Which Of The Following Is An Aldohexose
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
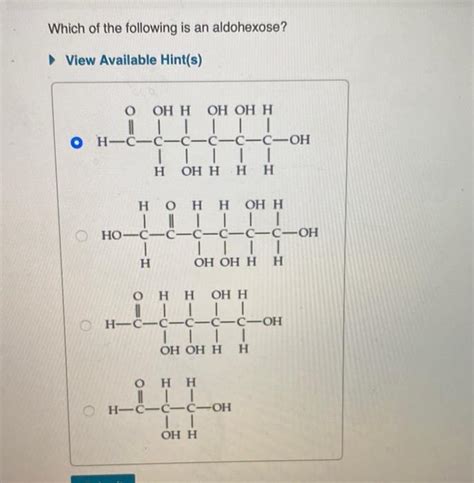
Table of Contents
Which of the following is an aldohexose? Understanding Carbohydrate Classification
Carbohydrates are fundamental biomolecules crucial for life, serving as energy sources, structural components, and signaling molecules. Understanding their classification is essential for grasping their diverse roles in biological systems. This article delves deep into the classification of carbohydrates, focusing specifically on aldohexoses and providing a detailed explanation to answer the question: which of the following is an aldohexose? We’ll explore the structural features that define aldohexoses, differentiate them from other carbohydrate types, and provide examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Carbohydrate Classification: A Foundation
Carbohydrates, also known as saccharides, are broadly classified based on their structural complexity and the number of sugar units they contain. This classification system forms the basis for understanding their individual properties and functions. The main categories include:
-
Monosaccharides: These are the simplest carbohydrates, also known as simple sugars. They cannot be hydrolyzed into smaller sugar units. Examples include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Monosaccharides are further classified based on:
- Number of carbon atoms: Trioses (3 carbons), tetroses (4 carbons), pentoses (5 carbons), hexoses (6 carbons), and so on.
- Functional group: Aldoses contain an aldehyde group (-CHO) at one end, while ketoses contain a ketone group (=C=O) within the carbon chain.
-
Disaccharides: These are formed by the condensation reaction of two monosaccharides, linked by a glycosidic bond. Examples include sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose (glucose + galactose), and maltose (glucose + glucose).
-
Oligosaccharides: These contain 3 to 10 monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic bonds.
-
Polysaccharides: These are complex carbohydrates composed of many monosaccharide units linked together. Examples include starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
Aldohexoses: The Focus of Our Exploration
The question "which of the following is an aldohexose?" necessitates a deeper understanding of this specific carbohydrate category. Aldohexoses are a subset of monosaccharides characterized by:
-
Six carbon atoms: The "hex" prefix indicates the presence of six carbon atoms in the molecule.
-
An aldehyde functional group: The "aldo" prefix signifies the presence of an aldehyde group (-CHO) at one end of the carbon chain. This aldehyde group is highly reactive and plays a crucial role in various biochemical reactions.
This combination of features gives aldohexoses their unique chemical properties and biological functions.
Identifying Aldohexoses: Structural Features and Isomerism
Several aldohexoses exist, differing in the arrangement of their hydroxyl (-OH) groups around the chiral carbon atoms. This isomerism leads to a variety of aldohexose molecules with distinct properties. The most common aldohexoses include:
-
D-Glucose: This is arguably the most important aldohexose, serving as the primary energy source for many living organisms. It is found in various forms, including its cyclic structures (pyranose and furanose forms).
-
D-Galactose: A constituent of lactose (milk sugar), D-galactose differs from D-glucose only in the configuration of the hydroxyl group at carbon 4.
-
D-Mannose: Another important aldohexose, D-mannose differs from D-glucose in the configuration of the hydroxyl group at carbon 2.
The "D" prefix in the names indicates the configuration of the chiral carbon furthest from the aldehyde group. Understanding the stereochemistry of these molecules is critical for understanding their interactions in biological systems. The difference in the arrangement of hydroxyl groups dramatically affects the properties and functions of these aldohexoses. For example, the subtle structural difference between glucose and galactose leads to distinct metabolic pathways and roles in the body.
Distinguishing Aldohexoses from other Carbohydrates
It's crucial to differentiate aldohexoses from other types of carbohydrates to accurately answer the "which of the following is an aldohexose?" question. Here's a comparison:
| Feature | Aldohexose | Ketohexose | Aldopentose | Ketopentose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Atoms | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| Functional Group | Aldehyde (-CHO) at one end | Ketone (=C=O) within the carbon chain | Aldehyde (-CHO) at one end | Ketone (=C=O) within the carbon chain |
| Example | Glucose, Galactose, Mannose | Fructose | Ribose, Arabinose | Xylulose, Ribulose |
As this table illustrates, the presence of six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group uniquely defines an aldohexose. Any molecule lacking either of these characteristics cannot be classified as an aldohexose.
The Importance of Aldohexoses in Biological Systems
Aldohexoses play vital roles in various biological processes. Their importance stems from their ability to:
-
Provide energy: Glucose, the most prevalent aldohexose, is the primary source of energy for cellular respiration. It undergoes glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to generate ATP, the cell's energy currency.
-
Form structural components: Certain aldohexoses contribute to the structural integrity of cells and tissues. For instance, galactose is a component of glycolipids and glycoproteins found in cell membranes.
-
Participate in signaling pathways: Some aldohexoses are involved in cellular signaling, regulating various biological processes. Glycosylation, the attachment of carbohydrates to proteins or lipids, often involves aldohexoses and affects protein function and cell recognition.
-
Serve as precursors for other biomolecules: Aldohexoses can be converted into other essential molecules, such as amino acids and nucleotides.
Solving the "Which of the Following is an Aldohexose?" Puzzle
To definitively identify an aldohexose from a given list, meticulously examine each molecule's structure:
-
Count the carbon atoms: Ensure the molecule possesses six carbon atoms.
-
Identify the functional group: Confirm the presence of an aldehyde group (-CHO) at one end of the carbon chain. If a ketone group (=C=O) is present within the chain, it's a ketohexose, not an aldohexose.
-
Consider the stereochemistry: While not always explicitly provided, the stereochemistry (D or L configuration) can further refine the identification. However, the presence of six carbons and an aldehyde group is the primary determinant.
Let's consider an example: Suppose you are given the following molecules: glucose, fructose, ribose, and galactose. By applying the above criteria:
- Glucose: Six carbons, aldehyde group – Aldohexose
- Fructose: Six carbons, ketone group – Ketohexose
- Ribose: Five carbons, aldehyde group – Aldopentose
- Galactose: Six carbons, aldehyde group – Aldohexose
Therefore, glucose and galactose are the aldohexoses in this list.
Conclusion: Mastering Carbohydrate Classification
Understanding carbohydrate classification, particularly the distinction between aldohexoses and other carbohydrate types, is fundamental to comprehending their diverse roles in biology and biochemistry. By meticulously examining the number of carbon atoms and the presence of the aldehyde group, one can accurately identify aldohexoses. Remember to consider the stereochemical configurations to differentiate between various aldohexose isomers. This detailed explanation should empower you to confidently answer the question "which of the following is an aldohexose?" and appreciate the significance of these essential biomolecules. Further exploration of carbohydrate chemistry will unveil the intricacies and beauty of these versatile molecules and their impact on life itself.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Steroid Hormone
Mar 24, 2025
-
The Layer Of Gases Surrounding Earth Is The
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is 3 Percent Of 18
Mar 24, 2025
-
In Triangle Abc The Measure Of Angle B Is 90
Mar 24, 2025
-
Write The Iupac Name Of The Compound Shown
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is An Aldohexose . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
