X 3 2x 2 5x 10
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
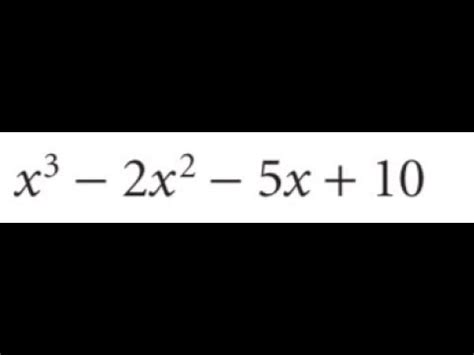
Table of Contents
Deconstructing the Expression: x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10
This seemingly simple algebraic expression, x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10, opens a door to a wealth of mathematical concepts, from basic factoring to more advanced polynomial manipulations and applications. This article will explore this expression in depth, examining its various properties, potential factorizations, and real-world applications, all while optimizing for search engines using relevant keywords and semantic SEO techniques.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Polynomials and Their Components
Before diving into the specifics of x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10, let's establish a strong foundation in polynomial terminology. A polynomial is an expression consisting of variables (like 'x'), coefficients (numbers multiplying the variables), and exponents (numbers indicating the power of the variable). Our expression is a polynomial because it follows this structure.
- Degree: The highest exponent of the variable in a polynomial determines its degree. In our case, the degree is 3 (cubic polynomial) because of the x³ term.
- Coefficients: The numbers in front of each term are the coefficients. Here, the coefficients are 1 (for x³), 2 (for 2x²), 5 (for 5x), and 10 (the constant term).
- Terms: A polynomial is composed of terms, which are separated by addition or subtraction. Our expression has four terms: x³, 2x², 5x, and 10.
- Constant Term: The term without a variable (10 in this case) is called the constant term.
Factoring the Polynomial: Unveiling Hidden Structures
Factoring a polynomial involves rewriting it as a product of simpler expressions. This process is crucial in solving equations, simplifying expressions, and understanding the polynomial's roots (the values of x that make the expression equal to zero).
Attempting Common Factoring: A straightforward first step is to look for common factors among all terms. In this case, there's no common factor besides 1, so we need more advanced techniques.
Grouping Method: For polynomials with four terms, the grouping method is often effective. We can group the terms as follows:
(x³ + 2x²) + (5x + 10)
Now, we factor out the greatest common factor (GCF) from each group:
x²(x + 2) + 5(x + 2)
Notice that (x + 2) is a common factor in both terms. We can factor it out:
(x + 2)(x² + 5)
Therefore, the factored form of x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10 is (x + 2)(x² + 5). This reveals a significant structural component of the polynomial.
Analyzing the Factors: We now have two factors: (x + 2) and (x² + 5).
-
(x + 2): This is a linear factor, meaning it's a polynomial of degree 1. Setting this factor to zero gives us one root of the polynomial: x = -2.
-
(x² + 5): This is a quadratic factor (degree 2). To find its roots, we set it to zero: x² + 5 = 0. This gives us x² = -5, which implies x = ±√(-5) = ±i√5, where 'i' is the imaginary unit (√-1). These are complex roots.
Exploring the Roots and Their Significance
The roots of a polynomial are the values of x that make the polynomial equal to zero. Our analysis reveals one real root (-2) and two complex roots (±i√5). The roots provide crucial information about the polynomial's behavior and its graphical representation.
Real Root and its Implications: The real root, x = -2, represents a point where the graph of the polynomial intersects the x-axis. This point is an x-intercept.
Complex Roots and Their Implications: The complex roots, ±i√5, don't correspond to x-intercepts on the real number plane. These roots indicate the polynomial's behavior in the complex plane. Complex roots often appear in pairs (conjugates) for polynomials with real coefficients.
Graphical Representation and Visualizing the Polynomial
Visualizing the polynomial's graph provides further insight into its properties. The graph of a cubic polynomial generally has a shape that resembles an 'S' curve. Knowing the real root (x = -2) helps us determine one point on the graph. The shape of the curve is influenced by the coefficients and the degree of the polynomial. While we can't directly visualize the complex roots on a standard Cartesian coordinate system, they influence the overall shape and behavior of the polynomial.
Applications of Cubic Polynomials: Real-World Connections
Cubic polynomials like x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10 find applications in various fields:
-
Physics and Engineering: Cubic equations are frequently used in problems involving motion, volume calculations, and the analysis of curves. For example, they could model the trajectory of a projectile or the shape of a curved beam.
-
Economics and Finance: Cubic polynomials can be used to model economic relationships, such as production functions or cost functions. They can also play a role in financial modeling, particularly in scenarios involving compound interest or complex investment strategies.
-
Computer Graphics and Animation: Cubic curves (specifically Bezier curves) are fundamental in computer graphics and animation for creating smooth, curved lines and surfaces. These curves are often defined using cubic polynomials.
Further Mathematical Explorations: Derivatives and Integrals
We can expand our analysis by exploring the derivative and integral of our polynomial:
Derivative: The derivative of a function represents its instantaneous rate of change. The derivative of x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10 is 3x² + 4x + 5. This derivative is a quadratic function that can tell us about the slope of the original cubic function at any given point.
Integral: The integral of a function represents the area under its curve. The indefinite integral of x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10 is (1/4)x⁴ + (2/3)x³ + (5/2)x² + 10x + C, where 'C' is the constant of integration. The definite integral (over a specific interval) would give us the numerical area under the curve of the original polynomial within that interval.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10
This comprehensive exploration of the algebraic expression x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10 has delved into its fundamental components, its factorization, its roots, its graphical representation, and its applications in various fields. By understanding these aspects, we gain a deeper appreciation of the power and versatility of polynomial expressions and their importance in mathematics and beyond. The techniques employed, such as factoring and analyzing roots, are essential tools in a mathematician's or scientist's arsenal. The exploration of derivatives and integrals further expands the analytical power we can bring to bear on such expressions. This detailed analysis demonstrates how seemingly simple mathematical objects can lead to profound insights and practical applications. The principles discussed here are relevant to a wide range of mathematical problems and form a cornerstone of advanced mathematical studies.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Trinomial
Mar 23, 2025
-
Select The Components Of An Atp Molecule
Mar 23, 2025
-
The Members Of A Homologous Pair Of Chromosomes
Mar 23, 2025
-
A Characteristic Of Human Wants Is That They Are
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons In Argon
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 3 2x 2 5x 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
