What Is The 5 Difference Between Photosynthesis And Respiration
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
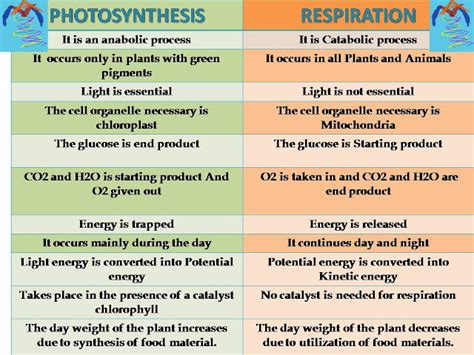
Table of Contents
5 Key Differences Between Photosynthesis and Respiration: A Deep Dive
Photosynthesis and respiration are two fundamental processes in biology, essential for the survival and sustenance of life on Earth. While they seem like opposites, a closer look reveals a fascinating interplay between the two, a continuous cycle of energy exchange that sustains ecosystems. Understanding their differences is crucial to grasping the intricate workings of the biological world. This article will delve into five key distinctions between photosynthesis and respiration, providing a comprehensive understanding of these vital processes.
1. The Nature of the Processes: Energy Production vs. Energy Consumption
The most fundamental difference between photosynthesis and respiration lies in their primary function: energy production versus energy consumption. Photosynthesis is an anabolic process, meaning it builds complex molecules from simpler ones, storing energy in the process. Respiration, on the other hand, is a catabolic process, breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones and releasing stored energy.
Photosynthesis: Capturing Sunlight's Energy
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants, absorbs sunlight's energy. This energy is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a simple sugar), a form of stored chemical energy, and oxygen. The overall equation for photosynthesis can be simplified as:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This process is critical because it forms the base of most food chains, providing the energy source for the vast majority of life on Earth.
Respiration: Releasing Stored Energy
Respiration is the process of releasing energy stored in organic molecules, primarily glucose. It's a series of chemical reactions that occur within the cells of organisms. These reactions break down glucose, releasing energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell's primary energy currency. Oxygen is typically required for aerobic respiration (the most common type), while anaerobic respiration (fermentation) occurs in the absence of oxygen. The simplified equation for aerobic cellular respiration is:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP
This released energy fuels all cellular activities, from growth and repair to movement and reproduction.
2. Location Within the Cell: Organelles Involved
The second significant difference lies in the location where these processes take place within the cell. Photosynthesis primarily occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, while cellular respiration predominantly takes place in the mitochondria.
Chloroplasts: The Photosynthetic Powerhouse
Chloroplasts are specialized organelles containing chlorophyll and other pigments essential for capturing light energy. Their internal structure, including thylakoid membranes and stroma, facilitates the complex reactions of photosynthesis.
Mitochondria: The Energy Factories
Mitochondria, often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell," are responsible for aerobic cellular respiration. Their inner membrane folds (cristae) provide a large surface area for the electron transport chain, a crucial step in ATP production.
3. Reactants and Products: A Reverse Relationship
The reactants and products of photosynthesis and respiration are essentially reversed. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and water as reactants, producing glucose and oxygen as products. Respiration uses glucose and oxygen as reactants, producing carbon dioxide and water as products. This reciprocal relationship highlights the cyclical nature of these processes in maintaining the balance of gases in the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis Reactants: CO₂ and H₂O
Photosynthesis takes in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water absorbed through the roots. These are combined using the energy from sunlight.
Photosynthesis Products: Glucose and O₂
The primary product of photosynthesis is glucose, a source of chemical energy for the plant. Oxygen, a byproduct, is released into the atmosphere.
Respiration Reactants: Glucose and O₂
Respiration utilizes glucose, the product of photosynthesis, and oxygen from the atmosphere.
Respiration Products: CO₂ and H₂O
Carbon dioxide and water are released as waste products of respiration, completing the cycle.
4. Light Dependency: Sunlight's Crucial Role
Photosynthesis is critically dependent on light, requiring sunlight as the primary energy source to drive the process. Respiration, however, can occur both in the presence and absence of light. While aerobic respiration requires oxygen, anaerobic respiration (fermentation) doesn't require it, allowing for energy production even in oxygen-depleted environments.
Photosynthesis: Light-Dependent Reactions
The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis are the initial steps where light energy is captured and converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
Respiration: Light-Independent Process
Respiration's reactions are not directly dependent on light. The energy released comes from breaking down glucose, regardless of light conditions.
5. Overall Energy Change: Energy Storage vs. Energy Release
The final key difference lies in the overall energy change associated with each process. Photosynthesis stores energy, converting light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This is an endergonic reaction, requiring energy input. Respiration releases energy, converting the chemical energy stored in glucose into ATP, a readily usable form of energy for cellular processes. This is an exergonic reaction, releasing energy.
Photosynthesis: Energy Storage
The energy from sunlight is absorbed and used to create the bonds in glucose, a process that requires energy input.
Respiration: Energy Release
The breaking of chemical bonds in glucose releases energy, which is harnessed to produce ATP, the cell's primary energy currency.
The Interconnectedness of Photosynthesis and Respiration
While these processes differ significantly, they are fundamentally interconnected. Photosynthesis produces the glucose and oxygen that respiration utilizes, while respiration produces the carbon dioxide and water that photosynthesis requires. This symbiotic relationship forms the basis of the carbon cycle and is crucial for maintaining life on Earth. The oxygen produced by photosynthesis is essential for aerobic respiration in most organisms, while the carbon dioxide produced by respiration is a key reactant in photosynthesis. This intricate dance between these two processes ensures the continuous flow of energy and matter through ecosystems.
Conclusion: Understanding the Vital Roles
Understanding the five key differences between photosynthesis and respiration – their nature (anabolic vs. catabolic), location (chloroplasts vs. mitochondria), reactants and products, light dependency, and overall energy change – provides a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of life. These processes are not merely independent reactions; they are tightly coupled, forming a fundamental cycle that sustains life on Earth. Their interplay demonstrates the remarkable efficiency and elegance of biological systems, highlighting the delicate balance necessary for the survival of all living things. Further research into these processes continues to reveal fascinating insights into the mechanisms of energy transfer and the intricate relationships between organisms and their environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Form Of Precipitation
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Statement About Natural Selection Is True
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Chamber Of Heart Has Thickest Wall
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 1 2 Miles
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The 5 Difference Between Photosynthesis And Respiration . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
