What Is The Molar Mass Of Ca3 Po4 2
News Leon
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
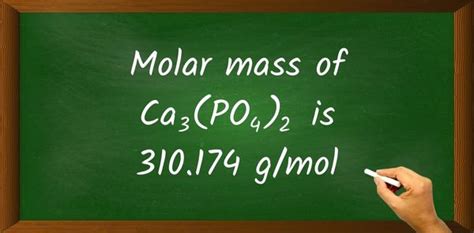
Table of Contents
What is the Molar Mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂? A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the molar mass of a compound is a fundamental concept in chemistry, crucial for various calculations and analyses. This article delves into the detailed process of calculating the molar mass of calcium phosphate, Ca₃(PO₄)₂, explaining each step clearly and comprehensively. We'll also explore the significance of molar mass and its applications in different fields.
Understanding Molar Mass
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is a unit representing Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10²³) of elementary entities, such as atoms, molecules, or ions. Therefore, the molar mass essentially tells us the mass of 6.022 x 10²³ particles of a given substance in grams. It's expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
Calculating molar mass requires knowing the atomic masses of the constituent elements, readily available in the periodic table. The atomic mass of an element represents the average mass of all its isotopes, weighted according to their natural abundance.
Calculating the Molar Mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂
Calcium phosphate, Ca₃(PO₄)₂, is an ionic compound composed of calcium (Ca²⁺) cations and phosphate (PO₄³⁻) anions. To calculate its molar mass, we need to consider the atomic masses of calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P), and oxygen (O).
Step 1: Identify the Elements and Their Atomic Masses
From the chemical formula Ca₃(PO₄)₂, we can see the compound contains:
- Calcium (Ca): 3 atoms
- Phosphorus (P): 2 atoms
- Oxygen (O): 8 atoms (4 oxygen atoms per phosphate ion, and 2 phosphate ions)
Using a periodic table, we find the approximate atomic masses:
- Ca: 40.08 g/mol
- P: 30.97 g/mol
- O: 16.00 g/mol
Step 2: Calculate the Mass Contribution of Each Element
Next, we multiply the number of atoms of each element by its atomic mass:
- Calcium (Ca): 3 atoms × 40.08 g/mol/atom = 120.24 g/mol
- Phosphorus (P): 2 atoms × 30.97 g/mol/atom = 61.94 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 8 atoms × 16.00 g/mol/atom = 128.00 g/mol
Step 3: Sum the Mass Contributions
Finally, we sum the mass contributions of all elements to obtain the molar mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂:
120.24 g/mol (Ca) + 61.94 g/mol (P) + 128.00 g/mol (O) = 310.18 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is approximately 310.18 g/mol. Slight variations might occur depending on the values of atomic masses used from different periodic tables.
Significance and Applications of Molar Mass
The molar mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂, and molar mass calculations in general, are crucial for various applications across different scientific disciplines:
1. Stoichiometric Calculations
Molar mass is fundamental in stoichiometry, which deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. It allows us to convert between mass and moles, enabling precise calculations of reactant amounts, product yields, and limiting reagents.
For example, knowing the molar mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ allows us to calculate how many grams of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ are required to react with a specific amount of another reactant in a chemical reaction.
2. Solution Chemistry
In solution chemistry, molar mass is used to prepare solutions of known concentrations. For instance, to prepare a 1 M (molar) solution of Ca₃(PO₄)₂, we need to dissolve 310.18 grams of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ in enough solvent to make one liter of solution.
3. Analytical Chemistry
Molar mass plays a vital role in analytical chemistry techniques, such as titration and gravimetric analysis. These methods often rely on precise mass measurements and molar mass conversions to determine the concentration or amount of a substance in a sample.
4. Biochemistry and Biology
Molar mass is essential in biochemistry and biology for understanding the properties and functions of biomolecules. Proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids all have specific molar masses, which are relevant to their interactions and biological roles.
5. Material Science
In material science, molar mass is crucial for determining the composition and properties of materials. The molar mass of components influences various physical properties, like density, melting point, and reactivity.
6. Environmental Science
In environmental science, molar mass helps quantify pollutants and their concentrations. This is crucial for understanding their impact on ecosystems and human health, as well as for developing effective remediation strategies.
7. Pharmaceutical Science
In pharmaceutical science, molar mass is used in drug formulation and dosage calculations. Precise determination of the molar mass of active pharmaceutical ingredients is critical for ensuring the safety and efficacy of medications.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Calculating Molar Mass
While the calculation seems straightforward, several common mistakes can lead to inaccurate results:
- Incorrectly interpreting chemical formulas: Pay close attention to subscripts and parentheses when counting the number of atoms of each element.
- Using incorrect atomic masses: Always refer to a reliable periodic table for the most accurate atomic masses. Slight differences in atomic mass values can lead to noticeable discrepancies in the final molar mass.
- Calculation errors: Double-check your arithmetic to avoid simple mistakes in addition and multiplication.
Conclusion
Calculating the molar mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂, and other compounds, is a fundamental skill in chemistry with far-reaching applications across various scientific disciplines. By carefully following the steps outlined above and avoiding common pitfalls, you can confidently determine the molar mass of any compound and utilize this essential value in a wide range of calculations and analyses. Mastering this concept opens doors to a deeper understanding of chemical reactions, solution chemistry, and the quantitative aspects of the natural world. The accurate determination of molar mass is critical for ensuring the reliability and precision of countless experiments and analyses across numerous scientific fields. Therefore, a thorough understanding of this fundamental concept remains paramount for any aspiring or practicing scientist or researcher.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Represents A Heterozygous Genotype
Apr 03, 2025
-
Is A Battery Potential Or Kinetic Energy
Apr 03, 2025
-
Why Do Noble Gases Have High Ionization Energies
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Are The Hereditary Changes Responsible For Evolution
Apr 03, 2025
-
Dna Serves As A Template For The Synthesis Of
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Molar Mass Of Ca3 Po4 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
