What Does 2 To 1 Ratio Mean
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
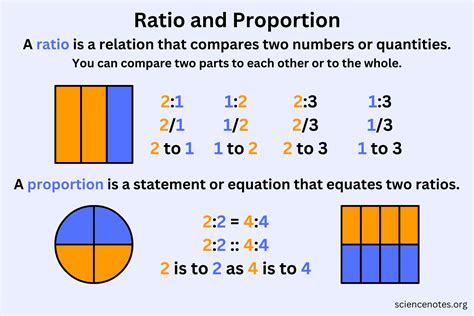
Table of Contents
What Does a 2:1 Ratio Mean? A Comprehensive Guide
The concept of ratios is fundamental to numerous fields, from cooking and construction to finance and science. Understanding ratios is crucial for interpreting data, making informed decisions, and solving problems effectively. This comprehensive guide will delve into the meaning of a 2:1 ratio, exploring its applications across various disciplines and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Ratios: The Basics
Before diving into the specifics of a 2:1 ratio, let's establish a foundational understanding of ratios themselves. A ratio is a mathematical comparison of two or more quantities. It shows the relative sizes of the quantities. Ratios are expressed in several ways:
- Using a colon: 2:1 (read as "two to one")
- Using the word "to": 2 to 1
- As a fraction: 2/1
- As a decimal: 2.0
The key is that a ratio expresses a relationship; it doesn't inherently represent a specific quantity. A 2:1 ratio means that for every two units of one thing, there is one unit of another thing. The absolute values of the quantities aren't fixed; only their relative proportion matters.
Decoding the 2:1 Ratio: What it Represents
A 2:1 ratio signifies that one quantity is twice the size of another. It's a simple yet powerful concept with widespread applications. Consider this: if you have a 2:1 ratio of apples to oranges, it means you have twice as many apples as oranges. If you have 10 oranges, you'd have 20 apples.
This principle extends beyond simple counting. A 2:1 ratio can describe:
- Concentration: A 2:1 concentration of sugar to water implies that there's twice as much sugar as water in a solution.
- Dimensions: A 2:1 aspect ratio in a photograph means the width is twice the height.
- Proportions: A 2:1 proportion of cement to sand in concrete mix dictates the relative amounts of each ingredient.
- Financial Ratios: In finance, a 2:1 debt-to-equity ratio signifies a company has twice as much debt as equity.
- Gear Ratios: In mechanics, a 2:1 gear ratio implies that for every two rotations of the input gear, the output gear makes one rotation.
Real-World Applications of the 2:1 Ratio
Let's explore some practical examples across diverse fields to illustrate the versatility of the 2:1 ratio:
1. Cooking and Baking
Recipes often utilize ratios to ensure consistent results. A 2:1 ratio of flour to sugar in a cake recipe, for example, means that for every 2 cups of flour, you'd use 1 cup of sugar. This precise proportion is critical for the cake's texture and taste.
2. Construction and Engineering
In construction, ratios are essential for maintaining structural integrity. The ratio of cement, sand, and aggregate in concrete, for instance, must be precise to ensure the concrete's strength and durability. A deviation from the optimal ratio can lead to structural weaknesses. Similarly, in engineering, ratios are used to calculate load-bearing capacities and design various components.
3. Finance and Investing
Financial ratios are vital tools for analyzing a company's financial health. A 2:1 debt-to-equity ratio, as mentioned earlier, indicates a higher level of debt relative to equity. While not inherently good or bad, it suggests a higher risk profile and needs careful evaluation. Other ratios, such as price-to-earnings ratios, are widely used to assess the valuation of stocks.
4. Science and Research
In scientific experiments and research, ratios are used to express concentrations, proportions, and other quantitative relationships. For example, in chemistry, a 2:1 molar ratio of reactants in a chemical reaction is crucial for understanding the reaction's stoichiometry and yield. In biology, ratios can be used to analyze population densities or genetic traits.
5. Photography and Design
The aspect ratio of images and videos significantly impacts their visual appeal. A 2:1 aspect ratio, while less common than 16:9 or 4:3, can be creatively used for specific artistic effects. Similar principles apply to graphic design, where the ratio of elements within a layout influences its overall aesthetic balance.
6. Music and Sound
In music production and sound engineering, ratios are used to tune instruments and create harmonic intervals. Certain intervals, such as the octave, are based on precise numerical ratios that determine the relative frequencies of notes.
Calculating with 2:1 Ratios: Practical Examples
Let's examine some practical calculations involving 2:1 ratios:
Example 1: Mixing Paint
You need to mix paint in a 2:1 ratio of blue to white. You have 6 liters of blue paint. How much white paint do you need?
- Solution: Since the ratio is 2:1, you need half as much white paint as blue paint. Therefore, you need 6 liters / 2 = 3 liters of white paint.
Example 2: Scaling a Recipe
A recipe calls for 4 cups of flour and 2 cups of sugar (a 2:1 flour-to-sugar ratio). You want to double the recipe. How much of each ingredient will you need?
- Solution: Doubling the recipe means multiplying both quantities by 2. You'll need 8 cups of flour (4 cups * 2) and 4 cups of sugar (2 cups * 2). The ratio remains 2:1.
Example 3: Analyzing Financial Data
A company has a debt-to-equity ratio of 2:1. If its total equity is $1 million, what's its total debt?
- Solution: The ratio indicates that debt is twice the equity. Therefore, the total debt is $2 million ($1 million * 2).
Beyond the 2:1 Ratio: Other Common Ratios
While the 2:1 ratio is prevalent, understanding other common ratios is equally important. Some frequently encountered ratios include:
- 1:1 Ratio (Equal Parts): This indicates equal quantities of both components.
- 3:1 Ratio: One quantity is three times the size of the other.
- 1:2 Ratio: One quantity is half the size of the other (the inverse of 2:1).
- Golden Ratio (approximately 1.618:1): A ratio found frequently in nature and art, possessing aesthetic properties.
Understanding these ratios allows for a more comprehensive interpretation of numerical relationships across various fields.
Mastering Ratios: Tips and Techniques
- Visual aids: Diagrams, charts, and graphs can make ratios easier to understand and visualize.
- Practice: Working through various examples helps build intuition and proficiency in ratio calculations.
- Context is key: Always consider the context of the ratio to correctly interpret its meaning.
- Unit consistency: Ensure consistent units when working with ratios to avoid errors.
Conclusion: The Ubiquity of the 2:1 Ratio
The 2:1 ratio, though seemingly simple, is a fundamental concept with vast applications. From mixing ingredients in the kitchen to analyzing financial statements in the boardroom, understanding this ratio and its implications is essential for success in numerous fields. By grasping the principles outlined in this guide, you'll be well-equipped to interpret and utilize ratios effectively in your daily life and professional endeavors. Remember that the ability to comprehend and manipulate ratios is a crucial skill for effective problem-solving and decision-making in a wide range of contexts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Continued Deforestation Will Most Likely Lead To
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Function Of Cell Membrane
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Ounces In Two Pounds
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Part Of The Appendicular Skeleton
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Opposite Of Inferior
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does 2 To 1 Ratio Mean . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
