Variable Cost Per Unit Of Output Produced Is
News Leon
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
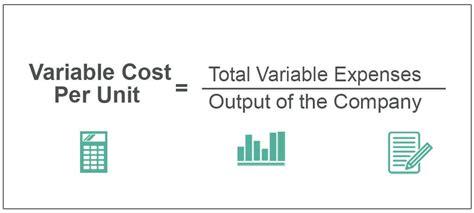
Table of Contents
Variable Cost Per Unit of Output Produced: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding variable cost per unit is crucial for businesses of all sizes. It directly impacts pricing strategies, profitability analysis, and overall financial health. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the concept, explaining its calculation, significance, and how it interacts with other cost elements within a business.
What is Variable Cost Per Unit?
Variable cost per unit refers to the direct cost associated with producing one unit of a good or service. Unlike fixed costs (like rent or salaries), variable costs fluctuate directly with the level of production. The more you produce, the higher your total variable costs; the less you produce, the lower your total variable costs. However, the per-unit cost often remains relatively constant, assuming consistent production processes and input prices.
Key Characteristics of Variable Costs:
- Directly Proportional to Output: The primary defining characteristic. As production increases, so do variable costs.
- Fluctuates with Production Volume: Changes depending on the number of units produced.
- Examples: Raw materials, direct labor (for production workers), packaging, and shipping costs are all common variable costs.
Calculating Variable Cost Per Unit
The formula for calculating variable cost per unit is straightforward:
Variable Cost Per Unit = Total Variable Costs / Total Number of Units Produced
Let's illustrate with an example:
Imagine a bakery producing loaves of bread. Their total variable costs for a month, including flour, sugar, yeast, and direct labor for bakers, amounted to $5,000. During that month, they produced 10,000 loaves of bread.
Therefore, their variable cost per unit is:
$5,000 / 10,000 loaves = $0.50 per loaf.
This means that each loaf of bread costs the bakery $0.50 in variable costs to produce.
Distinguishing Variable Costs from Fixed Costs
It’s vital to distinguish between variable and fixed costs to accurately analyze profitability and make informed business decisions. Confusing these two can lead to inaccurate cost estimations and flawed strategies.
Fixed Costs: These remain relatively constant regardless of production volume. Examples include:
- Rent: Monthly rent for the factory or office space.
- Salaries: Salaries of administrative staff or managers (not direct production workers).
- Depreciation: The decrease in value of assets over time.
- Insurance: Premiums for business insurance.
Variable Costs: As previously discussed, these change directly with production volume.
The Importance of Understanding Variable Cost Per Unit
Understanding variable cost per unit is essential for several reasons:
-
Pricing Strategies: Knowing the variable cost per unit is crucial for setting profitable prices. A business must cover its variable costs, and ideally, contribute towards covering fixed costs and generating profit. Pricing too low may lead to losses, while pricing too high may deter customers.
-
Break-Even Analysis: Determining the break-even point – the level of production where total revenue equals total costs – requires an understanding of both variable and fixed costs. The break-even point calculation helps businesses understand how many units they need to sell to avoid losses.
-
Cost Control: Tracking variable costs per unit allows businesses to identify areas for cost reduction. Analyzing changes in variable cost per unit over time can highlight inefficiencies or price increases in raw materials.
-
Profitability Analysis: By separating variable costs from fixed costs, businesses can analyze their profit margins more effectively. This analysis helps understand the impact of different production levels on overall profitability.
-
Decision Making: Accurate variable cost data is crucial for making informed decisions regarding production levels, pricing, and investment in new equipment or technologies.
-
Budgeting and Forecasting: Predicting future variable costs based on projected production levels is essential for accurate budgeting and forecasting.
Factors Affecting Variable Cost Per Unit
Several factors can influence the variable cost per unit:
-
Raw Material Prices: Fluctuations in the prices of raw materials directly impact the variable cost per unit. Increases in raw material prices lead to higher variable costs, unless mitigated through efficiency improvements or alternative sourcing.
-
Labor Costs: Changes in wages or labor productivity affect direct labor costs, a significant component of variable costs. Increases in wages or decreases in productivity increase the variable cost per unit.
-
Production Efficiency: Improved production efficiency can reduce variable costs per unit. Streamlined processes, better technology, and improved worker training can contribute to lower variable costs.
-
Economies of Scale: As production volume increases, businesses may achieve economies of scale, leading to lower variable costs per unit. This is because bulk purchasing of raw materials and efficient use of resources can reduce costs.
-
Technological Advancements: New technologies can improve production efficiency, leading to lower variable costs per unit. Automation, advanced machinery, and improved software can all contribute to cost reductions.
Variable Cost Per Unit and Profit Maximization
For businesses aiming for profit maximization, understanding variable cost per unit is paramount. It contributes to:
-
Optimal Production Levels: Businesses need to identify the production level where the difference between revenue and total costs (including variable and fixed costs) is maximized. This involves analyzing the relationship between production volume, variable cost per unit, and selling price.
-
Pricing Decisions: Profit maximization involves setting prices that consider both variable costs per unit and the elasticity of demand for the product or service. Setting prices too low may not cover costs, while setting them too high may reduce sales volume.
Advanced Considerations: Beyond Basic Calculation
While the basic formula is straightforward, understanding variable cost per unit often requires a more nuanced approach:
-
Stepped Costs: Some costs exhibit characteristics of both fixed and variable costs. For example, a machine might operate at a certain level of efficiency up to a certain production volume, and then efficiency (and therefore variable cost per unit) changes when you need to bring in a second machine. Understanding these stepped costs is critical for accurate cost accounting.
-
Activity-Based Costing (ABC): ABC is a more sophisticated costing method that assigns costs based on activities involved in production. It provides a more accurate view of variable costs, particularly in situations with multiple products or complex manufacturing processes.
-
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: This technique uses variable cost per unit and other cost information to analyze the relationship between cost, volume, and profit. CVP analysis helps businesses understand how changes in production volume or pricing will impact profitability.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Sound Business Decisions
Understanding variable cost per unit is a cornerstone of effective financial management. It's not just about calculating a simple number; it’s about using that number to inform strategic decisions related to pricing, production, and overall profitability. By mastering this concept and its related aspects, businesses can optimize operations, strengthen their competitive position, and pave the way for sustained growth and success. Regularly monitoring and analyzing variable cost per unit, coupled with a thorough understanding of other cost elements, allows businesses to make informed choices and achieve their financial objectives. The more refined your understanding of variable cost per unit, the more effectively you can navigate the complex landscape of business operations and maximize profitability.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Did David Used To Kill Goliath
Apr 01, 2025
-
Are Cells Depicted Plant Or Animal
Apr 01, 2025
-
Select Which Statements Are A Part Of Natural Selection
Apr 01, 2025
-
Why Electronic Configuration Of Calcium Is 2 8 8 2
Apr 01, 2025
-
1 Square Meter Is How Many Square Centimeters
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Variable Cost Per Unit Of Output Produced Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
