What Is The Molar Mass Of Ccl4
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
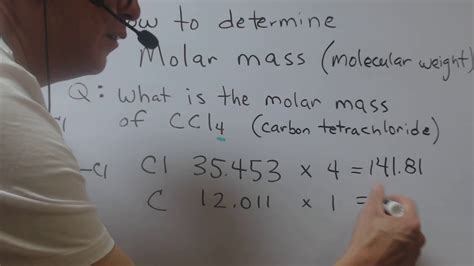
Table of Contents
What is the Molar Mass of CCl₄? A Deep Dive into Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄), also known as tetrachloromethane, is a colorless, volatile liquid with a characteristic ethereal odor. While once widely used in various applications, its toxicity has led to significant restrictions on its use. Understanding its properties, particularly its molar mass, is crucial in various chemical calculations and applications. This article will delve deep into the calculation and significance of the molar mass of CCl₄, exploring its chemical composition, applications, and safety concerns.
Understanding Molar Mass
Before calculating the molar mass of CCl₄, let's establish a clear understanding of the concept itself. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is a fundamental unit in chemistry, representing Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10²³) of entities (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.). Therefore, the molar mass essentially tells us the mass of 6.022 x 10²³ molecules of a given substance. The unit for molar mass is typically grams per mole (g/mol).
The molar mass of an element is numerically equivalent to its atomic weight (found on the periodic table), expressed in grams per mole. For compounds, the molar mass is calculated by summing the molar masses of all the atoms present in the molecule.
Calculating the Molar Mass of CCl₄
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄) consists of one carbon atom (C) and four chlorine atoms (Cl). To calculate its molar mass, we need the atomic masses of carbon and chlorine:
- Carbon (C): Approximately 12.01 g/mol
- Chlorine (Cl): Approximately 35.45 g/mol
Now, we can calculate the molar mass of CCl₄:
Molar Mass (CCl₄) = (1 × Atomic Mass of C) + (4 × Atomic Mass of Cl)
Molar Mass (CCl₄) = (1 × 12.01 g/mol) + (4 × 35.45 g/mol)
Molar Mass (CCl₄) = 12.01 g/mol + 141.80 g/mol
Molar Mass (CCl₄) ≈ 153.81 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄) is approximately 153.81 g/mol. This means that one mole of CCl₄ weighs approximately 153.81 grams.
Significance of Molar Mass in Chemical Calculations
The molar mass of CCl₄ is a crucial piece of information in various chemical calculations, including:
1. Mole Conversions:
Knowing the molar mass allows us to convert between mass and moles of CCl₄. For example, if we have 100 grams of CCl₄, we can calculate the number of moles using the following formula:
Moles = Mass (g) / Molar Mass (g/mol)
Moles = 100 g / 153.81 g/mol ≈ 0.65 moles
Conversely, if we know the number of moles, we can calculate the mass:
Mass (g) = Moles × Molar Mass (g/mol)
2. Stoichiometric Calculations:
Molar mass plays a vital role in stoichiometry, which deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. If CCl₄ participates in a reaction, its molar mass is essential for determining the amount of reactants needed or products formed.
3. Concentration Calculations:
Molar mass is crucial in calculating the concentration of solutions, particularly molarity (moles per liter). If we dissolve a certain mass of CCl₄ in a specific volume of solvent, we can use its molar mass to determine the molarity of the resulting solution.
4. Determining Empirical and Molecular Formulas:
The molar mass of a compound is essential in determining its molecular formula if only the empirical formula is known. The empirical formula provides the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound. The molar mass helps determine the actual number of atoms in the molecule.
Applications of Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl₄)
Despite its toxicity, CCl₄ has historically had several applications. However, due to its harmful effects on human health and the environment, many of these applications have been phased out. Some past and limited current uses include:
- Refrigerant: Historically used in refrigeration systems, but now largely replaced due to its ozone depletion potential.
- Solvent: Used as a solvent in various industrial processes, such as dry cleaning and degreasing, though its use is severely restricted.
- Fire Extinguisher: Used in some specialized fire extinguishers, but again, its use is limited due to toxicity and environmental concerns.
- Chemical Intermediate: Used in the synthesis of other chemicals, though this use is also declining due to safety concerns and the availability of safer alternatives.
Safety Concerns and Environmental Impact of CCl₄
Carbon tetrachloride is a highly toxic substance with significant health and environmental risks. Exposure can lead to:
- Liver damage: CCl₄ is a potent hepatotoxin, causing severe liver damage, even with relatively low exposure.
- Kidney damage: Exposure can also lead to kidney dysfunction.
- Nervous system effects: It can affect the central nervous system, potentially causing dizziness, headaches, and even coma.
- Cancer: Studies have linked CCl₄ exposure to an increased risk of certain types of cancer.
- Ozone depletion: It was a significant ozone-depleting substance, contributing to the thinning of the ozone layer. The Montreal Protocol successfully phased out its use for this reason.
Because of these significant risks, handling and use of CCl₄ require strict safety measures and adherence to regulations. Proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), and responsible waste disposal are crucial to minimize exposure risks.
Conclusion
The molar mass of CCl₄, approximately 153.81 g/mol, is a fundamental property with wide-ranging applications in various chemical calculations. Its accurate determination is essential for stoichiometric calculations, concentration determinations, and conversions between mass and moles. However, it's crucial to remember the significant toxicity and environmental hazards associated with CCl₄. Its use is now severely restricted due to its detrimental effects on human health and the environment. Safer alternatives are preferred in all applications where possible. Understanding its molar mass and associated risks is crucial for anyone working with or studying this compound. The information presented here should contribute to a better understanding of CCl₄, its properties, and its significance in chemistry and beyond. Always prioritize safety when dealing with any chemical substance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Like Charges Repel And Unlike Charges Attract
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Are Three Properties Of A Magnet
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Polysaccharide
Mar 25, 2025
-
Lysosomes Are Membrane Bound Vesicles That Arise From The
Mar 25, 2025
-
Calculate The Radius Of Gyration Of A Cylindrical Rod
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Molar Mass Of Ccl4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
