What Is The Electron Configuration For Cobalt
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
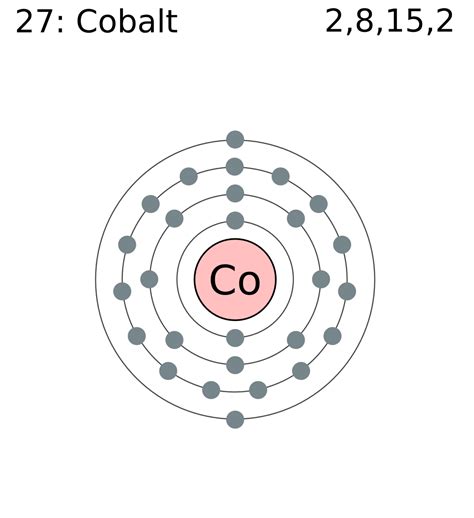
Table of Contents
What is the Electron Configuration for Cobalt? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Cobalt, a fascinating transition metal with the symbol Co and atomic number 27, plays a crucial role in various fields, from industrial catalysts to vital biological functions. Understanding its electronic structure, specifically its electron configuration, is key to grasping its unique properties and behaviors. This comprehensive article delves into the electron configuration of cobalt, exploring its underlying principles, variations, and implications.
Understanding Electron Configuration
Before diving into cobalt's specifics, let's establish a foundational understanding of electron configuration. This describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom's various energy levels and sublevels. It's dictated by the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy, and the Pauli exclusion principle, which limits each orbital to a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins. Hund's rule further refines this by stipulating that electrons will individually occupy orbitals within a subshell before pairing up.
These principles guide us in predicting the electron configuration of any element, including cobalt. The arrangement is typically represented using a notation that indicates the principal quantum number (n), the subshell (s, p, d, or f), and the number of electrons in each subshell.
Deriving Cobalt's Electron Configuration
Cobalt, with its atomic number of 27, possesses 27 electrons. Following the Aufbau principle, we systematically fill the orbitals:
- 1s²: The lowest energy level, the first shell, contains the 1s subshell, accommodating two electrons.
- 2s² 2p⁶: The second shell consists of the 2s and 2p subshells, holding a total of eight electrons (two in 2s and six in 2p).
- 3s² 3p⁶: The third shell similarly houses eight electrons (two in 3s and six in 3p).
- 4s² 3d⁷: This is where things get interesting. While the 4s subshell is slightly lower in energy than the 3d subshell in many cases, it fills first. Following this, the remaining seven electrons populate the 3d subshell.
Therefore, the ground state electron configuration for cobalt is typically written as: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁷. This configuration reflects the most stable arrangement of electrons in a neutral cobalt atom.
Variations and Exceptions
While the above configuration is the most common and accepted, it's crucial to acknowledge potential variations. The energy levels of orbitals, particularly those close in energy like 4s and 3d, can be affected by various factors, including the presence of other atoms in a molecule or the influence of external fields.
For instance, in certain chemical environments or excited states, an electron might be promoted from the 4s orbital to the 3d orbital, leading to an alternative configuration like 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s¹ 3d⁸. This, however, is less common in the ground state and usually occurs only under specific circumstances. Understanding these subtle differences is vital for advanced applications in chemistry and physics.
The Significance of the 3d Subshell
The presence of seven electrons in the 3d subshell is pivotal in explaining cobalt's unique characteristics. This partially filled d-orbital plays a significant role in:
-
Magnetic Properties: Cobalt is a ferromagnetic material, meaning it can retain a magnetic field even after the external field is removed. This strong magnetism is directly linked to the unpaired electrons in the 3d subshell. These unpaired electrons interact with each other and align their spins, creating a net magnetic moment.
-
Catalytic Activity: Cobalt's partially filled 3d orbitals enable it to act as a powerful catalyst in various chemical reactions. It can readily accept or donate electrons, facilitating the formation of intermediate complexes and lowering the activation energy of reactions. This makes cobalt essential in industrial processes, such as in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis for producing hydrocarbons.
-
Coordination Chemistry: Cobalt's ability to form coordination complexes with ligands is extensively utilized in coordination chemistry. The d-orbital electrons are involved in the formation of coordinate bonds with ligands, generating a wide range of complexes with diverse geometries and properties.
-
Biological Roles: Cobalt is an essential trace element in certain biological systems, notably as a component of vitamin B12 (cobalamin). The coordination chemistry of cobalt in vitamin B12 is crucial for its biological function as a coenzyme in various metabolic pathways.
Cobalt's Electron Configuration and its Chemical Behavior
The electron configuration directly influences cobalt's chemical reactivity. The partially filled 3d and 4s orbitals allow cobalt to exhibit variable oxidation states, primarily +2 and +3. These different oxidation states lead to distinct chemical properties and the formation of various compounds with different characteristics.
For example, cobalt(II) compounds often exhibit a pink or blue color, while cobalt(III) compounds tend to be more stable and less reactive. The different oxidation states and coordination environments profoundly impact the color, magnetism, and reactivity of cobalt compounds.
Applications Leveraging Cobalt's Electronic Structure
The unique electronic structure of cobalt makes it essential in a multitude of applications, including:
-
Magnets: Cobalt-based alloys, such as Alnico and samarium-cobalt magnets, are renowned for their high magnetic strength and are used in various applications, from electric motors to medical devices.
-
Catalysis: Cobalt catalysts are vital in various industrial processes, including the production of ammonia, petroleum refining, and the synthesis of fine chemicals.
-
Electroplating: Cobalt electroplating provides corrosion resistance and a hard, wear-resistant surface on various metal components.
-
Superalloys: Cobalt-based superalloys exhibit exceptional high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for jet engine components and other demanding applications.
-
Pigments and Dyes: Cobalt compounds are used as pigments and dyes in various applications, contributing to the vibrant colors in paints, ceramics, and glass.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Concepts
The electron configuration of cobalt, while seemingly simple in its notation, represents a complex interplay of fundamental forces governing atomic structure. Further exploration into advanced concepts, such as:
-
Spectroscopy: Analyzing the absorption and emission of light by cobalt atoms and ions provides detailed information about electronic transitions and energy levels.
-
Quantum Mechanics: A deeper understanding of quantum mechanics provides a more accurate and nuanced description of electron behavior and orbital energies.
-
Computational Chemistry: Computational methods allow scientists to predict and model the properties and behaviors of cobalt compounds and complexes with remarkable accuracy.
can provide a richer and more comprehensive understanding of this fascinating element.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of cobalt, 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁷, is not merely a symbolic representation; it's a key to unlocking its unique properties and behaviors. Its partially filled 3d subshell is the driving force behind its magnetism, catalytic activity, variable oxidation states, and extensive range of applications. A thorough understanding of electron configuration is essential for anyone seeking to delve deeper into the world of chemistry, materials science, and related fields. By exploring these concepts, we gain valuable insights into the fundamental building blocks of matter and their influence on the world around us. The intricate dance of electrons within the cobalt atom reveals a wealth of information that shapes its role in countless technological advancements and biological processes. Further research and exploration in this field will undoubtedly uncover even more of cobalt's fascinating secrets.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Oxidation Number Of Sulfur In So42
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Angular Position Of A Point On A Rotating Wheel
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Electron Transport Chain Occurs In The
Mar 20, 2025
-
Person Who Looks On The Dark Side
Mar 20, 2025
-
Dendrites Differ From Axons In That Dendrites
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Electron Configuration For Cobalt . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
