Which Of The Following Are Characteristics Of A Competitive Market
News Leon
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
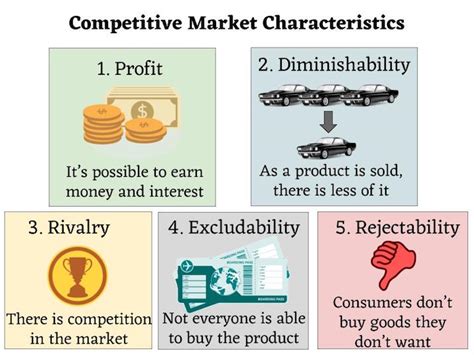
Table of Contents
Which of the Following are Characteristics of a Competitive Market? A Deep Dive
Understanding the characteristics of a competitive market is crucial for businesses of all sizes. A competitive market, far from being a battlefield of cutthroat tactics, is actually a dynamic ecosystem that drives innovation, efficiency, and ultimately, benefits consumers. This article will delve deep into the defining features of a competitive market, exploring nuances often overlooked in simplified explanations. We'll examine how these characteristics interact, the exceptions to the rules, and the implications for businesses navigating these landscapes.
Defining a Competitive Market: Beyond Simple Definitions
A competitive market, in its purest form, is one where numerous buyers and sellers interact, with no single entity having significant influence over price or supply. This idealized model, often referred to as perfect competition, serves as a benchmark against which real-world markets are compared. However, achieving perfect competition is exceedingly rare. Most markets exhibit elements of competition, but fall short of the ideal. This necessitates a nuanced understanding of the key characteristics.
Key Characteristics of a Competitive Market
Several essential elements define a competitive market, irrespective of whether it's a perfectly competitive market or a more realistic, imperfectly competitive one. These characteristics are interconnected and their presence, or absence, significantly impacts market dynamics.
1. Numerous Buyers and Sellers: The Foundation of Competition
The presence of a large number of buyers and sellers is the bedrock of competition. When many buyers and sellers exist, no single entity can dictate prices or control supply. This prevents monopolies or oligopolies (markets dominated by a few firms) from forming. The sheer number of participants ensures that each individual actor has limited market power.
Impact: This characteristic promotes price stability, as no single entity can manipulate prices significantly. It also fosters a more dynamic market, where businesses constantly strive to offer better products or services to attract customers.
Imperfect Competition Consideration: Even in markets with many participants, certain firms might hold a slightly larger market share. This, however, doesn't entirely negate the competitive aspect if the market still allows for relatively easy entry and exit for businesses.
2. Homogenous Products or Services: Differentiation and its Limits
In a perfectly competitive market, products or services are homogenous – essentially identical. This means buyers view the offerings of different sellers as perfect substitutes. This makes price the primary determinant of consumer choice.
Impact: Homogeneity pushes businesses to focus on efficiency and cost reduction to compete. Innovation often focuses on incremental improvements in production processes rather than significant product differentiation.
Imperfect Competition Consideration: In reality, perfect homogeneity is rare. Most markets feature product differentiation, where businesses strive to distinguish their offerings through branding, features, or quality. However, even with differentiation, competition can thrive if consumers perceive substantial substitutability between products.
3. Free Entry and Exit: The Engine of Dynamic Competition
The ability of firms to easily enter and exit a market is crucial for maintaining competition. Low barriers to entry prevent monopolies from forming, as new competitors can readily challenge established players. Similarly, the ease of exit prevents inefficient firms from clinging to the market, thus promoting resource allocation efficiency.
Impact: Free entry and exit ensure that resources flow to their most productive uses. Unprofitable businesses are forced to leave, while successful ones attract new entrants, keeping the market dynamic and responsive to changes in consumer demand.
Imperfect Competition Consideration: High barriers to entry, such as significant capital requirements, regulatory hurdles, or patent protection, can stifle competition and lead to less efficient outcomes. Similarly, significant sunk costs (investments that cannot be easily recovered) can make exit difficult, even for failing firms.
4. Perfect Information: Transparency and its Challenges
In a perfectly competitive market, buyers and sellers possess complete and accurate information about prices, product quality, and availability. This transparency ensures that transactions occur at efficient prices, reflecting the true value of goods and services.
Impact: Perfect information eliminates situations where consumers pay more than they need to or businesses sell below their costs. It also ensures that resources are allocated optimally.
Imperfect Competition Consideration: In the real world, perfect information is a utopian ideal. Information asymmetries—where one party has more information than the other—are common. This can lead to market inefficiencies, such as adverse selection (where low-quality products dominate the market) or moral hazard (where one party takes excessive risks knowing that the other party will bear the consequences).
5. Price Takers, Not Price Makers: The Power of the Market
In a perfectly competitive market, individual buyers and sellers are "price takers." They accept the market price as given and cannot influence it through their individual actions. This contrasts with markets where firms have pricing power, such as monopolies or oligopolies.
Impact: Price-taking behavior ensures that the market price reflects the equilibrium between supply and demand, leading to efficient resource allocation.
Imperfect Competition Consideration: In imperfectly competitive markets, firms often possess some degree of pricing power. This allows them to set prices above marginal cost (the cost of producing one additional unit), leading to reduced consumer surplus (the difference between what consumers are willing to pay and what they actually pay).
Imperfect Competition: The Reality of Most Markets
While perfect competition serves as a useful theoretical model, most real-world markets fall short of this ideal. Imperfect competition arises from deviations in one or more of the characteristics described above. Examples of imperfectly competitive market structures include:
- Monopoly: A market dominated by a single seller.
- Oligopoly: A market dominated by a few large firms.
- Monopolistic Competition: A market with many firms selling differentiated products.
Analyzing Markets for Competitive Characteristics
To analyze whether a specific market is competitive, consider the following steps:
- Identify the number of buyers and sellers: Are there many or few participants? A larger number suggests greater competition.
- Assess product homogeneity: Are products largely identical, or are there significant differences? Homogeneity points towards greater price competition.
- Examine barriers to entry and exit: Are there significant obstacles preventing firms from entering or exiting the market? High barriers suggest less competition.
- Evaluate information availability: Is information readily available to buyers and sellers? Imperfect information can reduce competition and efficiency.
- Determine pricing power: Do individual firms have significant influence over prices, or are they price takers? Price-making power suggests reduced competition.
The Importance of Understanding Competitive Markets
Understanding the characteristics of competitive markets is not just an academic exercise. It's crucial for businesses to:
- Develop effective strategies: Businesses can leverage an understanding of market structure to develop competitive pricing strategies, product differentiation approaches, and marketing campaigns.
- Make informed decisions: Understanding market dynamics aids in making strategic decisions about investment, expansion, and resource allocation.
- Anticipate market changes: By identifying shifts in the competitive landscape, businesses can adapt and remain competitive.
- Advocate for fair competition: An understanding of anti-competitive practices helps businesses and consumers advocate for fair market conditions.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Competitive Markets
The characteristics of a competitive market are multifaceted and often intertwined. While the idealized model of perfect competition offers valuable insights, the reality is that most markets exhibit some degree of imperfection. By understanding the key characteristics and the nuances of different market structures, businesses can navigate the complexities of the marketplace, make informed decisions, and ultimately, thrive in a dynamic and ever-evolving environment. The pursuit of understanding competitive landscapes, even with their imperfections, remains a constant challenge and a crucial element for success in the business world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Units Of Conductance
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is Mega In Scientific Notation
Apr 02, 2025
-
Is Lead Sulphate Soluble In Water
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many Seconds Is 2 Years
Apr 02, 2025
-
Electric Field For Infinite Line Of Charge
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Are Characteristics Of A Competitive Market . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
