What Is The Electron Configuration Of Aluminum
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
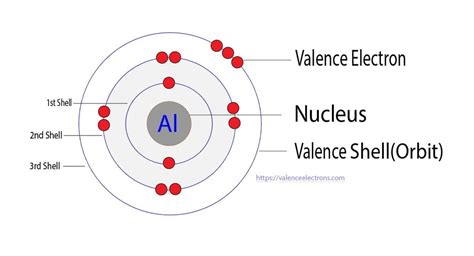
Table of Contents
What is the Electron Configuration of Aluminum? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Aluminum, a lightweight yet strong metal ubiquitous in everyday life, possesses a fascinating atomic structure that dictates its unique properties. Understanding its electron configuration is key to unlocking the secrets behind its reactivity, conductivity, and other characteristics. This article will delve deep into the electron configuration of aluminum, exploring its derivation, implications, and significance in various fields.
Understanding Electron Configuration
Before we dive into the specifics of aluminum, let's establish a foundational understanding of electron configuration. An electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in the various energy levels and sublevels within an atom. This arrangement is governed by the principles of quantum mechanics, which dictate that electrons occupy orbitals with specific energies and shapes.
These orbitals are grouped into shells and subshells. Shells represent the principal energy levels (n=1, 2, 3, etc.), while subshells within a shell are designated by letters (s, p, d, f). Each subshell can hold a specific number of electrons:
- s subshell: Holds a maximum of 2 electrons.
- p subshell: Holds a maximum of 6 electrons.
- d subshell: Holds a maximum of 10 electrons.
- f subshell: Holds a maximum of 14 electrons.
Electrons fill orbitals according to the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons first occupy the lowest energy levels available. The Pauli exclusion principle dictates that each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins. Finally, Hund's rule states that electrons will individually occupy each orbital within a subshell before doubling up in any one orbital.
Deriving the Electron Configuration of Aluminum
Aluminum (Al) has an atomic number of 13, meaning it has 13 protons and, in a neutral atom, 13 electrons. To determine its electron configuration, we follow the Aufbau principle and fill the orbitals in order of increasing energy:
- 1s²: The first shell (n=1) contains only the s subshell, which holds two electrons.
- 2s²: The second shell (n=2) starts with the s subshell, also holding two electrons.
- 2p⁶: The second shell also contains the p subshell, which can hold up to six electrons. This subshell is completely filled.
- 3s²: The third shell (n=3) begins with the s subshell, holding two electrons.
- 3p¹: Finally, we place the remaining electron in the 3p subshell.
Therefore, the complete electron configuration of aluminum is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p¹. This can also be written in a shorthand notation using the noble gas configuration: [Ne]3s²3p¹, where [Ne] represents the electron configuration of neon (1s²2s²2p⁶).
Understanding the Implications of Aluminum's Electron Configuration
Aluminum's electron configuration explains many of its properties:
Reactivity:
The single electron in the 3p subshell is relatively loosely held. This makes aluminum relatively reactive, readily losing this electron to form a +3 cation (Al³⁺). This explains why aluminum readily reacts with oxygen to form a protective aluminum oxide layer (Al₂O₃), which protects the underlying metal from further corrosion. This passivation is a crucial aspect of aluminum's widespread use.
Conductivity:
The presence of valence electrons in the 3s and 3p orbitals contributes to aluminum's excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. These valence electrons are relatively mobile and can easily move throughout the metal lattice, carrying charge and heat. This makes aluminum a valuable material in electrical wiring and heat sinks.
Bonding:
Aluminum's tendency to lose three electrons leads to the formation of ionic bonds with non-metals. It forms strong ionic bonds with electronegative elements such as oxygen, chlorine, and fluorine. It can also participate in metallic bonding, where valence electrons are delocalized throughout a lattice of aluminum atoms, contributing to its malleability and ductility.
Aluminum's Electron Configuration and its Applications
Aluminum's unique electron configuration translates to a variety of important applications across numerous industries:
Packaging:
Aluminum's resistance to corrosion and its light weight make it ideal for packaging applications. Aluminum foil, cans, and other packaging materials are commonplace due to its protective properties and recyclability. The reactivity which allows for the formation of the oxide layer is crucial for the longevity of these products.
Transportation:
The combination of strength and lightweight nature of aluminum makes it a popular choice in the transportation industry. Aluminum alloys are used in the construction of aircraft, automobiles, and trains. The high strength-to-weight ratio significantly improves fuel efficiency and performance.
Construction:
Aluminum's corrosion resistance and durability make it a suitable material for building and construction. Aluminum is used in window frames, doors, roofing, and siding. Its ability to withstand harsh weather conditions contributes to its popularity in exterior applications.
Electrical Applications:
As a highly conductive material, aluminum finds widespread use in electrical wiring, transmission lines, and electrical components. Its cost-effectiveness and high conductivity make it a valuable alternative to copper in many applications.
Other Applications:
Aluminum's versatility extends to various other applications including:
- Cookware: Aluminum's excellent heat conductivity makes it ideal for cookware.
- Medical Devices: Aluminum's biocompatibility makes it suitable for use in certain medical implants.
- Aerospace: Aluminum alloys are vital in aerospace due to their high strength-to-weight ratio.
Beyond the Basics: Excited States and Ionization
While the ground state electron configuration discussed above is the most stable arrangement, aluminum atoms can also exist in excited states. In an excited state, one or more electrons have absorbed energy and jumped to a higher energy level. These excited states are transient and the electron will quickly return to the ground state, releasing the absorbed energy often as light. This process is essential in understanding atomic spectroscopy.
Furthermore, the removal of one or more electrons from aluminum leads to the formation of aluminum ions. The first ionization energy, the energy required to remove the outermost electron (3p¹), is relatively low, reflecting the relatively weak hold on that electron. Subsequent ionization energies are progressively higher, requiring more energy to overcome the stronger electrostatic attraction of the nucleus.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of aluminum, [Ne]3s²3p¹, is not simply a theoretical construct. It's a fundamental description that dictates the atom's properties and explains its diverse applications. Understanding electron configuration allows us to predict the reactivity, conductivity, and bonding behavior of aluminum, ultimately leading to its widespread use in countless technological and everyday applications. From the aluminum can in your recycling bin to the aircraft soaring overhead, the principles of atomic structure are at play. By delving into the intricacies of electron configuration, we unlock a deeper appreciation for the remarkable properties of this ubiquitous metal and the scientific principles that govern its behavior. The study of electron configuration is not just an exercise in theoretical chemistry; it's the key to understanding the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Qualities Make A Good Leader Essay
Mar 21, 2025
-
Character Sketch Of Helen Keller For 10 Marks
Mar 21, 2025
-
Is Neon A Metal Nonmetal Or Metalloid
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is An Abbreviated Electron Configuration
Mar 21, 2025
-
How To Write A Letter To Bank
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Electron Configuration Of Aluminum . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
