Which Of The Following Types Of Muscles Is Voluntary Muscle
News Leon
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
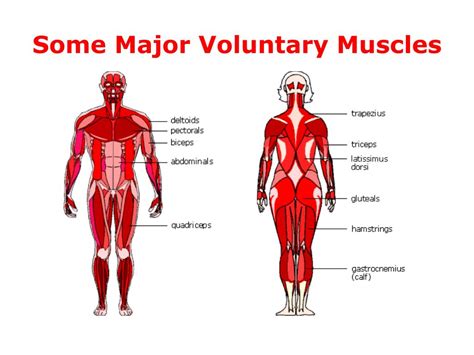
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Types of Muscles is Voluntary Muscle?
Understanding the different types of muscles in the human body is crucial for appreciating how we move, maintain posture, and perform various bodily functions. This article delves deep into the fascinating world of muscle tissue, focusing specifically on identifying the voluntary muscle type from a given selection. We’ll explore the characteristics of each muscle type – skeletal, smooth, and cardiac – to pinpoint the one under conscious control.
The Three Main Muscle Types: A Comparative Analysis
The human body possesses three distinct types of muscles, each with unique structural and functional characteristics:
1. Skeletal Muscle: The Workhorses of Movement
Skeletal muscles, also known as striated muscles, are attached to bones via tendons. These muscles are responsible for the voluntary movements we perform daily, from walking and talking to lifting weights and playing sports. Their characteristic striated appearance under a microscope results from the highly organized arrangement of contractile proteins – actin and myosin – within their fibers.
Key Characteristics of Skeletal Muscles:
- Voluntary Control: This is their defining feature. You consciously decide when and how to contract these muscles.
- Striated Appearance: The arrangement of actin and myosin filaments gives them a striped or striated look.
- Multinucleated Cells: Skeletal muscle fibers are long, cylindrical cells containing multiple nuclei.
- Rapid Contraction: They contract forcefully and relatively quickly.
- Fatigue: They can fatigue relatively quickly with prolonged or intense activity.
- Attached to Bones: They are primarily responsible for movement of the skeleton.
Examples of Skeletal Muscle Actions:
- Walking: The coordinated contraction and relaxation of leg muscles.
- Lifting: The powerful contractions of arm and shoulder muscles.
- Facial Expressions: The intricate movements of facial muscles controlled by the facial nerve.
- Breathing: The contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. While breathing is often automatic, it can also be consciously controlled (e.g., holding your breath).
- Posture Maintenance: Sustained low-level contractions of postural muscles keep the body upright.
2. Smooth Muscle: The Silent Workers
Smooth muscles, also called involuntary muscles or visceral muscles, are found in the walls of internal organs such as the stomach, intestines, bladder, blood vessels, and airways. They are responsible for a wide range of involuntary bodily functions. Unlike skeletal muscles, they lack the striated appearance.
Key Characteristics of Smooth Muscles:
- Involuntary Control: These muscles contract and relax automatically, without conscious control.
- Non-Striated Appearance: They lack the organized arrangement of actin and myosin filaments found in skeletal muscle.
- Single Nucleus per Cell: Smooth muscle cells are spindle-shaped and contain a single nucleus.
- Slow Contraction: They contract and relax slowly compared to skeletal muscles.
- Sustained Contractions: They can sustain contractions for extended periods without fatigue.
- Location: They are found in the walls of internal organs and blood vessels.
Examples of Smooth Muscle Actions:
- Digestion: The rhythmic contractions of smooth muscles in the digestive tract propel food through the system.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: The contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles in blood vessel walls regulate blood flow.
- Respiration: The smooth muscles in the bronchioles help regulate airflow to the lungs.
- Urination: The smooth muscles in the bladder wall control the release of urine.
3. Cardiac Muscle: The Heart's Dedicated Muscle
Cardiac muscle is the specialized muscle tissue found only in the heart. Its rhythmic contractions pump blood throughout the body. Similar to skeletal muscle, it exhibits striations, but unlike skeletal muscle, its contractions are involuntary.
Key Characteristics of Cardiac Muscle:
- Involuntary Control: Cardiac muscle contractions are regulated by the autonomic nervous system and the heart's intrinsic conduction system.
- Striated Appearance: Similar to skeletal muscle, it has a striated appearance due to the organized arrangement of actin and myosin filaments.
- Branched Cells: Cardiac muscle cells are branched and interconnected, forming a functional syncytium.
- Intercalated Discs: Specialized junctions between cardiac muscle cells facilitate rapid communication and coordinated contractions.
- Self-excitable: Cardiac muscle cells can generate their own electrical impulses, initiating contractions without external stimulation.
- Resistant to Fatigue: Cardiac muscle is highly resistant to fatigue, enabling continuous pumping of blood throughout life.
Examples of Cardiac Muscle Action:
- Heart Pumping: The rhythmic contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood to the lungs and the rest of the body.
- Maintaining Blood Pressure: The strength and rate of cardiac muscle contractions influence blood pressure.
Answering the Question: Which Muscle Type is Voluntary?
Based on the detailed analysis above, the answer is clear: Skeletal muscle is the voluntary muscle type. It's the only type of muscle tissue that is directly controlled by conscious thought. You can consciously decide to flex your bicep, extend your leg, or make a facial expression – all actions involving the voluntary contraction of skeletal muscles. Smooth and cardiac muscles operate autonomously, without conscious control.
Delving Deeper into Voluntary Control: The Neural Pathways
The voluntary control of skeletal muscles is a complex process involving the nervous system. It begins with a decision in the brain. This decision then triggers nerve impulses that travel down motor neurons to the skeletal muscle fibers. At the neuromuscular junction, the nerve impulse releases a neurotransmitter (acetylcholine), which triggers the muscle fibers to contract.
This intricate interplay between the brain, nervous system, and muscles allows for precise and coordinated movements. The brain receives feedback from sensory receptors in the muscles and joints, providing information about the muscle’s current state and position. This sensory feedback allows for adjustments and fine-tuning of movements, ensuring smooth and controlled actions.
Clinical Significance: Understanding Muscle Disorders
Understanding the differences between muscle types is also crucial in diagnosing and treating various muscle disorders. Problems with skeletal muscles can manifest as weakness, fatigue, cramps, or even paralysis. Disorders affecting smooth muscles might involve problems with digestion, urination, or blood pressure regulation. Cardiac muscle disorders, such as cardiomyopathy or heart failure, can have life-threatening consequences.
Conclusion: A Unified Perspective
This in-depth exploration of the three muscle types highlights the remarkable diversity and functionality of muscle tissue within the human body. While all three play vital roles, it's the skeletal muscle that stands out as the voluntary muscle, allowing for conscious control of movement and interaction with the environment. Further research into the intricacies of muscle physiology continues to unveil fascinating details about their structure, function, and crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. This knowledge underscores the importance of understanding the unique properties of each muscle type, facilitating advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation strategies for a wide range of muscle-related conditions. The intricate interplay between these muscle types, along with the nervous and other systems, truly reflects the remarkable complexity and elegance of the human body.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Intermolecular Forces Are Present In Ch4
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Man Was Murdered In His Office Riddle
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Coil Is Formed By Winding 250 Turns
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Rotating Fan Completes 1200 Revolutions
Mar 28, 2025
-
1 Meter Equals How Many Millimeters
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Types Of Muscles Is Voluntary Muscle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
