Which Of The Following Will Be The Strongest Acid
News Leon
Mar 29, 2025 · 4 min read
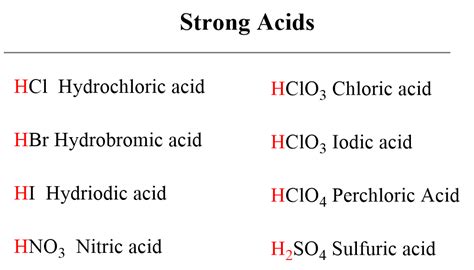
Table of Contents
Which of the following will be the strongest acid? A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the strongest acid from a given set requires a deep understanding of acid strength, the factors that influence it, and the application of relevant theories. This article will delve into the intricacies of acid strength, exploring the key concepts and providing a practical framework for making accurate comparisons. We'll explore various factors impacting acidity and demonstrate how to systematically analyze a group of acids to identify the strongest one.
Understanding Acid Strength: A Foundation
Acid strength refers to the extent to which an acid dissociates in a solution. A strong acid completely or almost completely dissociates into its ions (cations and anions) when dissolved in water, while a weak acid only partially dissociates. This dissociation is represented by the equilibrium constant, Ka (acid dissociation constant).
-
Strong Acids: Have high Ka values (Ka >> 1). They essentially completely dissociate in water. Examples include HCl (hydrochloric acid), HBr (hydrobromic acid), HI (hydroiodic acid), HNO₃ (nitric acid), and HClO₄ (perchloric acid).
-
Weak Acids: Have low Ka values (Ka << 1). They only partially dissociate in water. Examples include CH₃COOH (acetic acid), H₂CO₃ (carbonic acid), and HF (hydrofluoric acid).
The larger the Ka value, the stronger the acid. Conversely, a smaller Ka value indicates a weaker acid. Sometimes, pKa (the negative logarithm of Ka) is used. A smaller pKa value signifies a stronger acid.
Factors Influencing Acid Strength
Several factors contribute to an acid's strength. Understanding these factors is crucial for predicting relative acidities:
1. Bond Strength:
The strength of the bond between the acidic hydrogen (H⁺) and the rest of the molecule significantly impacts acidity. Weaker bonds lead to stronger acids. The hydrogen atom is more readily released as a proton (H⁺) when the bond is weaker, resulting in a higher degree of dissociation.
2. Electronegativity:
The electronegativity of the atom bonded to the acidic hydrogen plays a crucial role. Higher electronegativity of the atom pulls electron density away from the O-H bond, weakening it and making the proton more readily released. This leads to increased acidity.
3. Resonance Stabilization:
If the conjugate base (the species remaining after the acid donates a proton) is resonance-stabilized, the acid will be stronger. Resonance delocalizes the negative charge, making the conjugate base more stable. A more stable conjugate base means the acid is more likely to donate a proton, hence a stronger acid.
4. Inductive Effect:
Electron-withdrawing groups (EWGs) near the acidic hydrogen can increase acidity. These groups pull electron density away from the O-H bond, weakening it and facilitating proton release. Conversely, electron-donating groups (EDGs) decrease acidity.
5. Hybridization:
The hybridization of the atom bonded to the acidic hydrogen influences acid strength. Acids with the acidic hydrogen attached to a more electronegative atom (like oxygen in a carboxylic acid) tend to be stronger than those with the acidic hydrogen attached to a less electronegative atom (like carbon in an alkane).
6. Solvent Effects:
The solvent in which the acid is dissolved can affect its apparent strength. Protic solvents (those with O-H or N-H bonds) can stabilize the conjugate base through hydrogen bonding, increasing the acid's apparent strength.
Systematic Approach to Comparing Acid Strengths
Let's illustrate how to compare the strength of acids systematically. Consider the following set of acids:
- Acid A: CH₃COOH (Acetic Acid)
- Acid B: HClO₄ (Perchloric Acid)
- Acid C: H₂SO₄ (Sulfuric Acid)
- Acid D: HF (Hydrofluoric Acid)
- Acid E: HNO₃ (Nitric Acid)
1. Identify Strong vs. Weak Acids:
Immediately, we can identify HClO₄ (Perchloric Acid), H₂SO₄ (Sulfuric Acid), and HNO₃ (Nitric Acid) as strong acids. These are known to completely or almost completely dissociate in aqueous solutions. CH₃COOH (Acetic Acid) and HF (Hydrofluoric Acid) are weak acids.
2. Comparing Strong Acids:
Among the strong acids, perchloric acid (HClO₄) is generally considered the strongest. Its conjugate base, ClO₄⁻, is highly resonance-stabilized, making it exceptionally stable and contributing to the complete dissociation of HClO₄. Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) is a strong acid, but its second proton dissociation is weaker than the first. Nitric acid (HNO₃) is also a strong acid, but its conjugate base is less stable than perchlorate.
3. Comparing Weak Acids:
Comparing acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and hydrofluoric acid (HF), we can use the principles discussed above. The electronegativity of oxygen in acetic acid is higher than that of fluorine in hydrofluoric acid. However, HF’s high bond strength compensates for its lower electronegativity. While both are weak, HF is stronger than CH₃COOH due to its stronger inductive effect.
Conclusion: The Strongest Acid
Based on our analysis, HClO₄ (Perchloric Acid) is the strongest acid among the given options. While H₂SO₄ and HNO₃ are also strong acids, their dissociation is not as complete as that of perchloric acid due to the stability of its conjugate base. The weak acids, CH₃COOH and HF, are significantly weaker than the strong acids. Understanding the various factors influencing acid strength allows for a systematic and accurate determination of relative acidities. This methodology can be applied to any set of acids to identify the strongest among them. Remember to consider bond strength, electronegativity, resonance stabilization, inductive effects, hybridization, and solvent effects when making such comparisons.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Network Layer Firewall Works As A
Mar 31, 2025
-
Is Sodium Methoxide A Strong Nucleophile
Mar 31, 2025
-
The Amount Of Space An Object Occupies
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Small Object Begins A Free Fall From A Height
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Strand Of Dna Serves As The Template For Transcription
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Will Be The Strongest Acid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
