What Is In Car Battery Acid
News Leon
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
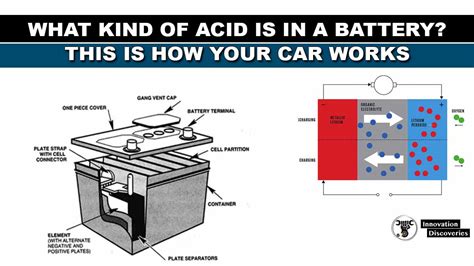
Table of Contents
What's in Car Battery Acid? Understanding Sulfuric Acid and its Role
Car batteries, the unsung heroes of our automotive world, wouldn't function without their potent core ingredient: sulfuric acid. While the term "acid" might conjure images of corrosive dangers, understanding the composition and function of battery acid is crucial for safe handling and responsible car maintenance. This comprehensive guide delves into the chemical makeup of car battery acid, its properties, how it works within the battery, safety precautions, and responsible disposal.
The Chemistry of Car Battery Acid: It's All About Sulfuric Acid
Car battery acid, more accurately described as electrolyte, is primarily a solution of sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and water (H₂O). It's not pure sulfuric acid; the concentration typically ranges from 30% to 38% sulfuric acid by weight, with the remaining percentage being distilled water. This specific concentration is crucial for optimal battery performance. A higher concentration might lead to increased corrosion and reduced lifespan, while a lower concentration would compromise the battery's ability to generate sufficient power.
Understanding Sulfuric Acid's Properties
Sulfuric acid itself is a powerful, highly corrosive mineral acid. Its key properties that make it ideal for car batteries include:
-
High conductivity: Sulfuric acid's ability to conduct electricity is paramount to the battery's function. It allows the flow of ions, facilitating the chemical reactions that generate electrical current.
-
Acidity: Its strong acidic nature allows it to participate in the electrochemical reactions within the battery, facilitating the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy.
-
Reactivity: Its reactivity with lead plates is key to the battery's charge-discharge cycle. We'll explore this further in the next section.
How Sulfuric Acid Powers Your Car Battery: The Electrochemical Reaction
A car battery is a lead-acid battery, employing a clever electrochemical process to store and release energy. The battery comprises several key components:
-
Lead plates (electrodes): Positive plates are made of lead dioxide (PbO₂), while negative plates are made of lead (Pb).
-
Sulfuric acid electrolyte: The solution of sulfuric acid and water acts as the conductive medium between the plates.
-
Separator: A porous material prevents direct contact between positive and negative plates, preventing short circuits.
The Charge-Discharge Cycle:
When the battery discharges (provides power), the following reaction occurs:
-
At the positive plate: Lead dioxide (PbO₂) reacts with sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and hydrogen ions (H⁺) to form lead sulfate (PbSO₄) and water (H₂O).
-
At the negative plate: Lead (Pb) reacts with sulfate ions (SO₄²⁻) to also form lead sulfate (PbSO₄).
This process releases electrons, creating an electrical current that powers your car. Crucially, lead sulfate builds up on both plates during discharge, reducing the battery's capacity.
During charging (e.g., from the alternator), the process reverses:
-
At the positive plate: Lead sulfate (PbSO₄) reacts with water (H₂O) to reform lead dioxide (PbO₂) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
-
At the negative plate: Lead sulfate (PbSO₄) reacts with sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) to reform lead (Pb) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
This reversal restores the battery's capacity, ready for another cycle of power delivery. The concentration of sulfuric acid in the electrolyte changes throughout this cycle. During discharge, the acid concentration decreases as it is consumed in the chemical reactions. During charging, the concentration increases as it is regenerated.
Monitoring Your Battery's Health: Acid Density and Specific Gravity
The state of charge of your car battery can be assessed by measuring the specific gravity of the electrolyte. Specific gravity is a measure of the density of a liquid relative to the density of water. A hydrometer is used to measure the specific gravity of the battery acid.
-
Fully charged battery: The specific gravity will be around 1.265 to 1.285. This indicates a high concentration of sulfuric acid.
-
Partially charged battery: The specific gravity will be lower, indicating less sulfuric acid.
-
Discharged battery: The specific gravity will be closer to 1.000 (the specific gravity of water), signifying a significant depletion of sulfuric acid.
Regularly checking the specific gravity provides valuable insights into your battery's health, allowing for early detection of potential problems.
Safety Precautions: Handling Sulfuric Acid with Care
Sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive substance. Improper handling can lead to severe burns and other injuries. Always follow these safety guidelines:
-
Eye protection: Always wear safety glasses or goggles when handling car battery acid.
-
Protective clothing: Wear gloves and protective clothing to prevent skin contact.
-
Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
-
Spills: In case of spills, neutralize the acid carefully using a suitable base, such as baking soda (sodium bicarbonate). Avoid direct contact with the spill.
-
Disposal: Never pour car battery acid down the drain or into the environment. Follow proper disposal procedures stipulated by local regulations. Many auto parts stores and recycling centers accept used car batteries.
Beyond Sulfuric Acid: Other Battery Components
While sulfuric acid is the main component of the electrolyte, a car battery contains other crucial elements:
-
Lead plates: The lead and lead dioxide plates provide the reactive surfaces for the electrochemical reactions.
-
Separators: These prevent short circuits by isolating the positive and negative plates.
-
Battery case and terminals: These provide structural support and electrical connections.
-
Vent caps: These allow for the release of gases produced during charging.
Conclusion: Respecting the Power of Sulfuric Acid
Understanding the composition and function of car battery acid—specifically the role of sulfuric acid—is vital for responsible car ownership. Knowing its corrosive nature and employing safe handling practices is crucial for personal safety. Regular maintenance, including monitoring the electrolyte's specific gravity, can help extend the life of your car battery and prevent unexpected breakdowns. Always remember to dispose of old batteries responsibly to protect the environment. By appreciating the chemistry behind this essential component, you can maintain a safer and more efficient driving experience.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Group Of Related Records Is Called A Table
Apr 01, 2025
-
Provides Long Term Energy Storage For Animals
Apr 01, 2025
-
The Average Propensity To Consume Refers To
Apr 01, 2025
-
Difference Between Independent Assortment And Law Of Segregation
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Oxidation Number For Sodium
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is In Car Battery Acid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
