Which Cell Organelle Is Found Only In Plant Cell
News Leon
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
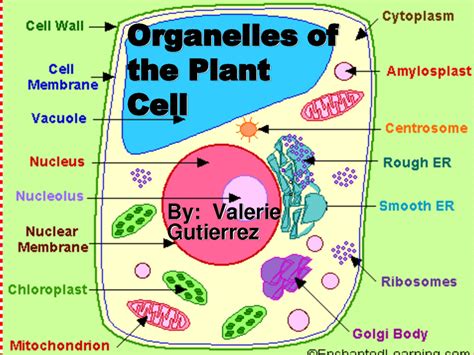
Table of Contents
Which Cell Organelle is Found Only in Plant Cells? A Deep Dive into Chloroplasts and Their Importance
The microscopic world of cells reveals fascinating differences between plant and animal cells. While both share fundamental organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes, one key structure distinguishes plant cells: the chloroplast. This remarkable organelle is not only unique to plant cells but also plays a pivotal role in sustaining life on Earth. Let's delve into the intricacies of chloroplasts, exploring their structure, function, and significance in the plant kingdom and beyond.
Understanding Chloroplasts: The Powerhouses of Photosynthesis
Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis, the vital process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This process is the foundation of most food chains, making chloroplasts essential for almost all life on our planet. Without photosynthesis, the oxygen we breathe and the food we eat would not exist.
Structure of a Chloroplast
To appreciate the function of chloroplasts, understanding their structure is crucial. They are double-membrane-bound organelles, meaning they have two lipid bilayer membranes surrounding their contents. This unique structure facilitates the complex biochemical reactions of photosynthesis. Key structural components include:
-
Outer Membrane: The outer membrane is permeable to small molecules, allowing for the passage of various substances into the chloroplast.
-
Inner Membrane: The inner membrane is less permeable and regulates the flow of substances into the stroma. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the chloroplast's internal environment.
-
Stroma: This is the fluid-filled space inside the inner membrane. It contains various enzymes and molecules necessary for the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis (the Calvin cycle).
-
Thylakoids: These are flattened, sac-like structures stacked into grana. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll and other pigments crucial for capturing light energy during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
-
Grana: These are stacks of thylakoids, maximizing the surface area for light absorption. The arrangement of grana within the stroma is highly efficient for light harvesting.
-
Chlorophyll: This green pigment is embedded within the thylakoid membranes and is responsible for absorbing light energy. Different types of chlorophyll, such as chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b, absorb light at different wavelengths, optimizing light absorption.
-
Carotenoids: These accessory pigments absorb light energy and protect chlorophyll from damage caused by excessive light. They contribute to the vibrant colors seen in leaves during autumn.
Photosynthesis: A Two-Stage Process
Photosynthesis is a two-stage process:
-
Light-dependent reactions: These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy, which is used to split water molecules (photolysis) and generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), energy-carrying molecules. Oxygen is released as a byproduct.
-
Light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle): These reactions take place in the stroma. ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions provide the energy to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into glucose, a simple sugar that serves as the plant's primary source of energy.
The Importance of Chloroplasts in Plant Life and the Ecosystem
Chloroplasts are undeniably crucial for plant life, enabling plants to:
-
Produce their own food: Through photosynthesis, plants synthesize glucose, providing them with the energy and building blocks for growth and development. This self-sufficiency distinguishes plants from animals, which must consume other organisms for energy.
-
Release oxygen: As a byproduct of photosynthesis, oxygen is released into the atmosphere. This oxygen is essential for the respiration of most living organisms, including animals and many microbes.
-
Support the food chain: Plants, as primary producers, form the base of most food chains. The energy they produce through photosynthesis is passed on to herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers, supporting the entire ecosystem.
-
Influence climate regulation: Photosynthesis plays a vital role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, from the atmosphere. This helps to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Chloroplast Evolution: Endosymbiotic Theory
The origin of chloroplasts is a fascinating topic in evolutionary biology. The endosymbiotic theory proposes that chloroplasts originated from cyanobacteria, photosynthetic bacteria, which were engulfed by a eukaryotic cell. Over time, a symbiotic relationship developed, with the cyanobacterium evolving into the chloroplast and providing the host cell with energy through photosynthesis. Evidence supporting this theory includes:
-
Double membrane: The double membrane surrounding chloroplasts is consistent with the engulfment process.
-
Circular DNA: Chloroplasts possess their own circular DNA, similar to bacteria, suggesting an independent origin.
-
Ribosomes: Chloroplasts contain ribosomes similar to those found in bacteria, further supporting their bacterial ancestry.
Chloroplast Beyond Photosynthesis: Other Functions
While photosynthesis is their primary function, chloroplasts also play other vital roles in plant cells:
-
Amino acid synthesis: Chloroplasts are involved in the synthesis of certain amino acids, essential building blocks of proteins.
-
Fatty acid synthesis: They participate in the synthesis of fatty acids, components of lipids important for cell membranes and energy storage.
-
Nitrogen metabolism: Chloroplasts play a role in nitrogen assimilation, converting inorganic nitrogen into organic forms that plants can use.
-
Stress response: Chloroplasts contribute to the plant's response to environmental stresses, such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures. They can produce protective compounds to mitigate the effects of these stresses.
Variations in Chloroplast Structure and Function
While the basic structure and function of chloroplasts are consistent across plant species, variations exist to adapt to different environments and lifestyles. For example:
-
Shade-adapted plants: These plants have chloroplasts with larger grana and more chlorophyll to efficiently capture low-light conditions.
-
Sun-adapted plants: These plants have chloroplasts with smaller grana and less chlorophyll to avoid damage from excessive sunlight.
-
C4 plants: These plants have evolved specialized chloroplast arrangements in bundle sheath cells to enhance photosynthetic efficiency in hot, dry environments.
-
CAM plants: These plants have chloroplasts adapted to store carbon dioxide at night and use it for photosynthesis during the day, conserving water in arid conditions.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Life on Earth
The chloroplast, found uniquely in plant cells, is an extraordinary organelle with a profound impact on life on Earth. Its ability to harness solar energy through photosynthesis forms the base of most food chains, provides the oxygen we breathe, and plays a vital role in regulating the Earth's climate. By understanding the intricacies of chloroplast structure and function, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of the natural world, and the remarkable role these organelles play in sustaining life. Further research into chloroplast biology continues to unlock new insights into plant growth, development, and their potential applications in various fields, including biofuel production and climate change mitigation. The journey into the world of chloroplasts is a continuous adventure in scientific discovery, promising to reveal even more of their intricate wonders in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Tertiary Amine
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Genetic Disorder
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Most Abundant Cation In The Icf
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Statement Is True Of The British Colony Of Jamestown
Mar 17, 2025
-
In The Figure What Is The Value Of X
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Cell Organelle Is Found Only In Plant Cell . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
