What Color Does Phenolphthalein Turn In A Base
News Leon
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
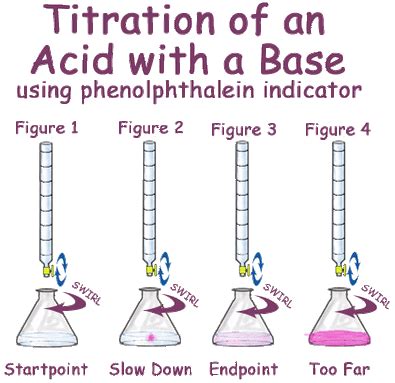
Table of Contents
What Color Does Phenolphthalein Turn in a Base? A Comprehensive Guide
Phenolphthalein, a common chemical indicator, is famous for its dramatic color change in the presence of bases. Understanding this change, and the chemistry behind it, is crucial for anyone working with acids and bases, from high school chemistry students to professional chemists. This comprehensive guide will delve into the fascinating world of phenolphthalein, explaining its color change in detail and exploring its various applications.
Understanding Phenolphthalein's Structure and Properties
Phenolphthalein is a weak organic acid with the chemical formula C₂₀H₁₄O₄. Its structure is complex, featuring a triphenylmethane backbone with two phenolic hydroxyl groups and a lactone ring. This seemingly simple structure is responsible for its remarkable color-changing properties. The key lies in the molecule's ability to exist in different forms, depending on the pH of the solution.
The Lactom Form: Colorless and Neutral
In acidic solutions (low pH), phenolphthalein exists primarily in its lactone form. This colorless form is a relatively stable, neutral molecule. The lactone ring is intact, and the molecule doesn't readily interact with hydrogen or hydroxide ions. This is why phenolphthalein remains colorless in acidic and mildly acidic solutions. The solution remains clear and transparent, giving no indication of the presence of the indicator.
The Quinoid Form: Pink and Charged
The magic happens in basic solutions (high pH). As the pH increases, the hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in the solution react with the phenolphthalein molecule. This reaction leads to the opening of the lactone ring and the formation of a quinoid structure. This is where the characteristic pink color emerges. The quinoid form is anionic; it carries a negative charge, which contributes to its interaction with light and its vibrant pink color. This dramatic color change is highly sensitive to pH, making phenolphthalein an excellent indicator for acid-base titrations.
The Chemistry Behind the Color Change: An In-Depth Look
The transition between the colorless lactone form and the pink quinoid form isn't instantaneous. It's a gradual process that depends on the concentration of hydroxide ions. At low concentrations of hydroxide ions (slightly basic solutions), only a small fraction of phenolphthalein molecules will convert to the quinoid form, resulting in a very faint pink color. As the concentration of hydroxide ions increases (more basic solutions), a larger proportion of phenolphthalein molecules undergo this transformation, leading to a more intense pink color. This gradual color change is what allows phenolphthalein to be used effectively as an indicator in titrations.
Equilibrium and pH Dependence
The color change of phenolphthalein is governed by an equilibrium between the colorless lactone form and the pink quinoid form. This equilibrium is highly sensitive to pH. The pKa of phenolphthalein (the pH at which half of the molecules are in the quinoid form) is approximately 9.4. Below this pH, the colorless lactone form predominates. Above this pH, the pink quinoid form is favored. This is why a distinct color change occurs around pH 8.2 to 10.0, making it a valuable indicator for determining the endpoint in titrations involving strong acids and strong bases.
The Role of Solvents
It's crucial to note that the color change of phenolphthalein can be influenced by the solvent used. In some organic solvents, the color change might be different or less pronounced compared to aqueous solutions. This is due to the interactions between phenolphthalein and the solvent molecules. The solvent's polarity affects the equilibrium between the lactone and quinoid forms, thereby influencing the color observed.
Applications of Phenolphthalein as an Indicator
Phenolphthalein's ability to change color dramatically in the presence of bases has made it an indispensable tool in various applications, particularly in chemistry and analytical techniques:
Acid-Base Titrations: The Most Common Use
The primary application of phenolphthalein is as an acid-base indicator in titrations. It allows chemists to precisely determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base by monitoring the color change during the titration process. The endpoint of the titration, which indicates the neutralization point, is easily identified by the change from colorless to pink (or vice versa). This precise determination of concentration is crucial in many chemical analyses and industrial processes.
Determining pH: A Simple Test
Phenolphthalein's color change can be used as a qualitative test to estimate pH. While not as precise as a pH meter, a visual observation of the color change can provide a rough estimate of whether a solution is acidic or basic. This simple test is useful in various situations where precise pH measurement might not be necessary.
Other Applications: Less Common but Still Significant
Beyond titrations and pH estimations, phenolphthalein has found applications in other areas, though less frequently:
- Medicine: While less common now due to safety concerns, phenolphthalein was once used as a laxative. However, due to potential carcinogenic effects, its use is largely discontinued.
- Research: Phenolphthalein continues to be used in research settings for various chemical studies and experiments involving acid-base reactions. Understanding its behavior helps in designing experiments and analyzing results.
Safety Precautions When Using Phenolphthalein
While phenolphthalein is generally considered safe at low concentrations, certain precautions must be taken:
- Avoid ingestion: As mentioned earlier, phenolphthalein was once used as a laxative but has since been associated with potential carcinogenic effects. Therefore, ingestion should be strictly avoided.
- Handle with care: Always use appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, when handling phenolphthalein solutions to avoid skin or eye contact.
- Proper disposal: Dispose of phenolphthalein solutions according to local regulations to prevent environmental contamination.
Conclusion: A Versatile Indicator with a Striking Transformation
Phenolphthalein, with its dramatic color change from colorless to pink in basic solutions, remains a valuable tool in chemistry. Its simplicity, sensitivity, and distinct color change make it a reliable indicator for various applications. Understanding the chemistry behind this color change, from the structural modifications to the equilibrium involved, provides a deeper appreciation for the versatility of this important chemical. While caution should be exercised due to potential safety concerns, the proper use of phenolphthalein continues to be an essential skill for students and professionals alike in the chemical sciences. Its unique properties continue to provide insights into the fascinating world of acid-base chemistry and its applications. From simple classroom demonstrations to sophisticated analytical techniques, phenolphthalein's contribution remains significant. Remember to always prioritize safety when working with this chemical.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Find The Boiling Point Of A Solution
Apr 02, 2025
-
Balance Equation Fes2 O2 Fe2o3 So2
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Is Not A Physical Property
Apr 02, 2025
-
Australia Is The Worlds Leading Producer Of
Apr 02, 2025
-
Geometric Mean Of 8 And 18
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Color Does Phenolphthalein Turn In A Base . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
