What Ph Does Salivary Amylase Work Best At
News Leon
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
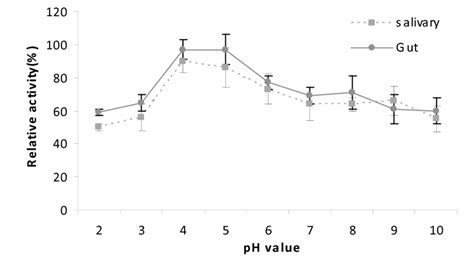
Table of Contents
What pH Does Salivary Amylase Work Best At?
Salivary amylase, also known as ptyalin, is a crucial enzyme in the initial stages of digestion. Understanding its optimal pH is key to comprehending the human digestive process and potential digestive issues. This comprehensive article delves into the intricacies of salivary amylase's functionality, its optimal pH range, the impact of pH variations, and the broader implications for human health.
Understanding Salivary Amylase and its Role in Digestion
Salivary amylase is an enzyme secreted by the salivary glands in the mouth. Its primary function is the hydrolysis of starch, a complex carbohydrate, into simpler sugars like maltose and dextrins. This process initiates carbohydrate digestion even before the food reaches the stomach. The efficiency of this initial breakdown directly impacts the overall digestive process and the body's ability to absorb nutrients.
The Chemical Mechanism of Amylase Action
Amylase works by binding to starch molecules and breaking the glycosidic bonds that link glucose units together. This enzymatic action is highly specific, meaning it only targets α-1,4 glycosidic linkages found in starch and glycogen. This specificity ensures that other molecules within the food are not mistakenly broken down. The breakdown products, maltose and dextrins, are smaller and more easily absorbed in the later stages of digestion.
Optimal pH for Salivary Amylase Activity
The activity of salivary amylase, like many enzymes, is highly dependent on the pH of its environment. Its optimal pH is slightly acidic to neutral, ranging from 6.7 to 7.0. At this pH range, the enzyme's three-dimensional structure is most stable and its active site is optimally configured to bind to starch molecules and catalyze the hydrolysis reaction. Deviation from this optimal pH significantly impacts its enzymatic activity.
The Impact of pH Variations
Deviation from the optimal pH, whether more acidic or more alkaline, leads to a decrease in salivary amylase activity. This happens because changes in pH disrupt the enzyme's delicate protein structure. The amino acid residues that form the active site and contribute to its catalytic function can become altered, leading to a reduced catalytic efficiency or even complete inactivation of the enzyme.
-
Acidic pH (below 6.7): Increased acidity denatures the enzyme, causing it to lose its three-dimensional shape and functionality. The acidic environment of the stomach (pH around 1.5-3.5) inactivates salivary amylase. This is a crucial protective mechanism ensuring that the enzymatic action of salivary amylase is limited to the mouth and upper esophagus where the pH is more suitable.
-
Alkaline pH (above 7.0): While a slightly alkaline pH doesn't immediately denature salivary amylase, it still diminishes its activity. The enzyme’s active site becomes less efficient at binding to and breaking down starch molecules. The higher pH disrupts the electrostatic interactions that maintain the enzyme’s optimal conformation.
Factors Affecting Salivary Amylase Activity Beyond pH
While pH is a critical factor, several other factors influence the activity of salivary amylase. These include:
-
Temperature: Like other enzymes, salivary amylase exhibits optimal activity within a specific temperature range. Human body temperature (around 37°C) is ideal. Higher temperatures denature the enzyme, while lower temperatures slow down the reaction rate.
-
Substrate Concentration: The rate of the reaction is initially proportional to the concentration of the substrate (starch). However, at higher concentrations, the reaction rate levels off as the enzyme becomes saturated.
-
Enzyme Concentration: Increasing the concentration of salivary amylase will increase the rate of starch hydrolysis, up to a point. Beyond a certain concentration, there may be no further increase in the reaction rate.
-
Presence of Inhibitors: Certain substances can inhibit salivary amylase activity. For instance, some heavy metals can bind to the active site, preventing the enzyme from functioning.
Clinical Significance and Implications for Health
Understanding the optimal pH for salivary amylase activity has important implications for health and disease. Conditions affecting the pH of the mouth can influence the efficiency of starch digestion. For example:
-
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): GERD, where stomach acid reflux into the esophagus, can lower the pH of the mouth, potentially reducing salivary amylase activity and causing indigestion.
-
Xerostomia (Dry Mouth): Xerostomia, or dry mouth, is characterized by reduced saliva production. This can affect the concentration of salivary amylase, compromising starch digestion.
-
Pancreatic Insufficiency: While not directly related to salivary amylase pH, pancreatic insufficiency, where the pancreas doesn't produce enough digestive enzymes, can impact overall carbohydrate digestion, potentially leading to symptoms like bloating, diarrhea and nutrient deficiencies. While the initial starch breakdown in the mouth is impacted by salivary amylase activity at its optimal pH, the majority of starch digestion happens later in the small intestine aided by pancreatic amylase.
The Importance of Maintaining Optimal Oral pH
Maintaining an optimal oral pH is crucial for maintaining healthy oral flora and optimal salivary amylase function. Practices that can help include:
-
Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing helps remove food particles that could contribute to pH imbalances.
-
Balanced Diet: Avoiding excessive consumption of sugary and acidic foods and drinks helps prevent fluctuations in oral pH.
-
Regular Dental Checkups: Regular dental checkups allow for early detection and treatment of oral health issues that might affect salivary amylase function.
Conclusion: pH and Salivary Amylase's Pivotal Role
Salivary amylase plays a fundamental role in initiating carbohydrate digestion, and its activity is profoundly impacted by pH. Maintaining a slightly acidic to neutral oral pH (around 6.7-7.0) is essential for optimal salivary amylase function. Understanding the relationship between pH, salivary amylase activity, and overall digestive health can inform strategies to promote healthy digestion and address potential issues related to impaired salivary amylase function. Further research into the intricacies of this enzyme's activity in various pH conditions will contribute significantly to our understanding of human digestive physiology and related health conditions. By paying attention to factors influencing the optimal pH environment for salivary amylase, we can contribute to improved overall digestive health and wellbeing. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle including a balanced diet, good oral hygiene, and regular dental checkups plays a vital role in ensuring optimal salivary amylase functionality and efficient carbohydrate digestion. This ultimately leads to better nutrient absorption and overall well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 1 2 Miles
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lines Of Symmetry On A Trapezoid
Mar 18, 2025
-
Two Same Words With Different Meanings
Mar 18, 2025
-
Select The Correct Statement About Equilibrium
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Ph Does Salivary Amylase Work Best At . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
