Which Of The Following Is Not Part Of The Brain
News Leon
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
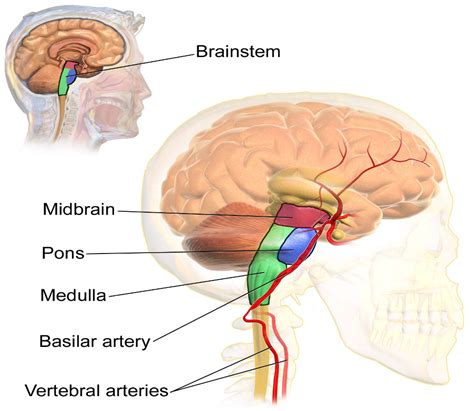
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is NOT Part of the Brain? A Deep Dive into Brain Anatomy
The human brain, a marvel of biological engineering, is a complex organ responsible for everything from basic bodily functions to higher-level cognitive processes. Understanding its intricate structure is crucial to appreciating its capabilities and the impact of neurological conditions. This article explores the components of the brain and definitively answers the question: which of the following is NOT part of the brain? We'll delve into the intricacies of brain anatomy, covering key structures and debunking common misconceptions.
The Major Parts of the Brain: A Quick Overview
Before we identify what isn't part of the brain, let's establish what is. The brain is broadly divided into three major parts:
1. Cerebrum: The Seat of Higher-Level Cognition
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, responsible for higher-level cognitive functions like:
- Conscious thought: This includes our awareness, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities.
- Language: Areas within the cerebrum are dedicated to understanding and producing speech.
- Memory: While memory is distributed across the brain, the cerebrum plays a critical role in forming, storing, and retrieving memories.
- Sensory processing: Information from our senses (sight, hearing, touch, taste, smell) is processed and interpreted in the cerebrum.
- Motor control: Voluntary movements are initiated and coordinated by the cerebrum.
The cerebrum is further divided into two hemispheres (left and right) and four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital. Each lobe specializes in different functions, though they work in concert to achieve complex tasks.
Frontal Lobe: Associated with higher-level cognitive functions, planning, decision-making, and voluntary movement.
Parietal Lobe: Processes sensory information related to touch, temperature, pain, and spatial awareness.
Temporal Lobe: Primarily involved in auditory processing, memory, and language comprehension.
Occipital Lobe: Responsible for processing visual information.
2. Cerebellum: The Master of Coordination and Balance
Often referred to as the "little brain," the cerebellum is located at the back of the brain, beneath the cerebrum. Its primary functions include:
- Motor coordination: The cerebellum fine-tunes voluntary movements, ensuring smooth and precise execution.
- Balance and posture: It plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and equilibrium.
- Motor learning: The cerebellum is involved in the learning and adaptation of motor skills.
3. Brainstem: Connecting the Brain to the Body
The brainstem is the stalk-like structure that connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord. It's responsible for several vital functions, including:
- Breathing: The brainstem controls the involuntary process of breathing.
- Heart rate: It regulates heart rate and blood pressure.
- Consciousness: Certain parts of the brainstem are essential for maintaining consciousness.
- Reflexes: Many basic reflexes are controlled by the brainstem.
The brainstem comprises three main parts: the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. Each plays a specific role in coordinating these vital functions.
Structures Often Confused with the Brain
Several structures are closely associated with the brain but are distinct entities. Understanding their roles clarifies the boundaries of the brain itself.
1. Spinal Cord: The Information Highway
The spinal cord is a long, cylindrical structure extending from the brainstem down the back. It acts as a vital communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body, transmitting sensory information to the brain and motor commands from the brain to muscles and glands. While intimately linked to the brain's function, the spinal cord is not considered part of the brain itself.
2. Meninges: Protective Layers
The meninges are three layers of protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord. These layers—the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater—provide cushioning and protection against trauma. They are crucial for brain health but are separate structures.
3. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): The Brain's Cushion
CSF is a clear, colorless fluid that circulates within the ventricles (fluid-filled cavities) of the brain and around the brain and spinal cord. It acts as a shock absorber, protecting the brain from impact, and provides nutrients to the brain tissue. While essential for brain function, CSF is a fluid, not a structural component of the brain itself.
4. Cranial Nerves: Direct Connections
Twelve pairs of cranial nerves emerge directly from the brainstem and extend to various parts of the head and neck. They transmit sensory information and motor commands to and from the brain, controlling functions like vision, hearing, taste, facial expressions, and swallowing. While crucial for brain function, these are distinct nerves, not integral parts of the brain structure.
Debunking Common Misconceptions
There are several common misunderstandings about brain anatomy. Let's address a few:
-
The pineal gland is not the "third eye": While located in the center of the brain, the pineal gland's function is to produce melatonin, a hormone regulating sleep-wake cycles. It doesn't possess any visual function.
-
The pituitary gland is not directly part of the brain structure: The pituitary gland, often called the "master gland," is located beneath the hypothalamus, a region of the brain. While it receives signals from the hypothalamus and regulates many hormonal functions, it's a separate endocrine organ.
-
The thalamus is not the "relay station" alone: While the thalamus does relay sensory information to the cortex, it's also involved in other functions, including motor control and sleep regulation. It's a much more complex structure than simply a relay station.
Which of the Following is NOT Part of the Brain? The Answer
Given the explanations above, we can confidently answer the question posed in the title. Any of the following could be the answer, depending on the options provided:
- Spinal cord: This is a distinct structure, a crucial part of the central nervous system but separate from the brain.
- Meninges: The protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): The fluid that cushions and nourishes the brain and spinal cord.
- Cranial nerves: The nerves that extend directly from the brainstem.
- Pituitary gland: An endocrine gland located beneath the hypothalamus.
- Pineal gland: A small endocrine gland involved in sleep-wake regulation.
The precise answer depends entirely on the multiple-choice options presented. However, understanding the distinct roles and anatomical locations of these structures clarifies their relationship to the brain itself.
Conclusion: The Amazing Complexity of the Brain
The human brain is a remarkably complex and fascinating organ. Understanding its intricate structure and function is essential for appreciating its capabilities and the impact of neurological disorders. While many structures are closely related and work in concert with the brain, it's crucial to differentiate between the brain itself and its associated structures. By clarifying the boundaries of the brain and understanding the functions of surrounding components, we can better grasp the intricacies of this amazing biological marvel. Remember, accurate knowledge is crucial for anyone interested in neuroscience, medicine, or simply the human body's incredible complexity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Do Stars Only Come Out At Night
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Does The Phrase Like Dissolves Like Mean
Mar 22, 2025
-
Draw 10 Water Molecules To Create A Cluster
Mar 22, 2025
-
Half Of 1 And 1 2 Teaspoons
Mar 22, 2025
-
Number Of Cells In The Interphase
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is Not Part Of The Brain . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
