What Is The Relationship Among Dna Gene And A Chromosome
News Leon
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
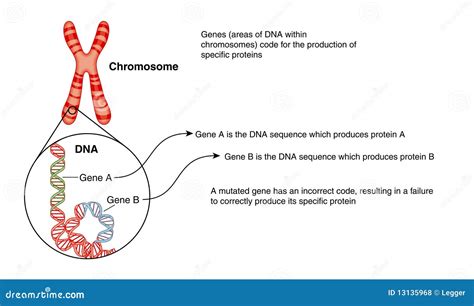
Table of Contents
Decoding the Trio: DNA, Genes, and Chromosomes
Understanding the intricate relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes is fundamental to grasping the basics of genetics and heredity. These three components work in concert to orchestrate the complex processes of life, from cell function to the inheritance of traits. While often used interchangeably in casual conversation, they represent distinct yet interconnected levels of biological organization. This article delves deep into their individual roles and their synergistic relationship, providing a comprehensive overview for both novice learners and those seeking a more detailed understanding.
What is DNA? – The Blueprint of Life
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the fundamental building block of life. This double-stranded helical molecule acts as the blueprint, containing the instructions for building and maintaining an organism. Imagine it as a vast library, filled with countless volumes of incredibly detailed instructions. These instructions, written in the language of the genetic code, dictate everything from eye color and height to susceptibility to certain diseases.
The Structure of DNA: A Closer Look
The DNA molecule resembles a twisted ladder, a structure known as a double helix. The sides of this ladder are formed by alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate molecules. The rungs of the ladder are formed by pairs of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A) paired with thymine (T), and guanine (G) paired with cytosine (C). This specific base pairing is crucial for DNA replication and transcription.
DNA Replication: Passing on the Legacy
The ability of DNA to replicate itself is paramount for the continuity of life. During replication, the double helix unwinds, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. This process ensures that each new cell receives an identical copy of the genetic information. The fidelity of DNA replication is remarkable, with errors being incredibly rare thanks to sophisticated proofreading mechanisms. However, occasional errors can lead to mutations, which can have varying effects, from inconsequential to severely detrimental.
Genes: The Functional Units of Heredity
Genes are the functional units of heredity. They are specific segments of DNA that code for a particular trait or characteristic. Think of genes as individual chapters within the vast library of the genome. Each chapter contains the instructions for a specific protein or functional RNA molecule. These proteins and RNA molecules are the workhorses of the cell, carrying out a vast array of functions crucial for life.
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein. First, DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA). Then, the mRNA is translated into a polypeptide chain, which folds into a functional protein. This process is fundamental to gene expression, which is the process by which the information encoded in a gene is used to synthesize a functional gene product.
Gene Regulation: Controlling Expression
Gene expression is not a constant, all-or-nothing process. Instead, it is tightly regulated, allowing cells to respond to internal and external signals. This regulation occurs at multiple levels, including transcription, translation, and post-translational modifications. Understanding gene regulation is crucial to understanding how cells differentiate and how organisms develop. Dysregulation of gene expression can lead to various diseases, including cancer.
Alleles: Variations on a Theme
A gene can exist in multiple forms called alleles. For example, a gene for eye color might have alleles for brown eyes, blue eyes, and green eyes. Individuals inherit two alleles for each gene, one from each parent. The combination of alleles determines the phenotype, or observable characteristics, of an individual.
Chromosomes: The Packaging of DNA
Chromosomes are the organized structures within the nucleus of a cell that contain DNA. Imagine them as meticulously organized volumes within the library, holding many chapters (genes) together. They are not simply bundles of DNA; they are complex structures composed of DNA tightly wound around proteins called histones. This packaging is crucial for efficiently storing and managing the vast amount of genetic information within a cell.
Chromosome Structure: A Complicated Organization
The DNA double helix is first wrapped around histone proteins, forming structures called nucleosomes. These nucleosomes then coil further, forming chromatin fibers. During cell division, these chromatin fibers condense even further, forming the highly compact structures we recognize as chromosomes. The level of compaction changes depending on the cell cycle stage.
Homologous Chromosomes and Karyotypes
In most organisms, chromosomes exist in pairs, called homologous chromosomes. One chromosome of each pair is inherited from each parent. A karyotype is a visual representation of an organism's complete set of chromosomes. It is used to identify chromosomal abnormalities, such as extra or missing chromosomes, which can cause various genetic disorders.
Chromosome Number: Species-Specific
The number of chromosomes varies greatly among different species. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46. Other organisms have vastly different numbers. The chromosome number is a characteristic feature of each species.
The Interplay: How DNA, Genes, and Chromosomes Work Together
The relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes is intricately interwoven. DNA is the fundamental molecule containing the genetic code. Genes are specific segments of this DNA that code for functional products. Chromosomes are the organized structures that package and manage the DNA, ensuring its proper replication and transmission to daughter cells.
Consider this analogy:
- DNA: The complete text of a vast encyclopedia.
- Genes: Individual chapters within that encyclopedia, each covering a specific topic.
- Chromosomes: The volumes that organize the chapters into manageable units.
This coordinated organization ensures the efficient storage, replication, and expression of genetic information. The proper functioning of this relationship is crucial for cell function, organismal development, and the inheritance of traits. Disruptions to this carefully orchestrated system can lead to a wide range of genetic disorders.
Beyond the Basics: Further Explorations
This article provides a foundational understanding of the relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes. However, the field of genetics is vast and ever-evolving. Further exploration might include topics such as:
- Epigenetics: The study of heritable changes in gene expression that do not involve changes to the underlying DNA sequence.
- Genome editing technologies: Techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9, which allow for precise modification of the genome.
- Genetic engineering: The application of genetic technologies to modify organisms for specific purposes.
- Genetic diseases and disorders: The study of diseases caused by mutations in genes or chromosomal abnormalities.
- Population genetics: The study of genetic variation within and between populations.
- Evolutionary genetics: The study of how genetic variation contributes to evolution.
Understanding the intricate relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes is essential for understanding life itself. From the simplest single-celled organism to the most complex multicellular life forms, these three components work in concert to orchestrate the processes of life. Further exploration of these topics will reveal a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of the genetic code. The more we understand, the better equipped we are to address challenges related to health, disease, and the very nature of life itself.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Formula For Coefficient Of Kinetic Friction
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is Required To Connect To The Internet
Apr 06, 2025
-
The Division Of A Cells Cytoplasm Is Called
Apr 06, 2025
-
All Enzymes Are Proteins True False
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Is A Voltmeter Connected In A Circuit
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Relationship Among Dna Gene And A Chromosome . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
