X 3 3x 2 X 3 Factor
News Leon
Mar 21, 2025 · 4 min read
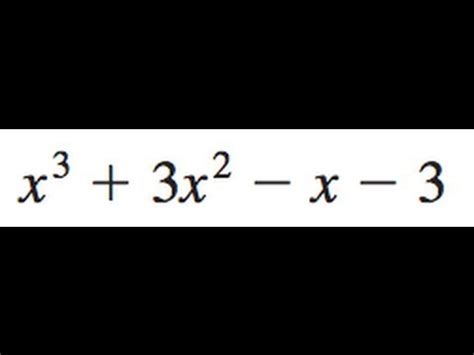
Table of Contents
Mastering the X³ + 3X² + 3X + 1 Factor: A Comprehensive Guide
Factoring cubic expressions can seem daunting, but with a structured approach, even complex polynomials become manageable. This comprehensive guide delves into the factorization of the specific cubic expression x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1, revealing its underlying structure and demonstrating various methods for solving similar problems. We'll explore the connection to binomial expansion, the use of synthetic division, and the importance of recognizing perfect cubes in polynomial factorization. This will equip you with the skills to confidently tackle similar cubic expressions.
Understanding the Structure: Recognizing a Perfect Cube
The expression x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 isn't just a random collection of terms; it's a perfect cube trinomial. This means it can be factored neatly using the binomial expansion formula. Recognizing this underlying structure is the key to efficient factorization.
The Binomial Expansion Connection
Recall the binomial expansion formula: (a + b)³ = a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³. If we compare this to our expression x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1, we can see a direct correspondence:
- a³ corresponds to x³ (implying a = x)
- 3a²b corresponds to 3x²
- 3ab² corresponds to 3x
- b³ corresponds to 1 (implying b = 1)
This clear correspondence reveals that x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 is the expansion of (x + 1)³.
Factorization Methods: Different Approaches to the Same Result
While recognizing the perfect cube structure provides the quickest solution, let's explore other methods to factor x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1, reinforcing the understanding of polynomial factorization techniques.
Method 1: Direct Application of the Binomial Expansion
The most straightforward method involves directly applying the binomial expansion formula. Since we've already identified a = x and b = 1, we can write:
x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 = (x + 1)³
This gives us the factored form immediately. This method highlights the importance of pattern recognition in simplifying complex algebraic expressions.
Method 2: Synthetic Division and the Remainder Theorem
Synthetic division is a powerful tool for factoring polynomials. It's particularly useful when you suspect a certain value might be a root of the polynomial. Since (x + 1)³ implies that x = -1 is a root (because if x = -1 then the expression = 0), we can use synthetic division to verify this and find the other factors.
Performing synthetic division with x = -1:
| -1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | -2 | -1 | ||
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
The remainder is 0, confirming that (x + 1) is a factor. The quotient is x² + 2x + 1, which is a perfect square trinomial and can be factored further as (x + 1)². Therefore:
x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 = (x + 1)(x² + 2x + 1) = (x + 1)(x + 1)² = (x + 1)³
This method reinforces the concept of roots and their relationship to polynomial factors.
Method 3: Grouping and Factoring by Parts
While less efficient for this particular expression, factoring by grouping can be applied to some cubic polynomials. However, this method isn't directly applicable to x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 without some manipulation that would ultimately lead us back to recognizing the perfect cube structure.
Expanding the Understanding: Applications and Extensions
Mastering the factorization of x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 is not just about solving a single problem; it provides a strong foundation for tackling more complex polynomial expressions.
Solving Cubic Equations
The factored form (x + 1)³ = 0 allows us to easily solve the cubic equation x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 = 0. The only real solution is x = -1 (with multiplicity 3, meaning this root appears three times). This demonstrates the link between factorization and solving polynomial equations.
Generalizing to Other Perfect Cubes
The principles illustrated here extend to other perfect cube trinomials. For instance, (2x + 3)³ would expand to 8x³ + 36x² + 54x + 27, following the same pattern. Recognizing this pattern allows you to factor similar expressions efficiently.
Factoring More Complex Polynomials
While this guide focuses on a specific perfect cube, the underlying techniques – binomial expansion, synthetic division, and recognizing patterns – are essential for factoring more complex polynomials. These skills become increasingly valuable when dealing with higher-degree polynomials or those requiring more intricate factorization methods.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
For truly complex polynomial factorization problems, advanced techniques such as the Rational Root Theorem, numerical methods (like Newton-Raphson), or computer algebra systems may be necessary. However, understanding the fundamentals of factoring simpler expressions like x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 is crucial before tackling these more advanced scenarios.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals for Future Success
The seemingly simple expression x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 provides a rich learning opportunity in polynomial factorization. By understanding its connection to binomial expansion, applying synthetic division, and appreciating the significance of perfect cubes, you've significantly enhanced your algebraic skills. This knowledge forms a solid foundation for tackling more complex polynomial factorization problems and solving cubic equations, opening doors to advanced mathematical concepts and problem-solving strategies. Remember to practice consistently; the more you work with these techniques, the more intuitive and efficient your approach will become.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Collection Of Objects Is Called
Mar 21, 2025
-
Explain Why Air Is A Mixture
Mar 21, 2025
-
Is Gravity A Non Contact Force
Mar 21, 2025
-
Difference Between Law Of Segregation And Law Of Independent Assortment
Mar 21, 2025
-
Is Rubber A Insulator Or Conductor
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 3 3x 2 X 3 Factor . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
