Which Organelles Are Involved In Energy Conversion
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
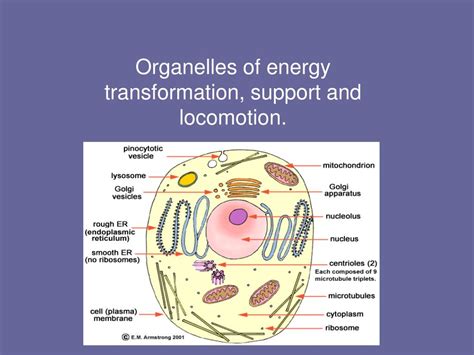
Table of Contents
Which Organelles Are Involved in Energy Conversion?
Energy conversion is a fundamental process in all living organisms. It's the process by which energy from one form is transformed into another, enabling cells to perform their vital functions. This conversion isn't a haphazard event; it's meticulously orchestrated within specific cellular compartments known as organelles. Understanding which organelles are involved and how they interact is crucial to understanding the intricacies of life itself. This article delves into the fascinating world of cellular energy conversion, focusing on the key organelles playing pivotal roles in this vital process.
The Powerhouses: Mitochondria and Their Role in Cellular Respiration
The mitochondria are arguably the most famous organelles involved in energy conversion. Often referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell, these double-membraned organelles are responsible for cellular respiration, the process that converts the chemical energy stored in glucose into a readily usable form of energy: ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This conversion occurs in a series of meticulously controlled steps.
Stages of Cellular Respiration within the Mitochondria:
-
Glycolysis: While technically not occurring within the mitochondria, glycolysis is the crucial initial step. It takes place in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP. The pyruvate then enters the mitochondria.
-
Pyruvate Oxidation: Inside the mitochondrial matrix (the space enclosed by the inner membrane), pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA, releasing carbon dioxide.
-
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Acetyl-CoA enters the Krebs cycle, a series of chemical reactions that further oxidize the carbon atoms, releasing more carbon dioxide and generating some ATP, NADH, and FADH2. These latter molecules are crucial electron carriers.
-
Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron Transport Chain & Chemiosmosis): This is the most significant ATP-producing stage. Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed along a chain of protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This electron transport generates a proton gradient across the membrane. The subsequent flow of protons back across the membrane, through ATP synthase, drives the synthesis of a large amount of ATP via chemiosmosis. Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor, forming water.
Keywords: Mitochondria, cellular respiration, ATP, glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, Krebs cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, electron transport chain, chemiosmosis, ATP synthase.
Chloroplasts: The Solar Power Plants of Plant Cells
In plant cells and some protists, chloroplasts are the primary organelles responsible for energy conversion. These fascinating organelles are the sites of photosynthesis, the process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Like mitochondria, chloroplasts are double-membraned organelles with a complex internal structure.
Stages of Photosynthesis within the Chloroplasts:
-
Light-Dependent Reactions: These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes, a complex network of interconnected flattened sacs within the chloroplast. Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments, exciting electrons. This electron flow drives the synthesis of ATP and NADPH, utilizing a process similar to chemiosmosis in mitochondria. Water is split, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
-
Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle): These reactions take place in the stroma, the fluid-filled space surrounding the thylakoids. ATP and NADPH produced during the light-dependent reactions are used to fix carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into glucose, a stable form of chemical energy. This process is also known as carbon fixation.
Keywords: Chloroplasts, photosynthesis, light-dependent reactions, light-independent reactions, Calvin cycle, chlorophyll, thylakoid membranes, stroma, carbon fixation, ATP, NADPH.
The Interplay Between Mitochondria and Chloroplasts: A Symbiotic Relationship
It's worth noting the remarkable evolutionary connection between mitochondria and chloroplasts. The endosymbiotic theory proposes that both organelles originated from free-living prokaryotic organisms that were engulfed by early eukaryotic cells. This symbiotic relationship resulted in a mutually beneficial arrangement: the host cell provided protection and resources, while the engulfed prokaryotes provided energy conversion capabilities. This evolutionary history helps explain the striking similarities in their structure and function, such as their double membranes and their use of chemiosmosis for ATP production.
Similarities and Differences:
Both mitochondria and chloroplasts share several similarities, including their double membranes and the use of electron transport chains and chemiosmosis for ATP production. However, they differ fundamentally in their energy sources and products. Mitochondria utilize organic molecules (glucose) to generate ATP, while chloroplasts use light energy to produce glucose. Mitochondria are found in nearly all eukaryotic cells, while chloroplasts are restricted to plant cells and certain protists.
Keywords: Endosymbiotic theory, endosymbiosis, prokaryotes, eukaryotes, symbiotic relationship, evolution.
Beyond Mitochondria and Chloroplasts: Other Organelles Involved in Energy Metabolism
While mitochondria and chloroplasts are the primary organelles involved in energy conversion, other organelles play supporting roles in energy metabolism.
Peroxisomes:
These single-membraned organelles are involved in various metabolic processes, including beta-oxidation, the breakdown of fatty acids to produce acetyl-CoA, which can then enter the Krebs cycle in mitochondria. Peroxisomes also play a role in detoxification, removing harmful substances from the cell.
Keywords: Peroxisomes, beta-oxidation, fatty acid metabolism, detoxification.
Cytoplasm:
The cytoplasm, the fluid-filled space surrounding the organelles, plays a vital role in glycolysis, the initial step of cellular respiration. Several enzymes involved in glycolysis are located in the cytoplasm.
Keywords: Cytoplasm, glycolysis, enzyme activity.
Nucleus:
The nucleus houses the genetic material (DNA) that encodes the instructions for building and regulating all cellular components, including those involved in energy conversion. Transcription and translation of genes involved in energy metabolism occur within the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Keywords: Nucleus, DNA, transcription, translation, gene regulation.
The Importance of Energy Conversion for Cellular Processes
The ATP produced by energy conversion is the primary energy currency of the cell. It powers a vast array of cellular processes, including:
- Active transport: Moving molecules across cell membranes against their concentration gradients.
- Muscle contraction: The process that allows muscles to move.
- Protein synthesis: The creation of new proteins, essential for cellular structure and function.
- Cell division: The process by which cells replicate.
- Signal transduction: Cell communication.
- Nerve impulse transmission: The rapid transmission of signals in nerve cells.
Keywords: ATP, active transport, muscle contraction, protein synthesis, cell division, signal transduction, nerve impulse transmission.
Conclusion: A Complex and Coordinated System
Energy conversion within cells is a remarkably intricate and precisely regulated process. While mitochondria and chloroplasts are the central players, many other organelles contribute to this vital function. The sophisticated interplay between these organelles ensures that cells can efficiently harvest and utilize energy to support the myriad of processes essential for life. Further research into the molecular mechanisms of energy conversion continues to reveal the breathtaking complexity and elegance of cellular machinery, ultimately deepening our understanding of life itself. This detailed exploration of energy conversion within various organelles hopefully provides a comprehensive overview for researchers and students alike.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Statement About Natural Selection Is True
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Chamber Of Heart Has Thickest Wall
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 1 2 Miles
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lines Of Symmetry On A Trapezoid
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Organelles Are Involved In Energy Conversion . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
