Which Of The Following Is The Correct Equation For Photosynthesis
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
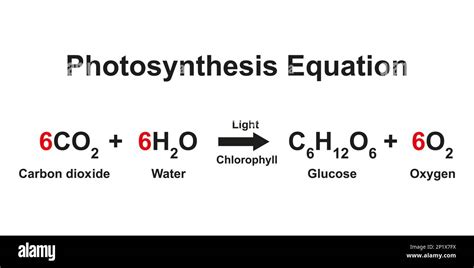
Table of Contents
Which of the following is the correct equation for photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis, the remarkable process by which green plants and certain other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, is a cornerstone of life on Earth. Understanding its intricacies, including its chemical equation, is crucial for comprehending the flow of energy through ecosystems and the impact of environmental changes on our planet. This article delves deep into the photosynthetic process, explores the various ways its equation is represented, and clarifies which equation most accurately reflects the complex reality of photosynthesis.
Decoding the Basics: What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis, at its core, is a redox reaction. It involves the reduction of carbon dioxide (CO₂) into glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and the oxidation of water (H₂O) to release oxygen (O₂). This transformation is driven by light energy, primarily absorbed by chlorophyll pigments within chloroplasts – the specialized organelles in plant cells where photosynthesis takes place.
The process is broadly divided into two main stages:
1. The Light-Dependent Reactions:
This stage occurs in the thylakoid membranes within the chloroplast. Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments, exciting electrons to a higher energy level. This energy is then used to:
- Split water molecules (photolysis): This process releases electrons, protons (H⁺), and oxygen (O₂). The oxygen is released as a byproduct.
- Generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate): ATP is the cell's primary energy currency.
- Produce NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate): NADPH is a reducing agent, carrying high-energy electrons needed for the next stage.
2. The Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle):
This stage occurs in the stroma, the fluid-filled space surrounding the thylakoids. The ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions are used to power the fixation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules. The Calvin cycle involves a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that ultimately produce glucose.
The Equations: A Comparative Analysis
Several equations are used to represent photosynthesis, each with varying levels of detail and accuracy. Let's examine some common variations and discuss their strengths and limitations:
1. The Simplified Equation:
This is the most commonly encountered equation, often taught in introductory biology courses:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This equation accurately depicts the overall inputs and outputs of photosynthesis. It shows that six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water react in the presence of light energy to produce one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen. However, it significantly oversimplifies the complex multi-step process. It doesn't reflect the intermediate steps, energy transformations, or the roles of ATP and NADPH.
2. A More Detailed Equation (Illustrating ATP and NADPH):
A more nuanced approach involves explicitly including ATP and NADPH:
6CO₂ + 12H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ + 6H₂O + 18ATP
This equation acknowledges the crucial role of ATP as an energy carrier. However, it still omits NADPH, which plays a vital role as a reducing agent in the Calvin cycle. Furthermore, it is an oversimplification as the actual number of ATP molecules used is not exactly 18 and may vary according to conditions and plants.
3. The Most Accurate Representation (Considering Multiple Factors):
Representing photosynthesis with a single equation is inherently a simplification. The actual process is incredibly complex, involving numerous enzyme-catalyzed reactions, electron transport chains, and regulatory mechanisms. To achieve a highly accurate representation, one would need a series of equations detailing each step of the light-dependent and light-independent reactions.
Why a Single Equation is Insufficient: Addressing the Nuances
Several factors contribute to the inadequacy of a single equation for completely capturing photosynthesis:
- Variability in Photosynthetic Pathways: Plants utilize different photosynthetic pathways depending on their environment and adaptations. C3, C4, and CAM plants, for instance, have different mechanisms for carbon fixation, impacting the precise details of the overall process. A single equation cannot encompass this diversity.
- Cyclic and Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation: The light-dependent reactions involve both cyclic and non-cyclic electron flow, leading to variations in ATP and NADPH production. A simplified equation cannot account for these nuances.
- Energy Losses: The conversion of light energy into chemical energy is not 100% efficient. Some energy is lost as heat during the process. A precise equation would need to account for these energy losses.
- Role of Enzymes and Cofactors: Numerous enzymes and cofactors are involved in each step of photosynthesis. A complete equation would need to incorporate these factors, but this is virtually impossible in a single equation.
The Importance of Understanding the Complexity
While the simplified equation provides a useful starting point for understanding the overall concept of photosynthesis, it's crucial to appreciate its limitations. The complexity of photosynthesis highlights the remarkable efficiency and adaptability of life on Earth. A deeper understanding of the intricate mechanisms involved is essential for tackling issues such as climate change, food security, and bioenergy production.
Conclusion: Choosing the "Correct" Equation
There isn't a single "correct" equation for photosynthesis that captures all its subtleties. The simplified equation (6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂) serves as a foundational understanding. However, recognizing its limitations and appreciating the multi-step nature of the process, with its intricate light-dependent and light-independent phases, involving ATP, NADPH, and varying photosynthetic pathways, is crucial for a complete grasp of this fundamental process. The true representation of photosynthesis is a complex network of reactions, far beyond the scope of any single equation. Therefore, focusing on the mechanistic details and the interplay of various factors rather than solely on a single equation is far more beneficial in comprehending the magnificence of photosynthesis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Primary Function Of The Excretory System Is To
Mar 21, 2025
-
A Solenoid That Is 95 0 Cm
Mar 21, 2025
-
Is Water A Conductor Or Insulator
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Number Is Divisible By 3 And 4
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 36 And 54
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is The Correct Equation For Photosynthesis . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
