Which Element Has 16 Protons In Its Nucleus
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
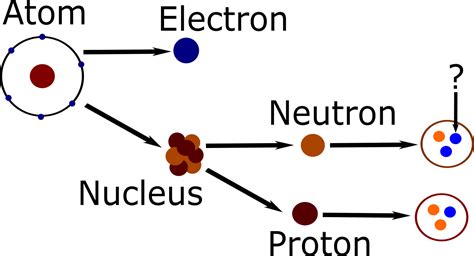
Table of Contents
Which Element Has 16 Protons in its Nucleus? Unlocking the Mystery of Sulfur
Determining an element based on the number of protons in its nucleus is a fundamental concept in chemistry. The number of protons, also known as the atomic number, uniquely identifies each element on the periodic table. So, which element boasts 16 protons residing within its atomic nucleus? The answer is sulfur (S). This article will delve deep into the properties, characteristics, and significance of sulfur, exploring its presence in various aspects of our world.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we dive into the specifics of sulfur, let's briefly revisit the basics of atomic structure. Every atom consists of three subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also found in the nucleus. The number of neutrons can vary within an element, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. The number of electrons usually equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
The atomic mass of an element is the sum of its protons and neutrons. Since the number of neutrons can vary, isotopes of the same element will have different atomic masses but the same atomic number (number of protons).
Sulfur (S): The Element with 16 Protons
With a clear understanding of atomic structure, we can confidently state that the element with 16 protons is sulfur, symbolized by the letter 'S'. This element occupies a prominent position on the periodic table, specifically in Group 16 (also known as the chalcogens) and period 3. Its atomic number, as mentioned earlier, is 16.
Isotopes of Sulfur: Variations on a Theme
While all sulfur atoms possess 16 protons, the number of neutrons can vary, resulting in different isotopes. The most common isotopes of sulfur are:
- Sulfur-32 (³²S): This is the most abundant isotope, constituting about 95% of naturally occurring sulfur. It has 16 protons and 16 neutrons.
- Sulfur-34 (³⁴S): This isotope accounts for roughly 4% of natural sulfur and has 16 protons and 18 neutrons.
- Sulfur-33 (³³S) and Sulfur-36 (³⁶S): These are less abundant isotopes, present in trace amounts in nature.
These isotopes exhibit similar chemical properties because they have the same number of protons and electrons. However, their slightly different masses can lead to subtle variations in physical properties.
Properties and Characteristics of Sulfur: A Detailed Look
Sulfur displays a fascinating array of physical and chemical properties that contribute to its diverse applications:
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Sulfur exists in various allotropic forms (different structural modifications of the same element), but commonly appears as a yellow, crystalline solid.
- Odor: Elemental sulfur has a characteristic faint odor, often described as resembling rotten eggs. This odor is associated with hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), a compound containing sulfur.
- Solubility: Sulfur is insoluble in water but soluble in some organic solvents like carbon disulfide.
- Melting and Boiling Points: Sulfur has relatively low melting and boiling points compared to many other elements.
Chemical Properties:
- Oxidation States: Sulfur exhibits multiple oxidation states, ranging from -2 to +6. This versatility allows it to form a wide variety of compounds.
- Reactivity: Sulfur is a moderately reactive element. It readily reacts with many metals and nonmetals, forming sulfides and other compounds.
- Combustion: Sulfur burns in air, producing sulfur dioxide (SO₂), a gas with a pungent odor.
- Acid-Base Reactions: Sulfur can participate in acid-base reactions, acting as both an acid and a base depending on the reaction conditions.
Sulfur's Significance in Various Fields: A Multifaceted Element
Sulfur's unique properties and reactivity make it an essential element in numerous applications across various fields:
Industrial Applications:
- Sulfuric Acid Production: Sulfur is the primary raw material in the production of sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), one of the most important industrial chemicals. Sulfuric acid is used in countless processes, including fertilizer production, metal refining, and petroleum refining.
- Rubber Vulcanization: Sulfur plays a crucial role in vulcanizing rubber, a process that strengthens and improves the elasticity of rubber. This is crucial for the production of tires, hoses, and other rubber products.
- Detergents and Pesticides: Sulfur and its compounds find applications in the production of detergents and pesticides.
Biological Significance:
- Amino Acids: Sulfur is a crucial component of certain amino acids, like cysteine and methionine, which are essential building blocks of proteins. These amino acids play vital roles in protein structure and function.
- Enzymes: Sulfur is present in several enzymes, which are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms.
- Vitamins: Sulfur is also found in certain vitamins, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Environmental Role:
- Greenhouse Gas: Sulfur dioxide (SO₂), released through industrial processes and volcanic eruptions, contributes to the formation of acid rain, impacting ecosystems and human health.
- Climate Change: Sulfur compounds can have a complex influence on climate change. While SO₂ can have a cooling effect, other sulfur compounds can contribute to warming.
Exploring the Abundance and Sources of Sulfur: Where to Find This Element
Sulfur is a relatively abundant element in the Earth's crust, ranking tenth among the elements. Its occurrence can be categorized into several forms:
- Elemental Sulfur: This form occurs naturally in volcanic regions and sedimentary deposits.
- Sulfide Minerals: Sulfur is a major component of various sulfide minerals, such as pyrite (iron sulfide), galena (lead sulfide), and sphalerite (zinc sulfide). These minerals are mined to extract valuable metals, often resulting in sulfur as a byproduct.
- Sulfate Minerals: Sulfur is also present in sulfate minerals, such as gypsum (calcium sulfate) and anhydrite (calcium sulfate). These minerals find applications in construction and other industries.
Conclusion: Sulfur - An Element with a Rich History and Diverse Applications
In conclusion, the element with 16 protons in its nucleus is sulfur (S). This versatile element has a rich history, playing a significant role in various industrial processes, biological functions, and environmental phenomena. From the production of sulfuric acid, a cornerstone of the chemical industry, to its role as a building block of life-sustaining proteins, sulfur's significance is undeniable. Understanding its properties, characteristics, and abundance provides valuable insight into the intricate workings of the natural world and the remarkable applications of this crucial element. Further research into sulfur and its compounds continues to reveal new discoveries and applications, highlighting its ongoing importance in scientific and technological advancements. The study of sulfur reminds us of the profound interconnectedness of different aspects of science and nature, emphasizing the importance of exploring the fundamental building blocks of our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
8 Is 20 Of What Number
Mar 18, 2025
-
Predict What Is Present In Each Of The Following
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Word Is Different From The Others
Mar 18, 2025
-
Reverse List Python Without Inbuilt Function
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Current Of One Ampere Is Passed Through
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Element Has 16 Protons In Its Nucleus . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
