What Is True About Ionic Compounds
News Leon
Apr 04, 2025 · 6 min read
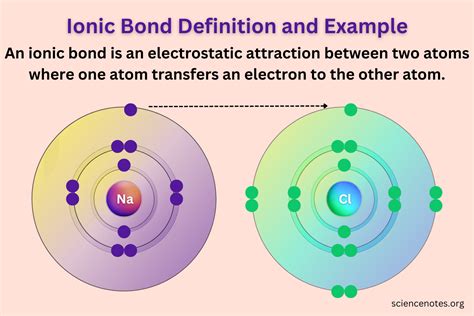
Table of Contents
What's Truly True About Ionic Compounds: A Deep Dive into Their Properties and Behaviors
Ionic compounds, the unsung heroes of chemistry, form the bedrock of numerous materials we encounter daily. From the table salt we sprinkle on our food to the minerals that comprise our planet's crust, understanding their unique properties is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the fascinating world of ionic compounds, dispelling common misconceptions and exploring the truths behind their behavior.
The Fundamental Truth: Electrostatic Attraction
At the heart of every ionic compound lies a fundamental truth: electrostatic attraction. This powerful force, born from the interaction of oppositely charged ions, dictates the compound's structure, properties, and reactivity.
Ions: The Building Blocks
Ionic compounds are formed through the transfer of electrons between atoms. This transfer creates ions – atoms or molecules with a net electrical charge.
- Cations: Positively charged ions, formed when an atom loses electrons. Metals, with their relatively low electronegativity, readily form cations. Think of sodium (Na⁺) or magnesium (Mg²⁺).
- Anions: Negatively charged ions, formed when an atom gains electrons. Nonmetals, with their higher electronegativity, tend to form anions. Consider chloride (Cl⁻) or oxide (O²⁻).
The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions is what constitutes the ionic bond. The strength of this bond is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charges and inversely proportional to the distance between the ions. Larger charges and shorter distances lead to stronger bonds.
Crystal Lattices: Order from Chaos
Unlike covalent compounds which often exist as discrete molecules, ionic compounds arrange themselves in highly ordered, three-dimensional structures known as crystal lattices. These lattices maximize the electrostatic attraction between cations and anions, minimizing repulsive forces. The specific arrangement within the lattice depends on the size and charge of the ions involved. This inherent orderliness profoundly influences the properties of ionic compounds.
Key Properties of Ionic Compounds: Truths Revealed
The unique properties of ionic compounds stem directly from the strong electrostatic forces holding them together and their crystalline structure. Let's explore some key characteristics:
1. High Melting and Boiling Points:
The strong electrostatic attractions between ions require a significant amount of energy to overcome. Consequently, ionic compounds typically possess high melting and boiling points. It takes considerable heat to break the strong ionic bonds and transition the compound from a solid to a liquid or a gas. This is a defining characteristic that distinguishes them from many covalent compounds.
2. Brittleness:
Ionic crystals are brittle and shatter easily when subjected to stress. This fragility arises from the rigid arrangement of ions within the lattice. When force is applied, it can cause a shift in the lattice, bringing like charges into close proximity. The resulting repulsive forces overcome the attractive forces, causing the crystal to fracture along planes of weakness.
3. Conductivity: The Role of the State
Ionic compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity in their solid state. The fixed positions of ions in the crystal lattice prevent the free flow of charge. However, when dissolved in water or melted, they become excellent conductors. This is because the ions are free to move and carry electrical current. The process of dissolving or melting essentially breaks the crystal lattice, freeing the ions to migrate.
4. Solubility: A Matter of Balance
The solubility of ionic compounds in water is a complex phenomenon. While some dissolve readily (like table salt), others are virtually insoluble. The solubility depends on the balance between the lattice energy (the energy required to break the ionic bonds) and the hydration energy (the energy released when water molecules surround and stabilize the ions). If the hydration energy is greater than the lattice energy, the compound will dissolve. Conversely, if the lattice energy is greater, the compound will remain insoluble.
Beyond the Basics: Delving Deeper into Ionic Compound Behavior
The properties discussed above represent the foundational truths about ionic compounds. However, a more nuanced understanding requires delving into more advanced concepts:
1. Polarization: Distorting the Perfect
While the ideal ionic bond involves a complete transfer of electrons, in reality, there's often some degree of polarization. This happens when the cation's positive charge distorts the electron cloud of the anion, leading to a slight covalent character in the bond. The degree of polarization depends on several factors, including the size and charge of the ions. Smaller, highly charged cations exert a greater polarizing effect.
2. Lattice Energy: A Quantitative Measure
Lattice energy is a crucial parameter in understanding the stability and properties of ionic compounds. It represents the energy released when gaseous ions combine to form a solid crystal lattice. Higher lattice energy indicates a stronger ionic bond and thus higher melting and boiling points. The Born-Haber cycle provides a method for calculating lattice energy experimentally.
3. Complex Ions: Beyond Simple Combinations
Many ionic compounds involve complex ions, which are groups of atoms covalently bonded but carrying a net charge. Examples include sulfate (SO₄²⁻), nitrate (NO₃⁻), and ammonium (NH₄⁺). These complex ions behave as single units within the crystal lattice, influencing the overall properties of the compound.
4. Applications: A World Built on Ions
Ionic compounds play vital roles in numerous applications, from everyday life to advanced technologies:
- Table Salt (NaCl): A crucial nutrient and food preservative.
- Calcium Carbonate (CaCO₃): A primary component of limestone and marble, used in construction and as a supplement.
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): Used in various industrial processes, from soap making to paper production.
- Potassium Permanganate (KMnO₄): A strong oxidizing agent with applications in water treatment and medicine.
- Batteries: Many batteries rely on the movement of ions between electrodes to generate electrical current.
Debunking Common Misconceptions
Let's address some common misunderstandings surrounding ionic compounds:
- Myth: Ionic compounds always involve a metal and a nonmetal. Truth: While this is a common scenario, some ionic compounds involve polyatomic ions, which can contain only nonmetals.
- Myth: All ionic compounds are soluble in water. Truth: Solubility depends on the balance between lattice energy and hydration energy. Many ionic compounds are insoluble.
- Myth: Ionic bonds are purely electrostatic interactions. Truth: While electrostatic attraction is dominant, a degree of covalent character is often present due to polarization.
Conclusion: A Continuing Journey of Discovery
The world of ionic compounds is rich and complex, filled with fascinating intricacies. This article has explored the fundamental truths underlying their behavior, addressing key properties, advanced concepts, and dispelling common misconceptions. Understanding these truths is crucial not only for appreciating the materials around us but also for advancing scientific and technological progress. Further exploration into the vast literature on ionic compounds will continue to reveal even more intriguing aspects of their behavior. The ongoing research promises further exciting discoveries in the field. So, the next time you encounter a crystal of salt or a mineral sample, remember the powerful electrostatic forces at play, the intricate crystal lattice structure, and the incredible diversity of these fundamental building blocks of our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Purpose Of Simple Staining
Apr 05, 2025
-
Even Natural Numbers Less Than 12
Apr 05, 2025
-
Balanced Equation For Sodium Carbonate And Calcium Chloride
Apr 05, 2025
-
Which Statement Describes Mendels Hypotheses Regarding Gametes
Apr 05, 2025
-
A Perfectly Competitive Firm Is A Price Taker Because
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is True About Ionic Compounds . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
