The Production Possibilities Frontier Will Shift Outward
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
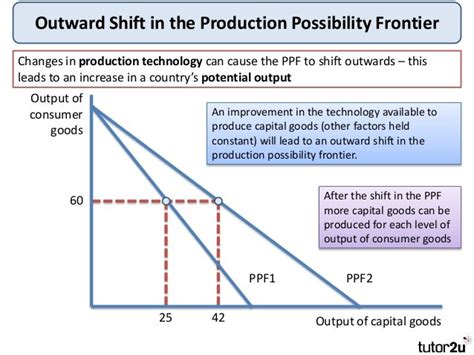
Table of Contents
The Production Possibilities Frontier: Shifting Outward Towards Growth
The Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF), also known as the Production Possibility Curve (PPC), is a fundamental concept in economics illustrating the maximum potential output of two goods or services an economy can achieve given its resources and technology. A key aspect of understanding the PPF lies in recognizing the factors that cause it to shift outward, representing economic growth and increased productive capacity. This article delves deep into the mechanisms that drive this outward shift, examining the crucial roles of technological advancements, increased resource availability, and improvements in human capital.
Understanding the Production Possibilities Frontier
Before exploring the outward shift, let's briefly review the core principles of the PPF. The curve itself represents the various combinations of two goods that an economy can produce when all its resources are fully and efficiently utilized. Points on the curve represent efficient production; points inside the curve indicate inefficient resource allocation, while points outside the curve are unattainable with the current resources and technology.
The PPF's downward slope reflects the concept of opportunity cost: producing more of one good requires sacrificing the production of another. The slope's steepness indicates the trade-off between the two goods. A steeper slope suggests a higher opportunity cost of producing one good in terms of the other.
Factors Shifting the PPF Outward: The Engines of Economic Growth
The outward shift of the PPF signifies economic growth, enabling an economy to produce more of both goods simultaneously. This expansion is fueled by several interconnected factors:
1. Technological Advancements: Innovation as a Catalyst
Technological advancements are arguably the most significant driver of PPF outward shifts. Innovation in production techniques, machinery, and processes leads to increased efficiency and productivity. This means that with the same amount of resources, an economy can now produce a greater quantity of goods and services.
-
Example: The invention of the assembly line drastically improved manufacturing efficiency, allowing for the mass production of automobiles and shifting the PPF outward. Similarly, advancements in agricultural technology, such as high-yield crop varieties and precision farming techniques, have significantly boosted food production.
-
Specific Impacts: Technological progress can manifest in several ways:
- Increased Productivity: New technologies often lead to higher output per unit of input (labor, capital, land).
- Reduced Costs: Innovations can lower the cost of production, making goods more affordable and increasing overall output.
- New Products and Services: Technological breakthroughs can create entirely new industries and products, expanding the possibilities beyond the initial two goods considered in the PPF model.
2. Increased Resource Availability: Expanding the Productive Base
An increase in the quantity or quality of resources available to an economy directly contributes to an outward shift of the PPF. This includes:
-
Labor: A growing and increasingly skilled workforce expands the potential labor input for production. Immigration, improved education and training, and increased female participation in the workforce all contribute to a larger and more productive labor pool.
-
Capital: Investment in physical capital (machinery, equipment, infrastructure) and human capital (education, training, healthcare) significantly enhances productivity. More advanced capital goods allow for greater efficiency and output.
-
Land: The discovery of new resources, improved land management techniques, and reclamation of previously unusable land all increase the productive capacity of an economy. However, the availability of land is often a more limiting factor than labor or capital, especially in densely populated regions.
-
Natural Resources: The discovery of new natural resources, such as oil reserves or mineral deposits, or improvements in extraction technologies, allows for increased production of goods reliant on these resources. Sustainable resource management is crucial to ensure long-term resource availability and avoid environmental degradation.
3. Improvements in Human Capital: Investing in People
Human capital, encompassing the skills, knowledge, and experience of the workforce, is a critical determinant of productivity. Investments in education, training, healthcare, and overall well-being directly impact the quality of the labor force and consequently shift the PPF outward.
-
Education and Training: A highly educated and skilled workforce is more productive and adaptable to technological changes. This leads to higher output per worker and an overall improvement in economic efficiency.
-
Healthcare: A healthy population is a productive population. Improved healthcare leads to a healthier and more energetic workforce, reducing absenteeism and increasing overall productivity.
-
Skills Development: Continuous learning and adaptation to technological advancements are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Investing in lifelong learning and skills development programs helps workers adapt to changing job demands.
4. Institutional Improvements: Creating a Conducive Environment
While often overlooked, improvements in the institutional framework of an economy play a significant role in driving economic growth and shifting the PPF outward. This includes:
-
Strong Property Rights: Secure property rights encourage investment and innovation, as individuals and businesses are confident that their investments will be protected.
-
Stable Political Environment: A stable and predictable political environment reduces uncertainty and encourages long-term investment.
-
Efficient Legal System: An efficient and impartial legal system is essential for resolving disputes and enforcing contracts, providing a stable framework for economic activity.
-
Reduced Corruption: Corruption undermines economic efficiency by diverting resources away from productive activities. Reducing corruption fosters a more transparent and efficient economic environment.
-
Sound Economic Policies: Effective macroeconomic policies, such as fiscal and monetary policies, can stabilize the economy, promote investment, and foster economic growth.
5. International Trade: Access to Global Markets
International trade can also indirectly contribute to an outward shift of the PPF. By specializing in the production of goods and services where a country has a comparative advantage, trade allows for increased consumption beyond what the country could produce domestically. This is not a direct shift of the PPF, but rather an expansion of the consumption possibilities frontier.
Implications of an Outward Shift
The outward shift of the PPF signifies economic progress and improved living standards. It implies that the economy is becoming more efficient and productive, leading to:
- Increased Output: The economy can produce more of both goods simultaneously.
- Higher Standards of Living: Increased output translates into greater consumption possibilities, improved quality of life, and higher incomes.
- Greater Economic Opportunities: Economic growth creates new job opportunities and encourages innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Improved Social Welfare: Economic growth often leads to improvements in education, healthcare, and other social programs.
Limitations of the PPF Model
It's crucial to acknowledge that the PPF model, while valuable, simplifies a complex reality. It makes several assumptions:
- Fixed Resources: The model assumes a fixed quantity of resources in the short run. In the long run, resources can change, influencing the PPF's shape and position.
- Fixed Technology: The model assumes a fixed level of technology. Technological progress directly impacts the PPF's outward shift.
- Two Goods Only: The model simplifies the economy by focusing on only two goods, neglecting the diversity of products and services in a real-world economy.
- Full Employment: The PPF assumes full utilization of resources. In reality, economies often operate at less than full employment.
Conclusion: Sustainable Growth Through Strategic Investment
The outward shift of the Production Possibilities Frontier is a testament to economic growth and prosperity. Understanding the factors that drive this shift—technological advancements, increased resource availability, human capital development, and improved institutions—is crucial for policymakers seeking to foster sustainable and inclusive economic development. Strategic investments in these areas, coupled with sound economic policies, are vital for achieving long-term economic progress and improving the well-being of society. The challenge lies in harnessing these drivers of growth responsibly, considering environmental sustainability and equitable distribution of the benefits of economic progress. A focus on innovation, education, and good governance remains paramount to ensure a continual outward shift of the PPF and a brighter economic future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Helicopter Lifts A 72 Kg Astronaut
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Capacitance Is Required To Store An Energy Of
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Major Product Of The Following Reaction Sequence
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Lightyears Is The Sun
Mar 14, 2025
-
Convert Timestamp To Date Time Python
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Production Possibilities Frontier Will Shift Outward . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
