A Production Possibilities Frontier Can Shift Outward If
News Leon
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
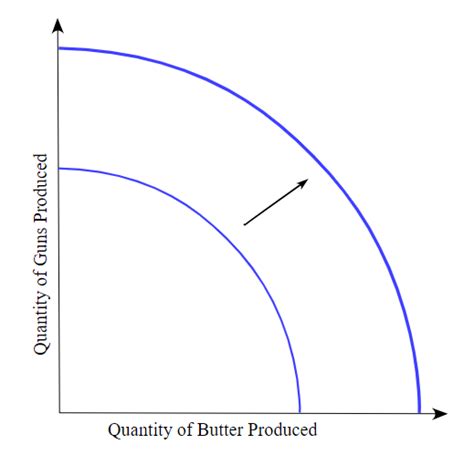
Table of Contents
- A Production Possibilities Frontier Can Shift Outward If
- Table of Contents
- A Production Possibilities Frontier Can Shift Outward If… Technological Advancement and Other Factors
- Technological Advancement: The Engine of Outward PPF Shifts
- Examples of Technological Advancement Shifting the PPF:
- Increased Resource Availability: Expanding the Production Capacity
- Improved Resource Allocation and Efficiency: Optimizing Production
- Institutional and Policy Changes: Fostering Economic Growth
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Driving Technological Advancements
- International Trade and Globalization: Expanding Market Access and Resource Pools
- Conclusion: Multiple Factors Contribute to Economic Growth and PPF Shifts
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
A Production Possibilities Frontier Can Shift Outward If… Technological Advancement and Other Factors
The Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF), also known as the Production Possibility Curve (PPC), is a fundamental concept in economics illustrating the maximum possible output combinations of two goods or services an economy can achieve with its given resources and technology. A crucial aspect of understanding the PPF lies in comprehending the factors that can cause it to shift outward, representing economic growth. This outward shift signifies an increase in an economy's productive capacity, allowing it to produce more of both goods or services simultaneously. This article delves deep into the various factors responsible for this expansion, exploring them in detail and providing real-world examples.
Technological Advancement: The Engine of Outward PPF Shifts
Arguably the most significant factor driving outward PPF shifts is technological advancement. Technological progress encompasses improvements in machinery, equipment, processes, and techniques used in production. These advancements can dramatically increase efficiency, productivity, and the overall output of an economy.
Examples of Technological Advancement Shifting the PPF:
-
Agricultural Revolution: The development of new farming techniques, improved seeds (like genetically modified crops), and advanced irrigation systems has significantly increased agricultural output. This allows a nation to produce more food (one good) while simultaneously producing more manufactured goods (another good) with the same amount of resources.
-
Industrial Revolution: The invention of the steam engine, the power loom, and other machinery revolutionized manufacturing. This led to a massive increase in the production of both consumer goods and capital goods, significantly shifting the PPF outward.
-
Automation and Robotics: The widespread adoption of robots and automated systems in various industries, from manufacturing to healthcare, boosts productivity and efficiency. This allows companies to produce more goods and services with fewer human resources, leading to an outward PPF shift.
-
Information and Communication Technology (ICT): The internet, mobile devices, and sophisticated software have revolutionized communication, data processing, and business operations. This has increased productivity across many sectors, contributing to economic growth and a subsequent outward shift of the PPF.
-
Biotechnology Advances: Innovations in biotechnology have led to breakthroughs in medicine, agriculture, and other fields. For instance, the development of new pharmaceuticals has improved healthcare outcomes, while advancements in genetic engineering have enhanced crop yields.
In essence: Technological progress enables economies to produce more output with the same or even fewer inputs. This is a key driver of long-term economic growth and is directly reflected in an outward shift of the PPF.
Increased Resource Availability: Expanding the Production Capacity
Another crucial factor contributing to an outward PPF shift is an increase in the availability of resources. This includes both:
-
Natural Resources: Discoveries of new oil reserves, the exploitation of previously untapped mineral deposits, or the expansion of arable land all contribute to increased productive capacity. For example, the discovery of large shale oil reserves in the United States shifted its PPF outward, allowing for increased energy production and related goods.
-
Human Resources: An increase in the size and/or skill level of the labor force can significantly expand an economy's productive potential. This can be achieved through population growth, improved education and training (leading to a more skilled workforce), and immigration. A country with a highly educated and skilled population is typically capable of producing more goods and services than a country with a less-educated population.
-
Capital Resources: An increase in the stock of capital goods – such as machinery, equipment, factories, and infrastructure – enhances productivity and allows for the production of a greater quantity of goods and services. Investments in infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and communication networks, can significantly improve efficiency and boost overall economic output.
Improved Resource Allocation and Efficiency: Optimizing Production
While not directly increasing the overall quantity of resources, improvements in resource allocation and efficiency can lead to an outward shift in the PPF by allowing economies to better utilize existing resources. This involves:
-
Specialization and Trade: Specialization, where individuals, firms, or countries focus on producing goods and services where they have a comparative advantage, enhances overall efficiency. Trade then allows for the exchange of these specialized goods, leading to a greater overall output for all participating parties.
-
Improved Management Techniques: Better management practices, organizational structures, and supply chain optimization can significantly enhance productivity and efficiency. This allows businesses to produce more with the same amount of resources, resulting in an outward shift of the PPF.
-
Reduced Waste and Improved Resource Management: Implementing strategies to reduce waste, conserve resources, and improve resource management techniques can enhance efficiency and contribute to an outward PPF shift. This includes recycling programs, sustainable practices, and efficient energy consumption.
Institutional and Policy Changes: Fostering Economic Growth
Government policies and institutional changes play a significant role in shaping an economy's ability to grow and shift its PPF outwards. This involves:
-
Investment in Education and Human Capital: Government investment in education, vocational training, and healthcare improves the skills and productivity of the workforce, leading to a more productive economy.
-
Infrastructure Development: Investments in infrastructure, such as transportation networks, communication systems, and energy infrastructure, are crucial for enhancing productivity and efficiency across various sectors.
-
Sound Macroeconomic Policies: Stable macroeconomic policies, including responsible monetary and fiscal policies, create an environment conducive to investment, economic growth, and outward PPF shifts. This includes controlling inflation and maintaining a stable exchange rate.
-
Property Rights Protection: A strong legal framework that protects intellectual property rights and enforces contracts encourages innovation, investment, and economic growth. A secure environment for businesses to operate in fosters investment and enhances productive capacity.
-
Reduced Bureaucracy and Regulation (to an extent): Streamlining bureaucratic processes and reducing excessive regulation can boost business efficiency and promote economic activity, leading to an outward PPF shift. However, it is important to note that some regulation is necessary to protect consumers, workers, and the environment.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Driving Technological Advancements
The driving force behind many technological advancements is innovation and entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurs and innovators are at the forefront of developing new products, processes, and technologies, constantly pushing the boundaries of what's possible. Their efforts lead to higher productivity and contribute significantly to outward PPF shifts.
International Trade and Globalization: Expanding Market Access and Resource Pools
International trade and globalization can significantly impact the PPF. Access to larger markets through international trade enables economies to specialize in producing goods and services where they have a comparative advantage. This leads to increased efficiency and higher overall output. Globalization also allows for access to a broader range of resources, technologies, and ideas, further contributing to an outward PPF shift.
Conclusion: Multiple Factors Contribute to Economic Growth and PPF Shifts
In conclusion, a Production Possibilities Frontier can shift outward due to a complex interplay of factors. While technological advancements are arguably the most significant driver of long-term economic growth, increases in resource availability, improved resource allocation, sound government policies, innovation, and international trade all play crucial roles. Understanding these factors is essential for policymakers, businesses, and individuals to foster economic growth and enhance the overall standard of living. The outward shift of the PPF represents a nation's enhanced ability to satisfy its citizens' wants and needs, signifying overall progress and prosperity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Most Abundant Wbc
Apr 01, 2025
-
Domain And Range For Y 1 X
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Mass Of A Beta Particle
Apr 01, 2025
-
12 Of 150 Is What Number
Apr 01, 2025
-
Draw The Organic Products Formed In The Following Reaction
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Production Possibilities Frontier Can Shift Outward If . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
