Which Is The Largest Gland In The Body
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
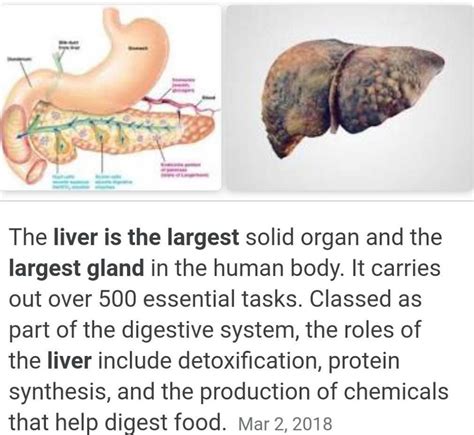
Table of Contents
Which is the Largest Gland in the Body? Unveiling the Secrets of the Liver
The human body is a marvel of intricate systems, each component playing a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Amongst this complex network of organs, glands stand out as crucial players, responsible for producing and secreting essential hormones and other substances. While many glands contribute to our physiological processes, one reigns supreme in terms of size: the liver. This article delves deep into the world of the liver, exploring its remarkable size, diverse functions, and significant impact on overall health.
The Liver: A Giant Among Glands
The liver, located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, is unequivocally the largest gland in the human body. Its sheer size is striking, often weighing between 3 and 3.5 pounds (1.4 and 1.6 kilograms) in adults. This substantial organ performs over 500 vital functions, making it an indispensable component of our survival. Its size reflects the immense workload it undertakes, constantly working to maintain a delicate balance within our internal environment.
Debunking the Myths: Why Other Glands Aren't the Biggest
Often, other glands, such as the thyroid or pituitary, are mistakenly considered the largest. However, a closer look at their size and function reveals the true champion. While the thyroid is crucial for regulating metabolism and the pituitary gland controls numerous hormonal processes, their size pales in comparison to the liver's substantial mass. Understanding the distinctions helps clarify the true identity of the body's largest gland.
The Multifaceted Roles of the Liver: A Deep Dive into its Functions
The liver's impressive size is directly linked to its remarkable versatility. Its functions are incredibly diverse, impacting nearly every aspect of our physiological well-being. Let's explore some of its key roles:
1. Metabolism: The Liver as a Central Processing Unit
The liver acts as the body's central metabolic hub, processing nutrients absorbed from the digestive system. It plays a critical role in:
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: Regulating blood glucose levels, storing glucose as glycogen, and converting glycogen back to glucose when needed. This ensures a stable supply of energy for the body's cells.
- Lipid Metabolism: Synthesizing cholesterol and lipoproteins, breaking down fats, and processing fatty acids. It plays a vital role in managing lipid levels in the bloodstream.
- Protein Metabolism: Synthesizing essential proteins, converting amino acids, and breaking down proteins. This process is essential for building and repairing tissues.
2. Detoxification: The Body's Internal Filter
The liver serves as a crucial detoxifying organ, filtering harmful substances from the bloodstream. This function is vital for eliminating:
- Toxins: Including alcohol, drugs, and environmental pollutants. The liver converts these substances into less harmful compounds that can be excreted.
- Metabolic Byproducts: Waste products generated during metabolic processes are processed and removed by the liver, preventing their accumulation in the body.
- Medications: The liver metabolizes many medications, influencing their effectiveness and duration. Understanding this process is vital for safe medication management.
3. Bile Production: Aiding Digestion
The liver produces bile, a crucial digestive fluid that aids in the breakdown and absorption of fats. Bile emulsifies fats, breaking them down into smaller particles that can be absorbed more easily in the small intestine. This process is essential for nutrient absorption and energy production.
4. Storage: A Reservoir of Essential Nutrients
The liver acts as a storage facility for various essential nutrients, providing a readily available supply when needed. These include:
- Glycogen: A stored form of glucose, providing a readily available energy source.
- Vitamins: Including vitamins A, D, E, and K, playing crucial roles in various physiological functions.
- Minerals: Including iron and copper, essential for various metabolic processes.
5. Synthesis of Proteins: Building Blocks of Life
The liver plays a key role in synthesizing various proteins that are crucial for various bodily functions. These include:
- Plasma Proteins: Essential components of blood, responsible for maintaining blood volume, clotting, and transporting various substances.
- Clotting Factors: Proteins vital for blood clotting, preventing excessive bleeding.
- Albumin: A major protein in blood plasma, maintaining osmotic pressure and transporting hormones and other substances.
The Liver and Overall Health: Maintaining Optimal Function
Maintaining a healthy liver is crucial for overall well-being. Several factors can impact liver function, including:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins supports liver health. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption is vital, as it can severely damage the liver.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves overall health and can indirectly benefit liver function.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the burden on the liver and minimizes the risk of liver diseases.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and fatty liver disease, can significantly impair liver function. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Liver's Immense Contribution
The liver, the largest gland in the body, is a remarkable organ that performs an astounding array of functions crucial for life. Its size reflects its immense workload, constantly working to maintain our physiological balance. Understanding the liver's importance and adopting lifestyle choices that support its health are essential for maintaining overall well-being and preventing liver-related diseases. From metabolism and detoxification to bile production and nutrient storage, the liver’s contributions are nothing short of extraordinary. By appreciating its vital role, we can actively work towards maintaining a healthy and functioning liver, contributing to a longer and healthier life. Remember, taking care of your liver is investing in your overall health and well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Derived Unit
Mar 22, 2025
-
Acceleration Is Always In The Direction
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Best Describes A Hormone
Mar 22, 2025
-
Is A Hydrogen Bond Stronger Than A Covalent Bond
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Equation
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Is The Largest Gland In The Body . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
