A Group Of 8 Bits Is Known As A
News Leon
Mar 27, 2025 · 6 min read
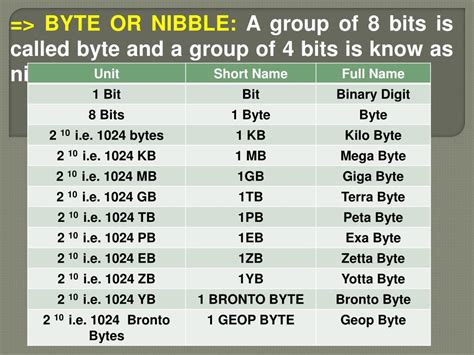
Table of Contents
A Group of 8 Bits is Known As a Byte: A Deep Dive into Digital Information
In the digital realm, where information reigns supreme, understanding the fundamental building blocks is paramount. At the heart of it all lies the humble bit, the smallest unit of data. But bits, on their own, are not very useful. To represent meaningful information, they need to be grouped together. So, what happens when you assemble eight of these tiny bits? You get a byte, the cornerstone of digital storage and processing. This article delves deep into the world of bytes, exploring their significance, applications, and implications in the ever-evolving landscape of digital technology.
Understanding Bits and Bytes: The Foundation of Digital Data
Before we dive into the specifics of a byte, let's briefly recap what a bit represents. A bit, short for "binary digit," is the most basic unit of data in computing. It can hold only one of two values: 0 or 1, representing the absence or presence of an electrical signal. Think of it as a simple on/off switch. While powerful in its simplicity, a single bit is insufficient to represent complex information.
This is where the byte comes in. A byte is a group of eight bits. This seemingly small increase in size dramatically expands the amount of information that can be represented. Because each bit can be either 0 or 1, a byte can represent 2<sup>8</sup>, or 256, different values. This enables the representation of a wide range of data, including letters, numbers, symbols, and even parts of images and sounds.
The Significance of the Byte in Data Representation
The byte's significance lies in its ability to efficiently represent various types of data. Let's explore some key applications:
1. Character Encoding: Representing Text
One of the most common uses of a byte is in representing characters. Different character encoding schemes, like ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) and Unicode, assign specific byte values to characters. ASCII, for instance, uses 7 bits to represent 128 characters, including uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and control characters. Unicode, a more extensive system, utilizes multiple bytes to accommodate a far wider range of characters from various languages.
The evolution from ASCII to Unicode showcases the growing need for efficient character representation in a globalized world. While ASCII's limitations were apparent with the rise of international communication, Unicode's flexibility allows for the encoding of virtually any character, fostering seamless cross-lingual communication in the digital age.
2. Numerical Representation: Storing Numbers
Bytes also play a crucial role in representing numbers. Depending on the encoding method used (e.g., signed or unsigned integers, floating-point numbers), a single byte can represent a range of numerical values. Unsigned integers, for instance, can represent values from 0 to 255, while signed integers can represent values from -128 to 127. Larger numbers require multiple bytes.
The use of different data types and their respective byte sizes allows for optimized storage and processing of numerical data. This optimization is critical for applications ranging from scientific simulations to financial modeling, ensuring efficient handling of massive datasets.
3. Image Representation: Pixels and Colors
Images are composed of pixels, tiny squares of color. Each pixel requires a certain number of bits to represent its color. In common image formats like JPEG and PNG, each pixel's color information is often stored as multiple bytes. For example, a 24-bit color image (often referred to as "true color") allocates 3 bytes per pixel, one byte each for red, green, and blue color components.
The size of an image file directly correlates to its resolution and color depth. Higher resolutions and deeper colors result in larger files, as more bytes are needed to represent the increased detail and color variations.
4. Sound Representation: Sampling and Encoding
Similar to images, sound is also represented digitally using bytes. Sound waves are sampled at regular intervals, and each sample is represented by a numerical value stored as one or more bytes. The sampling rate (samples per second) and the bit depth (number of bits per sample) determine the quality of the sound reproduction. Higher sampling rates and bit depths result in higher-quality audio but also larger file sizes.
The ability to digitally represent and manipulate sound waves has revolutionized the music industry and audio production, allowing for precise control over audio signals and the creation of complex soundscapes.
Beyond the Single Byte: Kilobytes, Megabytes, and More
While a single byte is a fundamental unit, it is rarely used in isolation. To represent larger amounts of data, we use multiples of bytes:
- Kilobyte (KB): Approximately 1,024 bytes (2<sup>10</sup> bytes)
- Megabyte (MB): Approximately 1,024 kilobytes (2<sup>20</sup> bytes)
- Gigabyte (GB): Approximately 1,024 megabytes (2<sup>30</sup> bytes)
- Terabyte (TB): Approximately 1,024 gigabytes (2<sup>40</sup> bytes)
- Petabyte (PB): Approximately 1,024 terabytes (2<sup>50</sup> bytes)
- Exabyte (EB): Approximately 1,024 petabytes (2<sup>60</sup> bytes)
- Zettabyte (ZB): Approximately 1,024 exabytes (2<sup>70</sup> bytes)
- Yottabyte (YB): Approximately 1,024 zettabytes (2<sup>80</sup> bytes)
These units are essential for understanding the storage capacity of various devices like hard drives, SSDs, and memory cards. The ever-increasing data demands of modern technology necessitate the use of these larger units to measure and manage the massive amounts of digital information generated and consumed daily.
The Byte's Role in Modern Computing Architectures
The byte is not just a unit of data; it is deeply integrated into the architecture of modern computers. Central Processing Units (CPUs) are designed to work with bytes and their multiples, efficiently processing instructions and manipulating data. Memory addresses, pointers, and other fundamental elements of computer architecture are frequently expressed in terms of bytes.
The byte-oriented nature of computer systems simplifies data handling and memory management, contributing to the overall efficiency and performance of digital systems. This consistency ensures seamless interaction between hardware and software components, fostering smooth operation and preventing data corruption.
The Future of the Byte: Continued Relevance in a Changing Digital Landscape
Despite the emergence of more advanced technologies, the byte remains a fundamental unit of data. While the size and complexity of digital data continue to increase, the byte's fundamental role in data representation and processing remains unchanged. Its simplicity and efficiency make it an enduring cornerstone of digital information management.
As technology advances, we will likely see continued innovation in data compression and storage techniques, further optimizing the use of bytes. However, the foundational role of the byte, as the fundamental unit of data, will likely persist for the foreseeable future.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the Byte
In essence, a group of 8 bits is known as a byte, and its significance in the world of computing cannot be overstated. From representing simple characters to storing complex images and sounds, the byte serves as the backbone of digital information. Understanding its role in data representation and processing is crucial for anyone working with computers or digital technology. Its enduring legacy speaks to its fundamental importance in the evolution and continued development of the digital world. The humble byte, while seemingly small, is a giant in the realm of digital information, silently powering the technology that shapes our lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Graph Of A Function F Is Given
Mar 30, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Measurement Is More Accurate
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is The Conjugate Base Of H2so4
Mar 30, 2025
-
Find The Measure Of Each Lettered Angle In The Figure
Mar 30, 2025
-
Which Issue Does Terrace Farming Help Solve
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Group Of 8 Bits Is Known As A . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
