What Are Two Categories Of Software
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
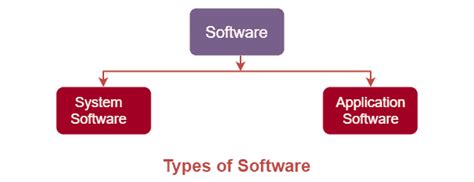
Table of Contents
What Are the Two Main Categories of Software? A Deep Dive into System and Application Software
The world of software is vast and complex, encompassing everything from the operating system on your phone to the intricate algorithms powering e-commerce giants. While seemingly limitless in its applications, software can be broadly categorized into two fundamental types: system software and application software. Understanding the differences between these two categories is crucial for anyone working with computers, from casual users to seasoned developers. This comprehensive guide delves deep into each category, exploring their functionalities, key characteristics, and examples to provide a clear and concise understanding.
System Software: The Unsung Hero Behind the Scenes
System software acts as the intermediary between the user and the computer's hardware. It manages and controls the computer's hardware resources, providing a platform for application software to run smoothly. Think of it as the foundation upon which everything else is built. Without robust system software, your computer would be nothing more than a collection of inert components.
Key Characteristics of System Software:
- Hardware Management: System software directly interacts with hardware components like the CPU, RAM, hard drive, and input/output devices. It manages memory allocation, processes data input and output, and ensures that all components work together harmoniously.
- Resource Allocation: It allocates resources efficiently, prioritizing tasks and ensuring that each application receives the necessary resources to function optimally. This involves managing CPU time, memory space, and access to peripherals.
- Provides a Platform for Application Software: System software creates the environment in which application software can run. It provides the essential services and tools needed for applications to interact with the hardware and with each other.
- Security and Protection: It incorporates mechanisms to protect the system from malware, viruses, and unauthorized access. This includes features like firewalls, anti-virus software (which is often part of, or closely integrated with, the system software), and user authentication.
- Hidden from the End-User (Mostly): While some aspects of system software are visible to users (e.g., the operating system's interface), much of its functionality operates invisibly in the background.
Examples of System Software:
- Operating Systems (OS): This is arguably the most crucial component of system software. Popular operating systems include Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. They manage all hardware and software resources, providing a user interface and the foundation for all other software.
- Device Drivers: These are small programs that allow the operating system to communicate with specific hardware devices. For instance, a printer driver allows your computer to send print jobs to a printer. Without the correct drivers, your hardware won't function properly.
- Firmware: This is a type of software embedded into hardware devices, providing low-level control. Examples include the firmware in your BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), which is responsible for booting up your computer, and the firmware in your router.
- BIOS/UEFI: The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or its modern equivalent, Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI), is firmware responsible for initializing hardware components and loading the operating system.
- Bootloaders: These programs load the operating system into the computer's memory. GRUB (Grand Unified Bootloader) is a common example.
- Utility Software: This category encompasses various tools designed to enhance the functionality of the operating system and manage system resources. Examples include disk defragmenters, system monitors, and backup utilities.
Application Software: Tools for Every Task
Application software is designed to perform specific tasks or provide specific services to users. Unlike system software, which is primarily concerned with managing the computer's resources, application software focuses on enabling users to accomplish their goals. It's the software you interact with directly to accomplish specific tasks, ranging from writing documents to playing games.
Key Characteristics of Application Software:
- User-Focused: Application software is designed to be user-friendly, providing tools and interfaces that enable users to perform tasks easily and efficiently.
- Specific Functionality: Each application software is designed for a specific purpose, whether it's word processing, image editing, web browsing, or playing games.
- Reliance on System Software: Application software relies on the underlying system software to function. It uses the services provided by the operating system to interact with hardware and other software.
- Diverse Range of Applications: The range of application software is incredibly broad, encompassing countless specialized applications for various industries and purposes.
- Continuously Evolving: Application software is frequently updated with new features, bug fixes, and improved performance.
Examples of Application Software:
The variety of application software is immense, and it's categorized further into subcategories based on their function:
- Productivity Software: These applications are designed to help users perform common tasks, such as writing documents (Microsoft Word, Google Docs), creating spreadsheets (Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets), and making presentations (Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides).
- Graphics and Multimedia Software: These applications are used for creating and editing images, videos, and audio. Examples include Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Premiere Pro, Audacity, and GIMP.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software: Used by large organizations to manage their resources, including financials, human resources, and supply chain management. SAP and Oracle are prominent examples.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software: These applications are used to manage customer interactions and data, improving customer service and sales. Salesforce and HubSpot are examples.
- Web Browsers: Software used to access and navigate the World Wide Web, such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
- Gaming Software: Covers a vast range from simple mobile games to complex PC and console titles.
- Database Management Systems (DBMS): Software used to store, manage, and retrieve data, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle Database.
- Communication Software: Email clients (Outlook, Thunderbird), instant messaging apps (WhatsApp, Telegram), and video conferencing software (Zoom, Skype).
- Educational Software: Software designed for educational purposes, such as learning platforms, interactive simulations, and educational games.
The Interdependence of System and Application Software
It's crucial to remember that system and application software are not isolated entities. They are intricately intertwined, each relying on the other to function effectively. Application software relies on system software to provide the necessary resources and services, while system software provides the platform upon which applications can run and interact with the hardware.
Imagine trying to run a sophisticated game (application software) on a computer without a properly functioning operating system (system software). The game simply wouldn't launch, or if it did, it would likely crash frequently due to resource conflicts or a lack of essential services. Similarly, a powerful operating system is useless without applications to utilize its capabilities.
The Future of Software Categorization
As technology continues to advance, the lines between system and application software may become increasingly blurred. The rise of cloud computing and virtualization, for instance, has led to the development of software that blurs the traditional distinctions. However, the fundamental concepts of managing resources (system software) and performing specific tasks (application software) remain core principles in the world of computing.
This detailed exploration highlights the crucial roles system and application software play in the modern technological landscape. Understanding their differences and interdependencies is essential for navigating the increasingly complex world of computing and utilizing its potential to its fullest extent. By appreciating the intricate interplay between these two software categories, we gain a deeper understanding of the power and potential of the technology shaping our lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Barium Chloride Reacts With Sodium Sulphate
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is Half Of 1 1 2 Tsp
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Is Not A Cranial Bone
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Type Of Symmetry Do Echinoderms Have
Mar 21, 2025
-
90 Is What Percent Of 120
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are Two Categories Of Software . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
