What Kingdom Does A Paramecium Belong To
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
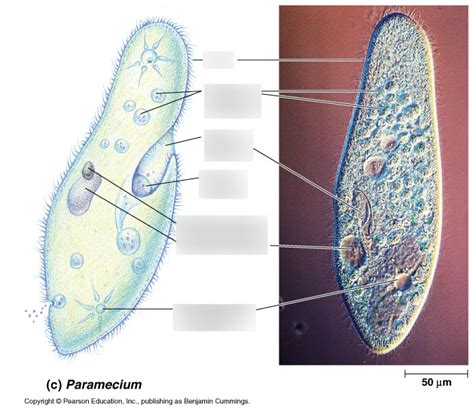
Table of Contents
What Kingdom Does a Paramecium Belong To? A Deep Dive into Protista
The seemingly simple paramecium, a single-celled organism often encountered in introductory biology classes, actually holds a fascinating place in the biological world. Pinpointing its exact kingdom, however, requires a deeper understanding of the complexities of biological classification and the evolution of our understanding of the Protista kingdom. This article will delve into the intricacies of paramecium classification, exploring its characteristics, its place within the Protista kingdom, and the ongoing debates within the scientific community regarding the classification of single-celled eukaryotes.
The Elusive Kingdom Protista: A Melting Pot of Life
Before we pinpoint the kingdom of Paramecium, let's establish a clear understanding of the kingdom Protista itself. This kingdom, often considered a "catch-all" category, encompasses a vast array of eukaryotic organisms that aren't plants, animals, or fungi. This diversity is immense; protists exhibit incredible variation in their structure, physiology, and lifestyle. Some are single-celled, others are multicellular; some are photosynthetic, others are heterotrophic; some are motile, others are sessile. This inherent diversity is a major reason why the classification of protists remains a dynamic and evolving field.
Defining Characteristics of Protists
Several key characteristics help define organisms within the Protista kingdom:
- Eukaryotic Cells: Protists possess membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum, which distinguishes them from prokaryotic organisms like bacteria and archaea.
- Diverse Nutritional Modes: Protists demonstrate a wide range of nutritional strategies. Some are autotrophs, producing their own food through photosynthesis (like algae). Others are heterotrophs, obtaining nutrients by consuming other organisms or organic matter. Still others are mixotrophs, combining both autotrophic and heterotrophic methods.
- Varied Locomotion: Protists exhibit diverse methods of movement. Some use cilia, like the Paramecium, for locomotion. Others utilize flagella or pseudopodia (temporary extensions of the cytoplasm). Some are non-motile.
- Mostly Unicellular: While some protists form colonies or are multicellular, the majority are unicellular organisms. This unicellular nature often leads to complex adaptations for survival in diverse environments.
Paramecium: A Ciliate Superstar
Now, let's turn our attention to the Paramecium, a well-known and extensively studied ciliate protist. These tiny organisms are easily recognized by their slipper-like shape and the abundance of cilia that cover their surface. These cilia beat rhythmically, propelling the Paramecium through its aquatic environment.
Key Features of Paramecium that Place it in Protista
- Cilia: The defining characteristic of Paramecium is its use of cilia for locomotion and feeding. These hair-like structures beat in a coordinated fashion, creating currents that draw food particles towards the cell's oral groove.
- Two Nuclei: Paramecium possesses two types of nuclei: a large macronucleus and a small micronucleus. The macronucleus controls the cell's daily functions, while the micronucleus is involved in sexual reproduction.
- Contractile Vacuoles: These specialized organelles regulate the water balance within the cell, a crucial adaptation for survival in hypotonic environments. They actively pump excess water out of the cell, preventing it from bursting.
- Food Vacuoles: Paramecium engulfs food particles through phagocytosis, forming food vacuoles where digestion occurs. Waste products are expelled through an anal pore.
- Eukaryotic Cell Structure: As mentioned earlier, the presence of membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus and mitochondria, firmly places Paramecium within the domain Eukarya.
The Kingdom Protista: Why Paramecium Belongs There
Based on the characteristics discussed above, it's clear that Paramecium fits comfortably within the kingdom Protista. Its eukaryotic nature, diverse nutritional strategies (heterotrophic), unique locomotion mechanism (cilia), and unicellular structure align perfectly with the defining features of this diverse kingdom. While other kingdoms share some individual characteristics with Paramecium, no other kingdom encompasses all of its defining features.
Distinguishing Paramecium from Other Kingdoms
Let's briefly compare Paramecium to the other three eukaryotic kingdoms:
- Plantae: Plants are primarily photosynthetic autotrophs with cell walls made of cellulose. Paramecium is heterotrophic and lacks a cell wall.
- Animalia: Animals are multicellular heterotrophs that typically ingest their food. Paramecium is unicellular and uses a different method of feeding.
- Fungi: Fungi are heterotrophs with cell walls made of chitin. Paramecium lacks a cell wall and has a different cellular structure.
Ongoing Debates in Protist Classification
Despite the seemingly straightforward placement of Paramecium in the Protista kingdom, the classification of protists remains a subject of ongoing debate within the scientific community. The vast diversity within this kingdom has led to proposals for alternative classification systems, with some researchers advocating for the division of Protista into several smaller kingdoms or phyla. This ongoing work reflects the complexity of evolutionary relationships within this group of organisms and highlights the challenges inherent in classifying life based on observable characteristics.
The Challenges of Protist Classification
Several factors contribute to the difficulty of classifying protists:
- Extensive Diversity: The sheer diversity of protists makes it challenging to establish a universally accepted classification system.
- Convergent Evolution: Similar traits can evolve independently in different lineages, obscuring evolutionary relationships.
- Limited Fossil Record: The fossil record for protists is incomplete, making it difficult to reconstruct evolutionary histories.
- Advances in Molecular Biology: The development of molecular techniques has provided new insights into protist relationships, challenging traditional classifications based solely on morphology.
The Future of Protist Classification
The field of protist classification is constantly evolving as new data from molecular analyses and improved microscopic techniques become available. Researchers are using advanced phylogenetic methods to construct more accurate evolutionary trees, revealing previously unknown relationships among protist lineages. This ongoing work promises to refine our understanding of the evolutionary history of this remarkable group of organisms and ultimately lead to a more robust and accurate classification system.
Conclusion: Paramecium's Secure Place in Protista
In conclusion, Paramecium unequivocally belongs to the kingdom Protista. Its eukaryotic cell structure, heterotrophic nutrition, unique ciliated locomotion, and other distinctive features clearly distinguish it from plants, animals, and fungi. While the classification of protists as a whole remains a complex and dynamic area of research, the placement of Paramecium within this kingdom is firmly established. The ongoing debates and refinements in protist classification highlight the ever-evolving nature of scientific understanding and the challenges inherent in organizing the vast diversity of life on Earth. The humble Paramecium, therefore, serves as a powerful example of the intricate beauty and ongoing scientific exploration within the fascinating world of eukaryotic microorganisms. Its study continues to contribute significantly to our understanding of cellular biology, evolutionary processes, and the overall diversity of life on Earth.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Organelle Is The Site For Photosynthesis
Mar 20, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is The Correct Equation For Photosynthesis
Mar 20, 2025
-
Which Three Dimensional Figure Has Exactly Three Rectangular Faces
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Milligrams And Milliliters
Mar 20, 2025
-
Metals Are Good Conductors Of Electricity
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Kingdom Does A Paramecium Belong To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
