What Is The Name For N2o5
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
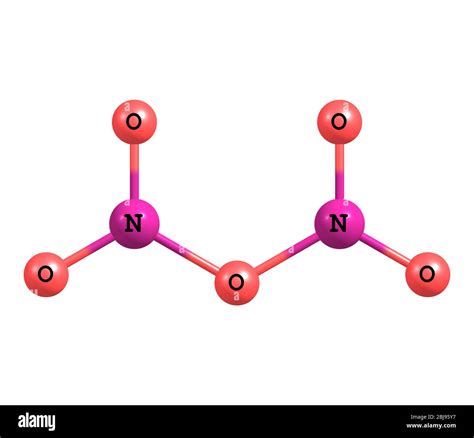
Table of Contents
What is the Name for N₂O₅? A Deep Dive into Dinitrogen Pentoxide
Dinitrogen pentoxide, often written as N₂O₅, is a powerful oxidizer and a relatively unstable compound. Understanding its properties, nomenclature, and applications requires a deeper look beyond its simple chemical formula. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted nature of N₂O₅, exploring its various names, synthesis methods, reactivity, and significant uses in different fields.
Understanding Chemical Nomenclature
Before we delve into the specifics of N₂O₅, let's briefly refresh our understanding of chemical nomenclature. This system of naming chemical compounds is crucial for unambiguous communication within the scientific community. The naming conventions for binary covalent compounds, like N₂O₅, involve using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the molecule.
- Mono-: One atom
- Di-: Two atoms
- Tri-: Three atoms
- Tetra-: Four atoms
- Penta-: Five atoms
- Hexa-: Six atoms
and so on.
Applying this to N₂O₅, we have two nitrogen atoms ("di-nitrogen") and five oxygen atoms ("penta-oxide"). Therefore, the systematic name, as per IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) guidelines, is dinitrogen pentoxide.
Other Names and Synonyms for N₂O₅
While dinitrogen pentoxide is the preferred and most commonly used name, N₂O₅ is also known by a few other names or synonyms. These alternative names might appear in older literature or specialized contexts. Some of these include:
- Nitrogen pentoxide: This is a shorter, less formal version, though technically less precise because it omits the number of nitrogen atoms.
- Nitric anhydride: This name is derived from its relationship with nitric acid (HNO₃). N₂O₅ can be considered the anhydride of nitric acid, meaning that it can be formed by the dehydration of nitric acid and, conversely, reacts with water to produce nitric acid.
Synthesis of Dinitrogen Pentoxide (N₂O₅)
The synthesis of dinitrogen pentoxide involves several methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages concerning yield, purity, and safety considerations. The most common routes involve dehydration of nitric acid or the reaction of nitric acid with dehydrating agents.
Dehydration of Nitric Acid
One primary method involves carefully dehydrating nitric acid (HNO₃) using a suitable dehydrating agent like phosphorus pentoxide (P₄O₁₀). This process removes water molecules from nitric acid, resulting in the formation of N₂O₅. The reaction is often conducted at low temperatures to prevent unwanted side reactions and decomposition of the product.
Other Synthetic Pathways
Other less common synthesis methods exist, involving reactions of nitrogen oxides with ozone or other oxidizing agents under controlled conditions. These methods are often more complex and may require specialized equipment and expertise.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Dinitrogen Pentoxide
Dinitrogen pentoxide possesses distinct physical and chemical properties that contribute to its unique reactivity and applications.
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: At low temperatures, N₂O₅ is a colorless, crystalline solid.
- Melting point: Relatively low, around 30°C (86°F). This means it readily melts into a liquid at slightly above room temperature.
- Solubility: It is soluble in certain non-polar organic solvents but readily decomposes in water, reacting to form nitric acid.
- Volatility: It's relatively volatile, meaning it readily transitions from solid to gas phase.
Chemical Properties:
- Powerful Oxidizer: This is arguably its most significant chemical characteristic. It readily accepts electrons, leading to its oxidizing power. This property underpins many of its applications.
- Reactivity with Water: As mentioned, N₂O₅ reacts violently with water to produce nitric acid (HNO₃). This reaction demonstrates its anhydride nature.
- Thermal Instability: It's thermally unstable, decomposing at higher temperatures into nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and oxygen (O₂).
- Reactivity with Organic Compounds: It can react with organic compounds, often resulting in oxidation or nitration reactions.
Applications of Dinitrogen Pentoxide (N₂O₅)
The potent oxidizing and nitrating properties of dinitrogen pentoxide have led to its use in various applications, primarily within specialized industrial processes and research settings.
Nitration Reactions in Organic Chemistry
One of the main applications of N₂O₅ is as a nitrating agent in organic chemistry. Nitration is a critical reaction in the synthesis of many organic compounds, particularly nitroaromatics which have importance in explosives, dyes, and pharmaceuticals. N₂O₅ facilitates the introduction of nitro groups (-NO₂) into aromatic rings, providing a route to these valuable compounds.
Synthesis of Other Nitrogen Compounds
Its use extends to the synthesis of other nitrogen-containing compounds. Due to its reactivity, it serves as a precursor in the preparation of certain nitrates and other nitrogen oxides. It acts as a convenient source of the nitronium ion (NO₂⁺), a highly reactive electrophile involved in many nitration reactions.
Rocket Propellant Applications (Historically)
While not as prevalent today due to safety and handling concerns, N₂O₅ has historically been considered as a potential component in rocket propellants. Its high oxidizing power makes it theoretically suitable for this application; however, its instability and hazardous nature have limited its practical use in this area. Safer and more stable oxidizers are predominantly used in modern rocketry.
Safety Precautions and Handling of Dinitrogen Pentoxide
Dinitrogen pentoxide is a highly reactive and potentially hazardous compound. Its handling requires strict adherence to safety protocols to minimize risks.
- Strong Oxidizer: Its strong oxidizing nature necessitates careful handling to prevent ignition or explosions when in contact with combustible materials.
- Reactivity with Water: Contact with water leads to the formation of corrosive nitric acid, requiring protective measures.
- Toxic and Irritating: Inhaling N₂O₅ fumes can be toxic and cause respiratory irritation. Therefore, proper ventilation and respiratory protection are essential.
- Storage: N₂O₅ must be stored in inert containers under controlled temperature and humidity conditions to prevent decomposition.
Environmental Considerations
The release of dinitrogen pentoxide into the environment can have negative consequences. Its decomposition products, such as nitrogen dioxide, contribute to air pollution and acid rain. Its high reactivity can damage various ecosystems. Therefore, responsible handling, storage, and disposal practices are critical for mitigating its potential environmental impact. Strict regulations govern its production, use, and disposal to minimize any environmental risks.
Conclusion: A Powerful but Hazardous Compound
Dinitrogen pentoxide (N₂O₅), also known as nitrogen pentoxide and nitric anhydride, is a potent oxidizer with significant applications in organic chemistry, particularly in nitration reactions. Its unique properties and reactivity, however, necessitate careful handling and strict adherence to safety protocols. While its use in rocket propellants has been largely superseded by safer alternatives, its importance in specialized chemical synthesis remains undeniable. Understanding its properties, synthesis methods, and safety concerns is vital for anyone working with or studying this fascinating and powerful compound. The correct and unambiguous name remains dinitrogen pentoxide, adhering to the IUPAC nomenclature system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Speedometer Of An Automobile Reads
Mar 23, 2025
-
The Substance That Dissolves The Solute
Mar 23, 2025
-
Do Strong Electrolytes Dissociate In Water
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Is A Similarity Between Alcohol Fermentation And Aerobic Respiration
Mar 23, 2025
-
Integrate 1 X 2 X 1
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Name For N2o5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
