What's The Difference Between Rough Er And Smooth Er
News Leon
Mar 29, 2025 · 5 min read
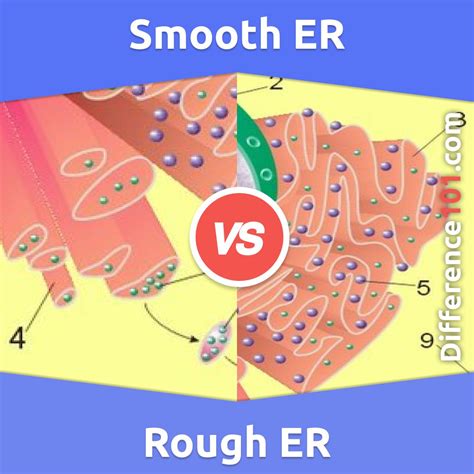
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between Rough ER and Smooth ER? A Deep Dive into Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a vast, interconnected network of membranous tubules and flattened sacs (cisternae) that extends throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It’s a critical organelle involved in a staggering array of cellular processes, from protein synthesis and modification to lipid metabolism and calcium storage. The ER is broadly categorized into two distinct regions: rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER), each with its own unique structure and functions. Understanding the differences between these two subcompartments is crucial to comprehending the complex machinery of the cell.
Structural Differences: The Rough vs. Smooth Appearance
The key visual distinction between the RER and SER lies in their appearance under an electron microscope. This difference is directly related to their primary functions.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER): A Ribosome-Studded Surface
The RER is characterized by its studded appearance, owing to the numerous ribosomes attached to its cytosolic surface. These ribosomes are the protein synthesis factories of the cell. The RER's membrane-bound structure provides a crucial platform for the synthesis and processing of proteins destined for secretion, insertion into cellular membranes, or transport to other organelles. The ribosomes are not permanently attached; they bind to the RER membrane only when actively translating specific mRNAs encoding these proteins. This association is mediated by a signal recognition particle (SRP) that recognizes a signal sequence on the nascent polypeptide chain.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER): A Tubular Labyrinth
In contrast, the SER lacks ribosomes and appears as a network of interconnected tubules, often forming a more extensive three-dimensional network than the RER. This lack of ribosomes reflects its different functional roles, which focus primarily on lipid metabolism, detoxification, and calcium storage. Its smooth, tubular structure optimizes its surface area for the enzymatic activities crucial to these processes.
Functional Differences: A Tale of Two ERs
The structural differences between the RER and SER directly reflect their distinct roles in cellular function.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER): The Protein Factory
The RER is the primary site for the synthesis and processing of proteins destined for various locations within and outside the cell. Its functions include:
-
Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes bound to the RER translate mRNA molecules into polypeptide chains. As the polypeptide chain grows, it is threaded into the lumen of the RER.
-
Protein Folding and Modification: Inside the RER lumen, chaperone proteins assist in the proper folding of nascent polypeptide chains, preventing misfolding and aggregation. Other enzymes modify the proteins through processes like glycosylation (addition of sugar moieties) and disulfide bond formation. These modifications are crucial for the proper function and stability of many proteins.
-
Quality Control: The RER employs a sophisticated quality control mechanism to ensure that only correctly folded and modified proteins are transported to their final destinations. Misfolded proteins are targeted for degradation.
-
Protein Targeting: Proteins synthesized on the RER are sorted and packaged into transport vesicles, which bud from the RER membrane and carry their cargo to the Golgi apparatus for further processing and eventual delivery to their final destinations. This includes secretion out of the cell, insertion into the plasma membrane, or transport to other organelles like lysosomes.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER): A Multifaceted Worker
The SER plays a diverse range of roles, many of which are distinct from those of the RER:
-
Lipid Synthesis: The SER is the primary site for the synthesis of lipids, including phospholipids, cholesterol, and steroid hormones. These lipids are essential components of cell membranes and play crucial roles in various cellular processes.
-
Carbohydrate Metabolism: In some cell types, the SER is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, including glycogen synthesis and breakdown.
-
Detoxification: In liver cells, the SER plays a crucial role in detoxification. Enzymes within the SER modify or break down harmful substances, such as drugs and toxins, making them less toxic or easier to excrete.
-
Calcium Storage: The SER acts as a reservoir for calcium ions (Ca²⁺). The controlled release of Ca²⁺ from the SER is essential for various cellular signaling pathways, including muscle contraction and neurotransmission.
-
Steroid Hormone Synthesis: In cells that produce steroid hormones, the SER is the primary site of synthesis. The enzymes involved in converting cholesterol to steroid hormones reside within the SER membranes.
Interdependence and Communication: A Coordinated Effort
While the RER and SER have distinct functions, they are not isolated entities. They are physically connected and often work in concert. For instance, lipids synthesized in the SER are crucial components of the RER membrane. Moreover, proteins synthesized in the RER can influence SER function, and vice versa. This intricate interplay underscores the interconnected nature of cellular processes.
Clinical Significance: ER Dysfunction and Disease
Disruptions in the normal function of the ER, whether in the RER or SER, can have significant consequences for cellular health and contribute to the development of various diseases. Examples include:
-
Genetic disorders affecting protein folding: Mutations in genes encoding chaperone proteins or other components of the protein quality control system in the RER can lead to the accumulation of misfolded proteins, causing cellular dysfunction and potentially contributing to diseases like cystic fibrosis or various neurodegenerative disorders.
-
Liver diseases: Disruptions in the detoxification function of the SER in the liver can lead to a build-up of toxic substances, potentially contributing to liver damage and liver diseases.
-
Metabolic disorders: Defects in lipid synthesis or carbohydrate metabolism within the SER can contribute to various metabolic disorders.
-
Muscle diseases: Disruptions in calcium regulation within the SER can impact muscle function, contributing to muscle diseases.
-
Cancer: Abnormal ER function has been implicated in the development and progression of various cancers. Changes in ER structure and function can affect cellular growth, proliferation, and survival.
Conclusion: A Cellular Powerhouse
The rough and smooth endoplasmic reticula are two functionally distinct but interconnected subcompartments of the ER, playing crucial roles in a wide array of cellular processes. Their structural and functional differences reflect their specialized roles in protein synthesis and processing (RER) versus lipid metabolism, detoxification, and calcium storage (SER). Understanding the intricate workings of these organelles is essential for comprehending cellular function in health and disease. Further research into the complex interactions between the RER and SER promises to unlock further insights into cellular biology and its relevance to human health. This detailed exploration highlights the complexity and importance of the ER within the eukaryotic cell, underscoring its vital contribution to cellular life and its implications for human health. Continued research in this area will undoubtedly reveal further nuances and complexities within this essential organelle.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Cell Organelle Does Photosynthesis Occur
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Isotopes Does Fluorine Have
Mar 31, 2025
-
Refraction Causes The Bottom Of A Swimming Pool To Appear
Mar 31, 2025
-
Glucagon Stimulates Glycogenolysis In The Liver True Or False
Mar 31, 2025
-
Classify The Following Mixtures As Heterogeneous Or Homogeneous
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Difference Between Rough Er And Smooth Er . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
