Which Of The Following Expressions Is Equal To
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
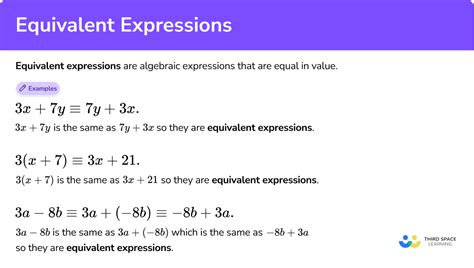
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Expressions is Equal To? A Deep Dive into Mathematical Equivalence
Determining which expressions are equal is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for simplifying equations, solving problems, and understanding algebraic manipulations. This article will delve deep into various methods and strategies for identifying equivalent expressions, focusing on how to approach this problem systematically and efficiently. We'll explore different mathematical concepts, such as order of operations, factoring, expanding expressions, and using properties of real numbers to demonstrate equivalence. The ultimate goal is to equip you with the skills to confidently tackle any "which of the following expressions is equal to" question.
Understanding the Problem: The Importance of Equivalence
The core of this type of problem lies in the concept of mathematical equivalence. Two expressions are considered equivalent if they produce the same result for all valid input values. This means that no matter what numbers you substitute for the variables, both expressions will yield the identical numerical outcome. Understanding this principle is crucial because it allows us to simplify complex expressions into more manageable forms, which often simplifies problem-solving.
Strategies for Identifying Equivalent Expressions
Several strategies can be used to determine if two expressions are equivalent. Let's explore some of the most common and effective ones:
1. Simplifying Expressions
The most straightforward approach often involves simplifying each expression individually until you find a common, simplified form. This involves applying the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS) consistently:
- Parentheses/Brackets: Evaluate expressions within parentheses or brackets first.
- Exponents/Orders: Calculate exponents or powers next.
- Multiplication and Division: Perform multiplication and division from left to right.
- Addition and Subtraction: Perform addition and subtraction from left to right.
Example:
Let's say we have the expressions:
- A: 2(x + 3) + 4x
- B: 6x + 6
To determine if they are equal, simplify expression A:
- Distribute the 2: 2x + 6 + 4x
- Combine like terms: 6x + 6
Now we see that expression A simplifies to 6x + 6, which is identical to expression B. Therefore, expressions A and B are equivalent.
2. Expanding Expressions
Expanding an expression involves removing parentheses or brackets by multiplying the terms within them. This often reveals the underlying structure and allows for easier comparison with other expressions. The distributive property is essential here: a(b + c) = ab + ac.
Example:
Consider:
- A: (x + 2)(x + 3)
- B: x² + 5x + 6
To check for equivalence, expand expression A:
- Use the FOIL method (First, Outer, Inner, Last): x² + 3x + 2x + 6
- Combine like terms: x² + 5x + 6
We see that expression A expands to x² + 5x + 6, which is identical to expression B, proving their equivalence.
3. Factoring Expressions
Factoring is the reverse of expanding. It involves breaking down a complex expression into simpler factors. This can be particularly useful when comparing expressions that appear different at first glance. Common factoring techniques include:
- Greatest Common Factor (GCF): Identify the largest number or variable that divides all terms.
- Difference of Squares: Factor expressions in the form a² - b² as (a + b)(a - b).
- Trinomial Factoring: Factor quadratic expressions (ax² + bx + c) into two binomial expressions.
Example:
Let's examine:
- A: x² - 9
- B: (x - 3)(x + 3)
Expression A is a difference of squares. Factoring it, we get (x - 3)(x + 3), which is identical to expression B. Thus, they are equivalent.
4. Using Properties of Real Numbers
The properties of real numbers (commutative, associative, distributive, etc.) are invaluable tools for manipulating expressions and demonstrating equivalence. Understanding these properties allows for flexible manipulation of equations to obtain a common form.
- Commutative Property: The order of addition or multiplication doesn't affect the result (a + b = b + a; ab = ba).
- Associative Property: The grouping of terms in addition or multiplication doesn't affect the result ((a + b) + c = a + (b + c); (ab)c = a(bc)).
- Distributive Property: a(b + c) = ab + ac.
Example:
Consider:
- A: 3x + 2y + 5x
- B: 8x + 2y
Using the commutative and associative properties, we can rearrange expression A: 3x + 5x + 2y = (3 + 5)x + 2y = 8x + 2y, which is equivalent to expression B.
5. Substituting Values (Caution!)
While substituting specific values for variables can be helpful in disproving equivalence, it's not sufficient to prove it. If two expressions yield different results for a single value, they are definitely not equivalent. However, if they produce the same result for several values, it doesn't guarantee equivalence. True equivalence holds for all valid input values.
Example:
Suppose we have:
- A: x² - 1
- B: x - 1
Substituting x = 2 in both expressions:
A: 2² - 1 = 3 B: 2 - 1 = 1
Since the results differ, we conclusively know that A and B are not equivalent.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
For more complex expressions, advanced techniques like completing the square, using the quadratic formula, or employing trigonometric identities might be necessary. Remember to always follow the order of operations precisely and apply the properties of real numbers consistently.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Incorrect order of operations: This is a common source of errors. Always follow PEMDAS/BODMAS meticulously.
- Incorrect distribution: Make sure you distribute terms correctly when expanding expressions.
- Losing negative signs: Keep track of negative signs carefully throughout the simplification process.
- Overlooking like terms: Ensure all like terms are combined correctly when simplifying.
Conclusion: Mastering Equivalence for Success
Mastering the ability to determine which expressions are equal is essential for success in algebra and many other areas of mathematics. By consistently applying the strategies discussed above – simplifying, expanding, factoring, using the properties of real numbers, and cautiously using substitution – you can confidently tackle any "which of the following expressions is equal to" problem. Remember that practice is key; the more you work with these concepts, the more intuitive they become, leading to faster and more accurate solutions. The systematic approach outlined here provides a strong foundation for tackling even the most challenging equivalence problems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Chamber Of Heart Has Thickest Wall
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 1 2 Miles
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lines Of Symmetry On A Trapezoid
Mar 18, 2025
-
Two Same Words With Different Meanings
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Expressions Is Equal To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
