What Are The Determinants Of Supply In Economics
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 7 min read
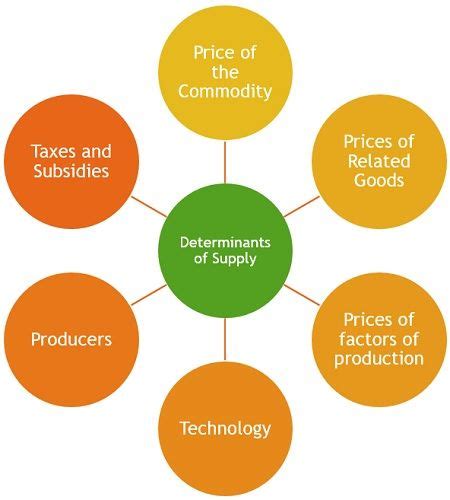
Table of Contents
What are the Determinants of Supply in Economics?
Supply, a fundamental concept in economics, refers to the total amount of a specific good or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at a given price in a given period. Understanding the factors that influence supply is crucial for analyzing market dynamics, predicting price changes, and formulating effective economic policies. This article delves deep into the determinants of supply, exploring each factor in detail and illustrating their impact with real-world examples.
Key Determinants of Supply: A Comprehensive Overview
Several factors interact to determine the quantity supplied of a good or service. These determinants can be broadly categorized as:
-
Price of the Good or Service: This is the most direct and immediate influence on supply. As the price of a good rises, producers are incentivized to supply more, and vice versa. This relationship is represented by the upward-sloping supply curve.
-
Prices of Related Goods and Services: This encompasses two key aspects:
-
Substitute Goods: If the price of a substitute good (a good that can be used in place of another) increases, the supply of the original good may decrease. Producers might switch production to the more profitable substitute. For example, if the price of aluminum increases significantly, some producers might shift from producing aluminum cans to steel cans, reducing the supply of aluminum cans.
-
Complementary Goods: Complementary goods are those used together (e.g., cars and gasoline). If the price of a complementary good decreases, the supply of the original good might increase. A lower gasoline price, for instance, might encourage more car production, boosting the supply of cars.
-
-
Input Prices (Cost of Production): The cost of raw materials, labor, capital, and energy significantly impacts a producer's willingness to supply. Higher input prices increase production costs, reducing profitability and potentially lowering the quantity supplied. Conversely, lower input costs can stimulate an increase in supply. For example, a drop in the price of cotton would likely increase the supply of cotton t-shirts.
-
Technology: Technological advancements can dramatically affect supply. Innovations that improve production efficiency, reduce waste, or automate processes allow producers to supply more at the same cost or even at a lower cost. The introduction of automated assembly lines, for example, significantly increased the supply of automobiles.
-
Government Policies: Various government regulations and policies directly or indirectly influence supply. These include:
-
Taxes: Taxes on production increase costs, reducing the profitability of production and therefore the quantity supplied.
-
Subsidies: Government subsidies, on the other hand, lower production costs, making production more attractive and increasing the quantity supplied.
-
Regulations: Environmental regulations, labor laws, and other regulations can increase compliance costs, impacting profitability and potentially lowering supply.
-
Import Quotas and Tariffs: Import quotas restrict the quantity of a good that can be imported, potentially increasing the domestic supply to meet the higher demand. Tariffs (taxes on imported goods) increase the price of imported goods, making domestically produced goods more competitive and increasing domestic supply.
-
-
Producer Expectations: Producers' beliefs about future prices, costs, and market conditions significantly impact their current supply decisions. If producers anticipate a future price increase, they might temporarily withhold supply, leading to lower current supply. Conversely, anticipated price decreases might lead them to increase current supply to avoid future losses.
-
Number of Sellers: The number of firms operating in a market directly affects the total quantity supplied. More sellers in a competitive market generally lead to higher supply, while fewer sellers lead to lower supply. This concept is especially relevant in understanding market structures like perfect competition and monopolies.
-
Natural Events and Disasters: Unforeseen events like natural disasters (earthquakes, floods, hurricanes), adverse weather conditions, or disease outbreaks can disrupt supply chains, damage production facilities, and significantly reduce the quantity supplied. The 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami, for instance, severely disrupted the global supply of electronic components.
Analyzing the Impact of Determinants: Real-World Examples
Let's explore the impact of these determinants with some real-world examples:
1. Price of the Good: Consider the market for coffee beans. If the price of coffee beans rises substantially, farmers will be incentivized to cultivate more coffee plants, expanding their acreage and increasing their output, thus boosting the supply.
2. Prices of Related Goods: The price of tea, a substitute for coffee, can influence the supply of coffee. If the price of tea significantly increases, some consumers might switch to coffee, increasing the demand and potentially encouraging coffee producers to increase their supply to meet the higher demand.
3. Input Prices: A rise in the price of fertilizer (an input for coffee production) would directly increase the cost of coffee production, potentially leading to a decrease in the supply of coffee beans.
4. Technology: The development of high-yield coffee plant varieties or improved processing techniques can increase the efficiency of coffee production, thereby boosting the supply of coffee beans.
5. Government Policies: A government subsidy for coffee farmers would lower their production costs, encouraging them to produce more coffee, leading to a higher supply. Conversely, a tax on coffee production would have the opposite effect.
6. Producer Expectations: If coffee farmers anticipate a future increase in coffee bean prices due to a predicted poor harvest in a major coffee-producing region, they might temporarily withhold some of their current supply, causing a temporary decrease in the supply.
7. Number of Sellers: An increase in the number of coffee farmers entering the market would naturally lead to a larger overall supply of coffee beans.
Supply Elasticity and its Determinants
Supply elasticity measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to changes in price. It's crucial to understand that not all goods and services exhibit the same degree of supply elasticity. Several factors influence supply elasticity:
-
Time Horizon: The longer the time horizon, the more elastic the supply. In the short run, producers might have limited capacity to increase output, resulting in inelastic supply. However, in the long run, they can expand their facilities, invest in new technology, or enter/exit the market, making supply more elastic.
-
Availability of Inputs: If inputs are readily available and easily substitutable, supply is more elastic. Conversely, scarcity of inputs constrains the ability of producers to increase supply, resulting in inelastic supply.
-
Production Capacity: Firms with excess production capacity can easily increase output in response to price changes, exhibiting more elastic supply. Firms operating at full capacity have less room for expansion, resulting in inelastic supply.
-
Storage Costs: Goods that can be easily stored at low cost tend to exhibit more elastic supply, as producers can adjust their supply to future price expectations. Perishable goods have less elastic supply due to the high storage costs and spoilage risks.
Understanding supply elasticity is crucial for policymakers in assessing the impact of policies on market outcomes. For example, a tax on a good with inelastic supply will likely lead to a larger price increase than a tax on a good with elastic supply.
The Interplay of Supply and Demand
Supply and demand are two sides of the same coin in market economics. The interaction between these two forces determines the market equilibrium price and quantity. Changes in any of the determinants of supply will shift the supply curve, leading to a new equilibrium point. The magnitude of the price and quantity adjustments depends on the elasticity of both supply and demand.
For example, an increase in the price of a key input (e.g., oil for transportation) will shift the supply curve to the left (decrease in supply), leading to a higher equilibrium price and a lower equilibrium quantity. The degree to which the price and quantity change will depend on the elasticity of demand. If demand is inelastic (consumers are not very responsive to price changes), the price will increase significantly, while the quantity will decrease only slightly. If demand is elastic (consumers are very responsive to price changes), the price increase will be smaller, and the quantity decrease will be more significant.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Force
Supply is a dynamic and multifaceted concept in economics, influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these determinants is essential for analyzing market behavior, predicting price fluctuations, and formulating effective economic policies. From technological advancements to government interventions and unpredictable natural events, various forces constantly shape the supply of goods and services, impacting our daily lives and the global economy. By appreciating the intricate relationship between supply and demand, and the elasticity of supply, economists and policymakers can better navigate the complexities of the marketplace and work towards creating efficient and equitable economic systems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
11 N 2 12 2n 1 Is Divisible By 133
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Figure Shows Two Charged Particles On An X Axis
Mar 15, 2025
-
Analysis Of Ode To The West Wind
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Meaning Of The Term Threshold Stimulus
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True About A Firewall
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Determinants Of Supply In Economics . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
