When Is Marginal Cost At Its Minimum
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
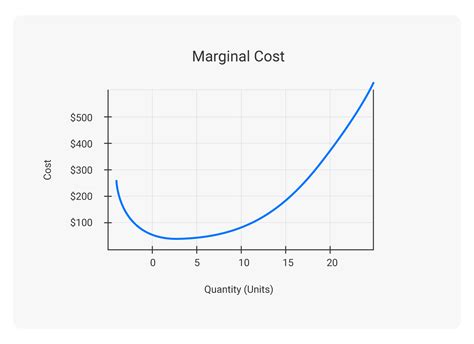
Table of Contents
When is Marginal Cost at its Minimum? Understanding the Relationship Between Marginal Cost and Average Cost
Understanding marginal cost and its minimum point is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize production and maximize profits. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of marginal cost, explaining when it reaches its minimum and the implications for businesses of all sizes. We will explore the relationship between marginal cost, average cost, and the crucial role they play in efficient production and pricing strategies.
What is Marginal Cost?
Marginal cost (MC) represents the additional cost incurred by producing one more unit of a good or service. It's not a fixed cost; rather, it's a variable cost directly tied to production volume. This means it fluctuates depending on factors like raw material prices, labor costs, and production efficiency. Understanding marginal cost is paramount for informed decision-making in areas such as:
- Production Optimization: Businesses can use MC to determine the optimal production level. Producing beyond the point where marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue leads to decreased profitability.
- Pricing Strategies: MC analysis helps businesses make informed decisions about pricing their products or services competitively.
- Resource Allocation: By identifying the minimum point of the marginal cost curve, companies can efficiently allocate resources to maximize their production capacity.
Calculating Marginal Cost
Marginal cost is calculated using a simple formula:
MC = (Change in Total Cost) / (Change in Quantity)
Let's illustrate this with an example:
If producing 10 units costs $100 and producing 11 units costs $108, the marginal cost of producing the 11th unit is:
MC = ($108 - $100) / (11 - 10) = $8
This means that producing one additional unit increased the total cost by $8.
The Relationship Between Marginal Cost and Average Cost
Average cost (AC), also known as average total cost, represents the total cost per unit of output. It's calculated by dividing total cost by the number of units produced. The relationship between MC and AC is dynamic and crucial for understanding cost behavior.
-
When MC < AC, AC is falling: If the marginal cost of producing an additional unit is less than the average cost, the average cost will decrease. This is because the lower marginal cost pulls down the average. Think of it like adding a low score to a set of higher scores; the average score will decrease.
-
When MC > AC, AC is rising: Conversely, if the marginal cost of producing an additional unit exceeds the average cost, the average cost will increase. The higher marginal cost raises the average. Adding a high score to a set of lower scores increases the average score.
-
When MC = AC, AC is at its minimum: The most important point in this relationship is when marginal cost equals average cost. This is the point where the average cost curve reaches its minimum. At this point, the addition of another unit neither increases nor decreases the average cost.
Why is Understanding the Minimum Point of Marginal Cost Important?
The minimum point of the marginal cost curve is significant for several reasons:
-
Optimal Production Level: While businesses aim to minimize average cost, focusing solely on it can be misleading. The minimum of the marginal cost curve indicates the point of optimal production efficiency. Producing beyond this point leads to diminishing returns and increased average costs, even if the marginal cost is still increasing.
-
Economies of Scale: The shape of the marginal cost curve can reveal information about economies of scale. A downward-sloping MC curve, initially, suggests economies of scale—meaning that increasing production reduces the cost per unit. However, eventually, the MC curve typically slopes upward due to diminishing returns. This point of inflection is critical for understanding the limits of cost efficiency.
-
Profit Maximization: Profit maximization occurs where marginal cost equals marginal revenue (MR). Understanding the minimum point of MC helps businesses analyze the relationship between MC and MR to determine the profit-maximizing output level.
Factors Affecting Marginal Cost
Several factors influence the shape and position of the marginal cost curve. These include:
-
Input Prices: Changes in the prices of raw materials, labor, and energy directly impact marginal cost. An increase in input prices leads to a higher marginal cost curve, and vice versa.
-
Technology and Productivity: Technological advancements and improvements in productivity can lower marginal cost. Automation, improved processes, and skilled labor contribute to cost efficiency.
-
Economies of Scale: As mentioned earlier, economies of scale can lead to a downward-sloping portion of the MC curve, where increasing production reduces the cost per unit. However, this effect is typically limited, eventually leading to increasing MC due to diminishing returns.
-
Capacity Constraints: As a business approaches its maximum production capacity, the marginal cost tends to increase rapidly. This is because resources become strained, leading to inefficiencies and higher costs.
The Marginal Cost Curve: A Visual Representation
The marginal cost curve is typically U-shaped. This reflects the interplay between economies of scale and diminishing returns.
-
Initially Decreasing MC: The curve initially slopes downwards, reflecting economies of scale. This is because the fixed costs are spread across a larger number of units, leading to a decrease in cost per unit. Increased efficiency from specialization and bulk purchasing also plays a role.
-
Minimum Point of MC: The curve then reaches its minimum point. This is the most efficient point of production where the addition of another unit costs the least.
-
Increasing MC: Beyond the minimum point, the marginal cost curve slopes upwards. This is due to diminishing returns; the addition of more resources leads to smaller increases in output, eventually causing the marginal cost to rise. This is often related to capacity constraints and the increased cost of acquiring additional resources.
Practical Applications for Businesses
Understanding the minimum point of marginal cost has significant practical implications for businesses:
-
Production Planning: Businesses can use the MC curve to determine the optimal production level that maximizes profitability. They need to aim for the point where marginal cost equals marginal revenue. Producing beyond this point leads to losses.
-
Pricing Decisions: Analyzing marginal cost helps businesses set appropriate prices. They can factor in the cost of producing additional units when establishing price points.
-
Cost Control: By carefully monitoring marginal cost, businesses can identify areas where cost reduction is possible. Analyzing production processes to minimize inefficiencies is key.
-
Investment Decisions: Understanding the factors that influence marginal cost helps businesses make informed investment decisions. Investing in technologies or processes that lower marginal cost can improve competitiveness and profitability.
Conclusion: Mastering Marginal Cost for Business Success
The minimum point of marginal cost is a critical concept for businesses of all sizes. By understanding the relationship between marginal cost and average cost, along with the factors affecting marginal cost, businesses can make informed decisions about production, pricing, and resource allocation. Optimizing production around the minimum point of the marginal cost curve is crucial for achieving efficiency and maximizing profitability in a competitive market. Mastering this concept is not just beneficial; it's essential for long-term business success. Continuously monitoring and analyzing marginal cost allows for adaptation to changing market conditions and the identification of opportunities for improvement. The minimum point of marginal cost is more than just a theoretical concept; it's a practical tool for achieving sustained growth and profitability.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Angle Of Elevation To The Top Of A Building
Mar 27, 2025
-
How Many Vertices Has A Sphere
Mar 27, 2025
-
Non Living Components Of An Ecosystem
Mar 27, 2025
-
Is Gravitational Force A Contact Force
Mar 27, 2025
-
Diffusion Of Respiratory Gases Takes Place At The
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about When Is Marginal Cost At Its Minimum . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
