Which Of The Following Genotypes Is Homozygous Dominant
News Leon
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
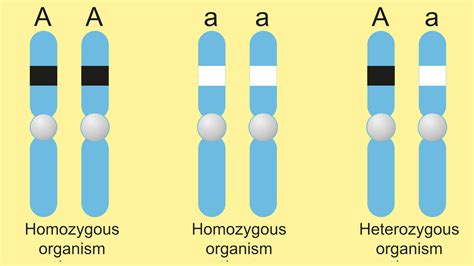
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Genotypes is Homozygous Dominant? Understanding Genotype and Phenotype
Understanding genetics can sometimes feel like navigating a maze. Terms like "homozygous dominant," "heterozygous," and "phenotype" might seem confusing at first, but with a little exploration, they become clear and fascinating. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of genotypes, focusing specifically on identifying homozygous dominant genotypes. We'll explore the concepts behind them, use examples to illustrate the key ideas, and clear up any potential confusion.
What are Genotypes and Phenotypes?
Before we dive into homozygous dominant genotypes, let's define the fundamental terms.
Genotype: This refers to the genetic makeup of an organism. It's the specific combination of alleles (different versions of a gene) an individual possesses for a particular trait. These alleles are inherited from parents, one from each. We typically represent genotypes using letters. For example, if we're looking at a gene that controls flower color, 'B' might represent the allele for purple flowers, and 'b' might represent the allele for white flowers.
Phenotype: This describes the observable characteristics of an organism. It's the physical expression of the genotype. Using our flower color example, the phenotype could be purple flowers or white flowers. The phenotype is the result of the interaction between the genotype and the environment.
Understanding Alleles and Their Interactions
Alleles are different versions of the same gene. For many genes, there are two alleles: one inherited from each parent. These alleles can interact in different ways to determine the phenotype:
-
Homozygous: This term describes a genotype where an individual has two identical alleles for a particular gene. There are two types:
- Homozygous dominant: Both alleles are the dominant allele (e.g., BB for purple flowers).
- Homozygous recessive: Both alleles are the recessive allele (e.g., bb for white flowers).
-
Heterozygous: This describes a genotype where an individual has two different alleles for a particular gene (e.g., Bb for purple flowers). In this case, the dominant allele usually masks the expression of the recessive allele.
Identifying Homozygous Dominant Genotypes
The key to identifying a homozygous dominant genotype is understanding the concept of dominance. Dominant alleles exert their effect even when only one copy is present. Recessive alleles, on the other hand, only exert their effect when two copies are present (homozygous recessive).
How to spot a homozygous dominant genotype:
- Look for the same dominant allele: The genotype will have two identical capital letters representing the dominant allele. Remember, we typically use capital letters to represent dominant alleles and lowercase letters to represent recessive alleles.
- Example: Let's say 'T' represents the dominant allele for tall plants, and 't' represents the recessive allele for short plants. A homozygous dominant genotype for tall plants would be TT.
Examples of Homozygous Dominant Genotypes in Different Traits
Let's explore some examples to solidify our understanding:
1. Flower Color (as mentioned above)
- Gene: Flower color
- Alleles: B (purple, dominant), b (white, recessive)
- Homozygous dominant genotype: BB (purple flowers)
- Homozygous recessive genotype: bb (white flowers)
- Heterozygous genotype: Bb (purple flowers – the dominant allele B masks the recessive allele b)
2. Seed Shape in Pea Plants
- Gene: Seed shape
- Alleles: R (round, dominant), r (wrinkled, recessive)
- Homozygous dominant genotype: RR (round seeds)
- Homozygous recessive genotype: rr (wrinkled seeds)
- Heterozygous genotype: Rr (round seeds)
3. Human Earlobe Attachment
- Gene: Earlobe attachment
- Alleles: E (attached earlobes, dominant), e (free earlobes, recessive)
- Homozygous dominant genotype: EE (attached earlobes)
- Homozygous recessive genotype: ee (free earlobes)
- Heterozygous genotype: Ee (attached earlobes)
4. Human Hair Color (Simplified Example)
This is a simplification as hair color is controlled by multiple genes.
- Gene: Simplified hair color gene
- Alleles: B (Brown, dominant), b (blonde, recessive)
- Homozygous dominant genotype: BB (Brown hair)
- Homozygous recessive genotype: bb (Blonde hair)
- Heterozygous genotype: Bb (Brown hair)
5. Human Widow's Peak
- Gene: Presence of a Widow's Peak (a hairline that comes to a point)
- Alleles: W (Widow's Peak, dominant), w (no Widow's Peak, recessive)
- Homozygous dominant genotype: WW (Widow's Peak)
- Homozygous recessive genotype: ww (no Widow's Peak)
- Heterozygous genotype: Ww (Widow's Peak)
Beyond Simple Mendelian Genetics
While the examples above illustrate simple Mendelian inheritance (where one gene controls one trait), many traits are more complex. Some traits are influenced by multiple genes (polygenic inheritance), while others are affected by both genes and environmental factors. However, the underlying principles of homozygous dominant genotypes remain the same – they represent the presence of two identical dominant alleles for a given gene.
Practical Applications of Understanding Genotypes
Understanding genotypes and phenotypes has far-reaching applications:
- Agriculture: Breeders use their knowledge of genetics to develop crops with desirable traits, like disease resistance or higher yields. Identifying homozygous dominant genotypes allows for predictable inheritance of these traits.
- Medicine: Genetic testing can identify individuals who are at risk for certain diseases. Understanding genotypes can help doctors tailor treatment plans to individual needs.
- Animal Breeding: Similar to agriculture, breeders use genetic knowledge to improve livestock traits, such as milk production or disease resistance. The identification of homozygous dominant genotypes is crucial in this process.
Conclusion: Mastering the Homozygous Dominant Genotype
Identifying homozygous dominant genotypes is a fundamental skill in genetics. By understanding the concepts of alleles, dominance, and the difference between genotype and phenotype, we can confidently determine whether a given genotype falls into this category. Remember, a homozygous dominant genotype is represented by two identical capital letters representing the dominant allele. This knowledge is vital in many fields, from agriculture and medicine to animal breeding, and it lays the foundation for a deeper understanding of the fascinating world of genetics. Keep practicing with different examples, and soon you'll be a pro at identifying homozygous dominant genotypes!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Explain Common Different And Conflicting Goals By Giving Appropriate Examples
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is The Major Product For The Following Reaction Sequence
Apr 02, 2025
-
Decomposers Are Important In The Environment Because They
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of Ca3 Po4 2
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Percent Of The Figure Is Shaded
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Genotypes Is Homozygous Dominant . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
