Classify The Following Mixtures As Heterogeneous Or Homogeneous
News Leon
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
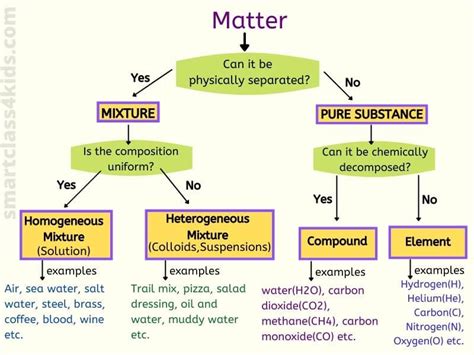
Table of Contents
Classify the Following Mixtures as Heterogeneous or Homogeneous: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures is fundamental to chemistry and numerous other scientific disciplines. This comprehensive guide will not only help you classify various mixtures but also delve deeper into the underlying principles, providing a solid foundation for your understanding. We'll explore various examples, clarifying the characteristics that distinguish one type of mixture from the other.
What are Mixtures?
Before we dive into the classification, let's define what a mixture is. A mixture is a substance composed of two or more components that are not chemically bonded. This means the components retain their individual chemical properties and can be separated using physical methods like filtration, distillation, or evaporation. Unlike compounds, mixtures don't have a fixed chemical formula.
Heterogeneous Mixtures: A World of Variation
A heterogeneous mixture is one in which the composition is not uniform throughout. You can easily see the individual components and their distinct boundaries. The properties of a heterogeneous mixture vary from one region to another.
Key Characteristics of Heterogeneous Mixtures:
- Non-uniform composition: The components are not evenly distributed.
- Visible components: Individual components are easily discernible with the naked eye or a simple microscope.
- Variable properties: The properties of the mixture (density, color, etc.) differ depending on the location within the mixture.
- Easily separable components: Components can often be separated using simple physical methods.
Examples of Heterogeneous Mixtures:
Let's explore some everyday examples to solidify your understanding:
- Sand and water: The sand particles are clearly visible and settle at the bottom, creating distinct layers.
- Oil and water: These two liquids don't mix; they form separate layers with a visible boundary.
- Salt and pepper: You can easily identify individual grains of salt and pepper.
- Granite: This rock is composed of various minerals, each with its own distinct color and texture.
- Trail mix: A delightful mix of nuts, seeds, and dried fruits, each component remains distinct.
- Pizza: A delicious example with various visible toppings.
- Concrete: A composite material containing cement, aggregate (gravel, sand), and water.
- Blood: A complex biological fluid with various cells and components suspended in plasma.
- Salad: A mix of different vegetables and other ingredients.
- Soil: A complex mixture of minerals, organic matter, water, and air.
Classifying Heterogeneous Mixtures: A Deeper Look
Heterogeneous mixtures can be further classified based on the size of the particles:
- Suspensions: These mixtures contain relatively large particles that settle out over time. Examples include muddy water and chalk in water.
- Colloids: These mixtures have particles that are intermediate in size, neither settling out nor dissolving completely. Examples include milk, fog, and mayonnaise.
Homogeneous Mixtures: Uniformity Reigns Supreme
A homogeneous mixture is one in which the composition is uniform throughout. The components are evenly distributed at a molecular level, making it impossible to visually distinguish individual components. The properties of a homogeneous mixture are consistent throughout the sample.
Key Characteristics of Homogeneous Mixtures:
- Uniform composition: The components are evenly distributed at a molecular level.
- Invisible components: Individual components are not visible to the naked eye.
- Constant properties: Properties remain consistent throughout the sample.
- Components difficult to separate: Separation often requires more complex methods like distillation or chromatography.
Examples of Homogeneous Mixtures:
Here are some common examples:
- Saltwater: When salt dissolves completely in water, it forms a homogeneous solution.
- Sugar water: Similarly, dissolved sugar in water creates a homogeneous mixture.
- Air: A mixture of various gases (nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc.) evenly distributed.
- Brass: An alloy of copper and zinc, with a uniform composition.
- Steel: Another alloy, typically composed of iron and carbon.
- Vinegar: A solution of acetic acid in water.
- Gasoline: A complex mixture of hydrocarbons.
- Tea (brewed): Once the tea leaves have been removed, the resulting liquid is homogeneous.
- Coffee (brewed): Similar to tea, after brewing, coffee is considered a homogeneous mixture.
- Many commercial drinks: Soft drinks and juices are often homogeneous mixtures.
Distinguishing Between Solutions and Other Homogeneous Mixtures
While all solutions are homogeneous mixtures, not all homogeneous mixtures are solutions. A solution is a specific type of homogeneous mixture where one substance (the solute) is dissolved completely in another (the solvent). Examples include saltwater and sugar water. Other homogeneous mixtures might involve alloys or gases mixed uniformly, but not necessarily fitting the strict definition of a solution.
Advanced Considerations and Challenges in Classification
While the concepts of heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures are relatively straightforward, some mixtures can present challenges in classification. For instance:
- Mixtures at different scales: A mixture might appear homogeneous at a macroscopic level but heterogeneous at a microscopic level. Consider a seemingly uniform sample of milk – under magnification, you’ll see distinct fat globules.
- Time-dependent changes: Some mixtures might change their nature over time. A suspension might initially appear homogeneous but settle into a heterogeneous mixture after standing.
- Complex mixtures: Many real-world mixtures are incredibly complex, containing numerous components with varying interactions. Accurate classification might require sophisticated analytical techniques.
Practical Applications and Real-World Relevance
The ability to classify mixtures as heterogeneous or homogeneous is crucial in various fields:
- Chemistry: Understanding mixture properties is fundamental to chemical reactions, separation techniques, and material science.
- Environmental science: Analyzing the composition of air, water, and soil requires differentiating between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
- Food science: Classifying food mixtures helps determine texture, stability, and overall quality.
- Materials science: Designing and characterizing materials often involves controlling the homogeneity or heterogeneity of mixtures.
- Medicine: Understanding blood composition as a heterogeneous mixture is crucial for diagnosing and treating various conditions.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Mixture Classification
The distinction between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures is a cornerstone of scientific understanding. By learning to identify the key characteristics of each type, you gain a powerful tool for analyzing substances and materials in various contexts. Remember that the classification sometimes involves nuance and considerations at different scales. However, with practice and a thorough understanding of the underlying principles, you’ll confidently navigate the world of mixtures. This knowledge will serve as a stepping stone to further explorations in chemistry and related scientific fields. Continue your learning by exploring the different separation techniques used to separate components of mixtures based on their classification. The more you practice, the better you'll become at identifying and classifying mixtures accurately.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Type Of Reaction Is Occurring Between I2 And Zn
Apr 02, 2025
-
During Glycolysis Glucose Is Broken Down Into Two Molecules Of
Apr 02, 2025
-
Arrange The Steps Of Glycolysis In The Correct Order
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is The Division Of Cytoplasm
Apr 02, 2025
-
Why Do Plant Cells Have Larger Vacuoles
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Classify The Following Mixtures As Heterogeneous Or Homogeneous . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
