What Element Has 7 Protons 8 Neutrons And 10 Electrons
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
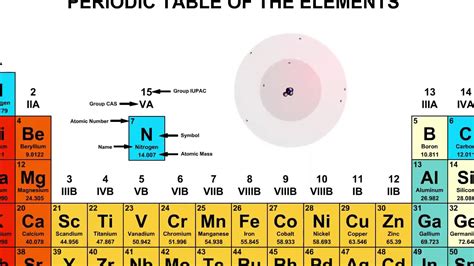
Table of Contents
What Element Has 7 Protons, 8 Neutrons, and 10 Electrons? Understanding Ions and Isotopes
The question "What element has 7 protons, 8 neutrons, and 10 electrons?" doesn't have a straightforward answer in terms of a naturally occurring element on the periodic table. The key to understanding this lies in grasping the concepts of atomic number, isotopes, and ions. Let's break down each concept to solve this puzzle.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Every atom is composed of three fundamental subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element. This is known as the atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also located in the nucleus. The number of neutrons can vary within the same element, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. The number of electrons usually equals the number of protons in a neutral atom. However, this can change, resulting in ions.
Atomic Number: The Defining Characteristic of an Element
The atomic number is the crucial piece of information for identifying an element. It corresponds to the number of protons in an atom's nucleus. Each element has a unique atomic number; no two elements share the same number of protons. An element with 7 protons is nitrogen (N).
Isotopes: Variations in Neutron Number
While the number of protons determines the element, the number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. These isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers (protons + neutrons). Nitrogen has several naturally occurring isotopes, but none has 8 neutrons. The most common isotopes are Nitrogen-14 (7 protons, 7 neutrons) and Nitrogen-15 (7 protons, 8 neutrons).
Ions: The Role of Electron Number
When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion. A cation is a positively charged ion (loss of electrons), and an anion is a negatively charged ion (gain of electrons). The specified atom has 10 electrons and 7 protons. Since the number of protons (7) is less than the number of electrons (10), it has 3 more electrons than protons, resulting in a net negative charge.
Putting It All Together: Nitrogen Anion
Let's synthesize the information:
- 7 protons: This unequivocally identifies the element as nitrogen (N).
- 8 neutrons: This indicates that the specific nitrogen atom is an isotope, specifically Nitrogen-15 (¹⁵N).
- 10 electrons: This signifies that the atom has gained 3 electrons, making it a nitride anion (N³⁻).
Therefore, the answer is a nitride anion (N³⁻), specifically the anion of Nitrogen-15 (¹⁵N³⁻). This is not a naturally occurring, stable species. It exists in various compounds and chemical environments due to the reactive nature of nitrogen and its propensity to gain electrons under certain conditions. It forms ionic bonds readily with positive metal ions.
The Significance of Ions in Chemistry and Biology
Ions play critical roles in various chemical and biological processes:
Chemical Reactions
Ions are fundamental to many chemical reactions. Their charges allow them to form ionic bonds, which are electrostatic attractions between oppositely charged ions. These bonds are essential in the formation of many compounds, including salts, minerals, and many other crucial materials.
Biological Processes
Ions are vital for life. For instance:
- Sodium (Na⁺) and Potassium (K⁺) ions are essential for nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction.
- Calcium (Ca²⁺) ions play a crucial role in muscle contraction, blood clotting, and bone formation.
- Chloride (Cl⁻) ions are critical for maintaining fluid balance and stomach acidity.
- Phosphate (PO₄³⁻) ions are essential components of DNA, RNA, and ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of cells.
The ability of atoms to gain or lose electrons, forming ions, is a cornerstone of chemical bonding and is crucial for the vast majority of chemical reactions which take place in the universe, from the formation of stars to the functions of living organisms.
Further Exploration: Isotopic Abundance and Nuclear Chemistry
The abundance of different isotopes varies significantly among elements. For nitrogen, the most abundant isotope is ¹⁴N, which makes up about 99.63% of naturally occurring nitrogen. ¹⁵N, with its extra neutron, is less abundant, comprising about 0.37%. The differences in isotopic abundance have applications in various fields, including:
- Geochemistry: Isotopic ratios can provide insights into geological processes and the age of materials.
- Archaeology: Carbon-14 dating relies on the decay of ¹⁴C to determine the age of organic artifacts.
- Medicine: Isotopes are used in medical imaging and treatments (e.g., PET scans).
The study of isotopes and their behavior falls under the realm of nuclear chemistry, a branch of chemistry that deals with the structure and behavior of atomic nuclei, including nuclear reactions and radioactivity.
Conclusion: Understanding the Fundamentals of Atomic Structure
The question regarding the element with 7 protons, 8 neutrons, and 10 electrons highlights the importance of understanding the fundamental concepts of atomic structure. While the number of protons defines the element (nitrogen in this case), the number of neutrons specifies the isotope (Nitrogen-15), and the number of electrons indicates the formation of an ion (a nitride anion, N³⁻). Each of these factors contributes to the overall properties and behavior of the atom. This seemingly simple question opens up a wider discussion of isotopes, ions, and their profound impact on chemistry and numerous scientific disciplines. The interplay between protons, neutrons, and electrons is crucial in defining the properties and reactivity of all matter in the universe. A deep understanding of these fundamental concepts is essential for any aspiring scientist or anyone curious about the building blocks of our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
X 3 3x 2 3 Factor
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Uniform Solid Sphere Rolls Down An Incline
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Homogeneous Mixtures
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Parallel Plate Capacitor Has Circular Plates
Mar 19, 2025
-
Distance From Earth To Moon In Meters Scientific Notation
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Element Has 7 Protons 8 Neutrons And 10 Electrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
