us to appreciate the depth and breadth of its significance in our world. The seemingly simple formula, A = πr², opens a window into a vast and fascinating world of mathematical exploration and practical application.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Subatomic Particle With A Positive Charge Is The
Mar 19, 2025
-
Select All Of The Statements Which Are True About Rainforests
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are The Differences Between Political Parties And Interest Groups
Mar 19, 2025
-
Only Moveable Bone In The Skull
Mar 19, 2025
-
In Which Stage Of Meiosis Is The Chromosome Number Halved
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Area Of A Circle With A Radius Of 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
