The Tongue Is Made Of Smooth Muscle
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
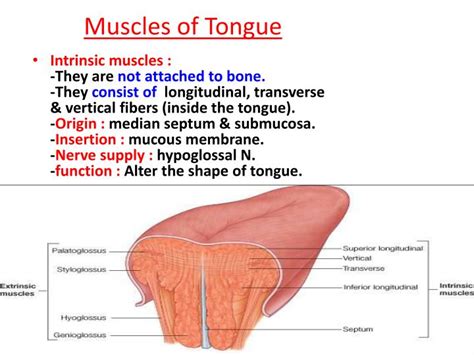
Table of Contents
The Tongue: A Symphony of Smooth Muscle
The human tongue, a marvel of biological engineering, is far more complex than a simple muscle. While skeletal muscle plays a significant role in its voluntary movements, the tongue's intricate structure and functionality rely heavily on the less-understood, yet equally crucial, smooth muscle. This article delves deep into the fascinating world of the tongue, highlighting the vital role smooth muscle plays in its diverse functions, from taste perception to speech articulation and swallowing.
The Multifaceted Anatomy of the Tongue
Before we delve into the specifics of smooth muscle, it's crucial to understand the tongue's overall anatomy. It's a complex organ composed of several types of muscle tissue, including:
-
Skeletal Muscle: The bulk of the tongue consists of intrinsic and extrinsic skeletal muscles. Intrinsic muscles, originating and inserting within the tongue, are responsible for fine movements like shaping the tongue for speech and manipulating food. Extrinsic muscles, originating outside the tongue and inserting into it, provide larger movements, controlling the tongue's position within the oral cavity.
-
Smooth Muscle: While less prominent than skeletal muscle, smooth muscle plays a critical, often overlooked role in various tongue functions. It is primarily located within the blood vessels supplying the tongue and in the walls of the glands that secrete saliva. This smooth muscle controls blood flow and glandular secretions, essential for maintaining the tongue's health and function.
-
Connective Tissue: Connective tissue provides structural support, binding the muscle fibers together and providing a framework for the tongue's shape. It also houses the tongue's rich network of blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels.
-
Mucous Membrane: The tongue is covered by a mucous membrane, a specialized epithelium that protects the underlying tissues and contributes to the sense of taste. This membrane contains taste buds, crucial for gustatory perception.
The Silent Maestro: Smooth Muscle's Role in Tongue Function
The seemingly minor presence of smooth muscle in the tongue belies its profound impact on overall function. Here's a breakdown of its crucial contributions:
1. Blood Flow Regulation: The Life Support System
Smooth muscle forms the walls of the blood vessels supplying the tongue. This muscle's ability to contract and relax allows precise regulation of blood flow, ensuring the tongue receives adequate oxygen and nutrients. This is critical for maintaining the health and functionality of the taste buds, muscle fibers, and other tongue tissues. Disruptions in smooth muscle function can lead to compromised blood supply, potentially impacting taste perception and tongue mobility.
Consider the physiological response to consuming spicy food. The increased blood flow to the tongue, partly regulated by the smooth muscle in its blood vessels, contributes to the sensation of heat and the resulting flush in the face.
2. Saliva Secretion: The Taste and Lubrication Engine
The tongue's salivary glands, vital for taste perception and lubrication during swallowing and speech, are heavily reliant on smooth muscle. Smooth muscle in the glandular walls controls the secretion of saliva, ensuring a constant, yet adjustable, supply. The precise control of salivary secretions by smooth muscle is crucial for maintaining optimal oral hygiene and facilitating comfortable swallowing. Insufficient saliva production can lead to dryness, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), and increased risk of oral infections.
3. Swallowing (Deglutition): A Coordinated Effort
Although skeletal muscle plays the primary role in the complex process of swallowing, smooth muscle contributes indirectly. The regulated blood flow, provided by the smooth muscle in the blood vessels, ensures adequate oxygen and nutrient supply to the skeletal muscles involved in swallowing. Moreover, the smooth muscle in the esophageal wall, although not strictly part of the tongue, plays a vital role in the peristaltic movements that propel the food bolus down the esophagus. This coordinated effort showcases the interconnectedness of muscle types in maintaining essential bodily functions.
4. Maintaining Tongue Structure and Integrity: The Underlying Support
The connective tissue framework of the tongue, while crucial for its structure, also requires the support of smooth muscle-regulated blood flow. This consistent blood supply ensures the health and integrity of this connective tissue, preventing degradation and maintaining the tongue's overall structural integrity. The smooth muscle's contribution to maintaining the connective tissue's health is often overlooked but essential for long-term tongue function.
Smooth Muscle Dysfunction and its Impact on the Tongue
Dysfunction in the smooth muscle of the tongue, though often subtle, can manifest in various ways:
-
Changes in Taste Perception: Compromised blood flow due to smooth muscle problems can lead to reduced sensitivity of taste buds, resulting in altered or diminished taste perception. This can be due to issues like vascular diseases or nerve damage affecting the smooth muscle control.
-
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia): Impaired smooth muscle function in the salivary glands can lead to insufficient saliva production, causing dry mouth. This can result in discomfort, difficulty swallowing, and an increased susceptibility to oral infections.
-
Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia): While primarily linked to skeletal muscle dysfunction, compromised smooth muscle in the esophageal wall can contribute to dysphagia. This can make swallowing difficult, sometimes painful, and might necessitate dietary modifications.
-
Structural Changes in the Tongue: Over time, inadequate blood supply caused by impaired smooth muscle function can lead to changes in the connective tissues, potentially altering the tongue's structure and flexibility.
Research and Future Directions
Further research is needed to fully understand the intricate role of smooth muscle in tongue function. Advanced imaging techniques and molecular studies could shed light on the precise mechanisms involved in smooth muscle regulation and its interplay with other tongue components. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to novel therapeutic strategies for various tongue-related disorders, including those affecting taste perception, swallowing, and overall tongue health.
Conclusion: A Holistic Perspective on the Tongue
The tongue, a seemingly simple organ, is a marvel of coordinated biological processes. While skeletal muscle commands the spotlight in terms of voluntary movement, smooth muscle quietly plays a crucial supporting role, ensuring optimal blood flow, saliva secretion, and overall tongue health. Understanding the intricacies of smooth muscle's contribution to tongue function is critical for advancing our knowledge of oral health, swallowing disorders, and taste perception. Further research is warranted to unlock the full potential of understanding this often-overlooked aspect of the human tongue. By appreciating the complex interplay of different muscle types, we can develop more comprehensive approaches to diagnosing and treating disorders related to the tongue and its vital functions. The future of this research promises a deeper understanding of the intricate mechanisms governing this remarkable organ and its contributions to our overall health and well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Approximate Range Of Human Hearing Is
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is Steel An Element Compound Or Mixture
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Is Not A Function Of The Respiratory System
Mar 28, 2025
-
Seven More Than Twice A Number Is Equal To 25
Mar 28, 2025
-
The Part Of Earth Where Life Exists
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Tongue Is Made Of Smooth Muscle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
