What Process Takes Place In The Cytoplasm
News Leon
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
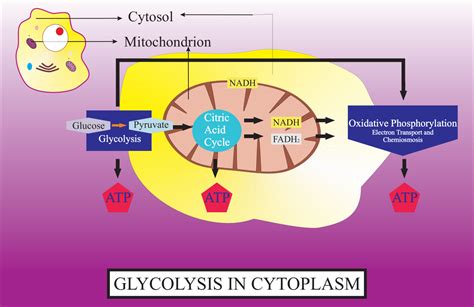
Table of Contents
What Processes Take Place in the Cytoplasm? A Deep Dive into the Cell's Dynamic Interior
The cytoplasm, that jelly-like substance filling the cell between the nucleus and the cell membrane, is far from inert. It's a bustling hub of activity, a dynamic environment where a vast array of crucial cellular processes occur. Understanding these processes is key to understanding life itself. This article will delve into the many intricate processes taking place within the cytoplasm, exploring its multifaceted role in cellular function and survival.
The Cytoplasm: More Than Just a Filling
Before we dive into the specific processes, let's establish a foundational understanding of the cytoplasm itself. It's primarily composed of water, salts, and various organic molecules, creating a solution known as cytosol. This cytosol isn't just a passive medium; it actively participates in numerous metabolic reactions. Embedded within the cytosol are various organelles, each with its specialized functions, creating a complex and highly organized internal environment. The cytoplasm's structure isn't static; it undergoes constant change, adapting to the cell's needs.
Major Processes Occurring in the Cytoplasm:
1. Glycolysis: The First Step in Energy Production
One of the most fundamental processes taking place in the cytoplasm is glycolysis, the initial stage of cellular respiration. This metabolic pathway breaks down glucose, a six-carbon sugar, into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon compound. This process doesn't require oxygen (anaerobic) and produces a small amount of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell's primary energy currency, along with NADH, an electron carrier crucial for later stages of energy production. The efficiency of glycolysis is crucial for the cell's immediate energy needs. Dysregulation of glycolysis is implicated in various diseases, highlighting its importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
2. Protein Synthesis: Building the Blocks of Life
The cytoplasm plays a central role in protein synthesis, the process of creating proteins from genetic information encoded in DNA. This multi-step process begins in the nucleus with transcription, where DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA then exits the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where it binds to ribosomes. Ribosomes, either free-floating in the cytosol or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, translate the mRNA sequence into a specific chain of amino acids, forming a polypeptide. These polypeptides then fold into functional proteins, which perform a myriad of tasks within the cell. The accuracy and efficiency of protein synthesis are vital for cellular function and survival. Errors in this process can lead to the production of non-functional or even harmful proteins.
3. Cell Signaling: Communication within and between Cells
The cytoplasm serves as the primary site for cell signaling, a complex communication network within the cell and between cells. Signal transduction pathways, initiated by extracellular signals binding to receptors on the cell membrane, often involve a cascade of events within the cytoplasm. These pathways can activate or inhibit specific enzymes, alter gene expression, or trigger changes in cell behavior. These signaling pathways are crucial for processes like cell growth, division, differentiation, and apoptosis (programmed cell death). Dysregulation of cell signaling is a hallmark of many diseases, including cancer.
4. Cytoskeleton Dynamics: Maintaining Cell Shape and Movement
The cytoplasm houses the cytoskeleton, a complex network of protein filaments that provides structural support to the cell, enables cell movement, and facilitates intracellular transport. This network consists of three main types of filaments: microtubules, microfilaments (actin filaments), and intermediate filaments. These filaments constantly undergo assembly and disassembly, adapting to the cell's needs. The cytoskeleton plays a vital role in cell division, intracellular transport of organelles and vesicles, and maintaining cell shape. Defects in cytoskeletal dynamics are associated with various diseases, highlighting its importance in cellular integrity.
5. Lipid Metabolism: Synthesizing and Breaking Down Fats
The cytoplasm is the site of many aspects of lipid metabolism. This includes the synthesis of fatty acids and other lipids, essential components of cell membranes and energy storage molecules. The cytoplasm also plays a role in the breakdown of lipids through beta-oxidation, a process that releases energy stored in fatty acids. Lipid metabolism is tightly regulated and crucial for maintaining cellular energy balance and membrane integrity. Disruptions in lipid metabolism are associated with various metabolic disorders.
6. Cellular Respiration (Part 2): Preparing for the Mitochondria
While glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm, it’s only the beginning. The pyruvate produced is then transported to the mitochondria, the cell's powerhouse, for further processing in the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) and oxidative phosphorylation. However, the preparatory steps for pyruvate's entry into the mitochondria are often cytoplasmic events, including the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA. This is a crucial linking step between glycolysis and the subsequent mitochondrial stages of cellular respiration.
7. Vesicular Transport: Intracellular Trafficking
The cytoplasm is a major highway for vesicular transport. Small membrane-bound sacs called vesicles shuttle materials throughout the cell, transporting proteins, lipids, and other molecules between different organelles. This transport is crucial for processes like protein secretion, endocytosis (taking up materials from outside the cell), and exocytosis (releasing materials from the cell). The cytoskeleton plays a crucial role in guiding the movement of vesicles along specific pathways. Disruptions in vesicular transport can have significant consequences for cellular function.
8. Enzyme Activity: The Catalysts of Life
A vast array of enzymes are found within the cytoplasm. These proteins act as biological catalysts, accelerating the rate of various chemical reactions crucial for cellular metabolism. These reactions include many metabolic pathways involved in energy production, protein synthesis, and the breakdown of waste products. Enzyme activity is highly regulated, ensuring that metabolic processes occur at the appropriate rate and time. Enzyme deficiencies can have severe consequences for cellular health.
9. Apoptosis: Programmed Cell Death
The cytoplasm also plays a key role in apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death that is essential for development and maintaining tissue homeostasis. This process involves a cascade of events within the cytoplasm, leading to the dismantling of the cell and its components in an orderly fashion. Apoptosis helps eliminate damaged or infected cells and is crucial for preventing the development of diseases like cancer. Dysregulation of apoptosis is implicated in several diseases.
10. Calcium Signaling: A Versatile Second Messenger
Calcium ions (Ca2+) act as important secondary messengers in many cellular signaling pathways. Changes in cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration trigger a variety of cellular responses, including muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release, and gene expression. The cytoplasm contains various proteins that regulate Ca2+ levels, ensuring that this crucial signaling molecule is used appropriately. Disruptions in Ca2+ signaling are associated with various diseases.
Conclusion: The Cytoplasm – A Dynamic and Essential Cellular Compartment
The cytoplasm is far more than a simple filling within the cell. It’s a complex, dynamic environment where a multitude of crucial cellular processes take place simultaneously and in a highly coordinated manner. From energy production and protein synthesis to cell signaling and cytoskeletal dynamics, the cytoplasm’s activities are central to the life of the cell. Understanding the intricate processes within this cellular compartment is fundamental to advancing our knowledge of biology, medicine, and biotechnology. Future research will undoubtedly continue to unravel further complexities and reveal additional details about this vital aspect of cellular life. By understanding the cytoplasm's bustling activity, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable complexity and efficiency of cellular life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
You Should Always Assign The Needs Met Rating Before
Apr 06, 2025
-
Which Is The Most Densely Populated Continent
Apr 06, 2025
-
Average Velocity On Velocity Time Graph
Apr 06, 2025
-
The First Scientist To Observe Cells With A Microscope Was
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Happens When The Price Of A Complementary Good Increases
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Process Takes Place In The Cytoplasm . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
