The Water Cycle Is Driven By The
News Leon
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
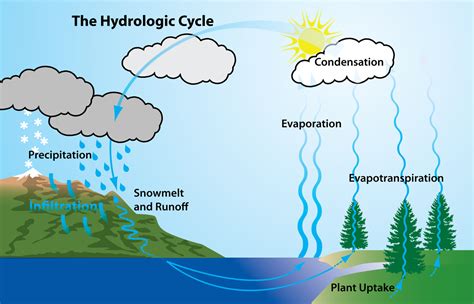
Table of Contents
The Water Cycle is Driven by the Sun: A Comprehensive Exploration
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. This vital process shapes our planet's landscapes, climates, and ecosystems, and is fundamental to all life. But what is the driving force behind this ceaseless circulation? The answer, simply put, is the sun. This article will delve deep into the sun's role in each stage of the water cycle, exploring the intricate mechanisms that power this essential planetary engine.
The Sun's Energy: The Engine of Evaporation
The sun, our nearest star, provides the primary energy source that fuels the water cycle. Its immense energy, delivered to Earth in the form of solar radiation, drives the process of evaporation. This is the first and arguably most crucial stage of the cycle.
Understanding Evaporation: More Than Just Heat
Evaporation isn't simply water turning into vapor due to heat. While temperature plays a significant role, other factors like air pressure, humidity, and wind speed also influence the rate of evaporation. However, the sun's heat provides the initial energy needed to break the hydrogen bonds holding water molecules together in liquid form. This allows them to escape into the atmosphere as water vapor.
Sources of Evaporation: A Diverse Range
Evaporation occurs from various sources, and the sun's influence is felt across them all:
-
Oceans: The vast expanse of the world's oceans is the primary source of evaporation. The sun's energy heats the ocean's surface, causing massive amounts of water to evaporate. This contributes significantly to atmospheric moisture.
-
Lakes and Rivers: Smaller bodies of water also contribute to evaporation. Sunlight heats these water bodies, leading to the release of water vapor into the atmosphere. The size and depth of these water bodies influence the rate of evaporation.
-
Soil: Even seemingly dry land contributes to evaporation. Soil moisture, absorbed by plants and released through transpiration (discussed below), also evaporates due to solar radiation.
-
Snow and Ice: Although seemingly counterintuitive, snow and ice also undergo sublimation, a process where ice directly transforms into water vapor without first melting. The sun's energy provides the necessary heat for this process, even in frigid conditions. This is particularly significant in polar regions and high-altitude areas.
Transpiration: Plants' Contribution to the Cycle
While evaporation focuses on water bodies, transpiration involves the release of water vapor from plants. This process is also driven by the sun's energy.
The Mechanism of Transpiration: A Botanical Pump
Plants absorb water through their roots and transport it to their leaves. The sun's energy facilitates the opening of stomata, tiny pores on the leaves' surface. Water vapor escapes through these stomata, contributing significantly to atmospheric humidity.
The Importance of Transpiration: More Than Just Water Loss
Transpiration is essential for plant survival. It helps to cool the plant, regulate water uptake, and transport nutrients throughout the plant's system. It also plays a crucial role in the water cycle, contributing a substantial amount of water vapor to the atmosphere, especially in vegetated areas.
Condensation: The Formation of Clouds
As water vapor rises into the atmosphere, it cools and condenses. This condensation process is facilitated by the presence of condensation nuclei, tiny particles like dust or pollen, which provide a surface for water molecules to cling to.
The Role of Altitude and Temperature: Key Factors in Condensation
As air rises, it expands and cools. Cooler air holds less water vapor, leading to condensation. This is why clouds form at higher altitudes where temperatures are lower. The sun's indirect role here lies in driving the air currents that lift the water vapor, creating the necessary conditions for condensation.
Cloud Formation: A Diverse Spectacle
The type of cloud formed depends on various factors, including temperature, altitude, and the amount of water vapor present. From wispy cirrus clouds to dense cumulonimbus clouds, all are the result of water vapor condensation, ultimately driven by the sun's energy.
Precipitation: Water Returns to Earth
Once water droplets in clouds become sufficiently large and heavy, they fall back to the earth as precipitation. This includes rain, snow, sleet, and hail. The sun's energy plays an indirect, yet crucial, role in this stage too.
The Sun's Influence on Precipitation Patterns: Indirect Yet Powerful
The sun's uneven heating of the Earth's surface creates atmospheric pressure differences, leading to wind patterns. These wind patterns influence the movement of clouds and the distribution of precipitation across the globe. Areas receiving more solar radiation experience higher temperatures, leading to increased evaporation and potentially heavier rainfall.
Precipitation's Importance: Sustaining Life and Shaping Landscapes
Precipitation is essential for replenishing water sources, sustaining plant and animal life, and shaping the Earth's landscapes through erosion and weathering. The distribution of precipitation is highly variable, leading to diverse ecosystems and climates around the world.
Runoff and Infiltration: Completing the Cycle
Once precipitation reaches the Earth's surface, it can either flow over the land as runoff or seep into the ground as infiltration. Both processes contribute to the continuous movement of water within the water cycle.
Runoff: Shaping Rivers and Landscapes
Runoff flows into streams, rivers, and eventually oceans, carrying dissolved minerals and sediments along the way. The speed and volume of runoff depend on factors like soil type, vegetation cover, and the intensity of rainfall. The sun's energy indirectly influences runoff by affecting the amount and intensity of precipitation.
Infiltration: Groundwater Recharge
Infiltration replenishes groundwater reserves, which act as vast underground reservoirs. The rate of infiltration is influenced by soil porosity and permeability. Infiltration plays a critical role in maintaining groundwater levels and supplying water to wells and springs.
The Interconnectedness of the Water Cycle Stages
It's crucial to understand that the stages of the water cycle are interconnected and constantly interacting. The sun's energy drives the continuous loop, ensuring the cycle's perpetuity. A change in one stage inevitably affects the others, highlighting the delicate balance within the hydrological system. For instance, deforestation can reduce transpiration, impacting cloud formation and precipitation patterns. Similarly, increased greenhouse gases can alter temperature patterns, leading to changes in evaporation and precipitation.
Conclusion: The Sun's Indispensable Role
The sun's energy is the fundamental driving force behind the water cycle. From the initial evaporation of water to the eventual return of precipitation, the sun's influence is felt at every stage. Understanding this interconnectedness is essential for managing our water resources effectively and adapting to the challenges of climate change. The sun's continued energy input is vital for maintaining the delicate balance of our planet's water cycle, ensuring the availability of this precious resource for all life on Earth. Further research into the intricacies of this cycle, particularly in the context of climate change, is crucial for securing a sustainable future. By appreciating the sun’s fundamental role, we can better understand and protect this vital process.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Charge Of A Sodium Ion
Apr 01, 2025
-
Do Lysosomes Have A Double Membrane
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True Of B Cells
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Many Parents Are Involved In Asexual Reproduction
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Order Of The Breakdown Products Of Hemoglobin
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Water Cycle Is Driven By The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
