The Number Of Protons In An Atom Is Called What
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
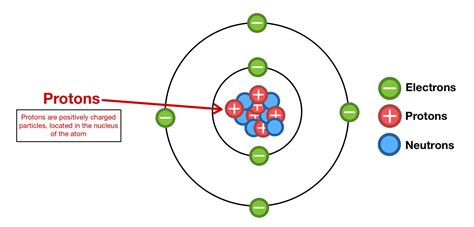
Table of Contents
- The Number Of Protons In An Atom Is Called What
- Table of Contents
- The Number of Protons in an Atom is Called What? Understanding Atomic Number and its Significance
- What is Atomic Number?
- Why is Atomic Number Important?
- How is Atomic Number Determined?
- Spectroscopy: A Powerful Tool
- Mass Spectrometry: Measuring Mass-to-Charge Ratio
- Atomic Number and the Periodic Table
- Periodic Trends
- Predicting Properties
- Atomic Number in Different Scientific Disciplines
- Chemistry
- Nuclear Physics
- Astrophysics
- Materials Science
- Medical Physics
- Conclusion: The Foundation of Chemistry and Beyond
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Number of Protons in an Atom is Called What? Understanding Atomic Number and its Significance
The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is a fundamental property defining its identity and behavior. This crucial number is known as the atomic number. Understanding atomic number is key to comprehending the structure of matter, the periodic table, and the behavior of elements in chemical reactions. This article delves deep into the concept of atomic number, exploring its significance, how it's determined, and its implications in various scientific fields.
What is Atomic Number?
The atomic number, often represented by the symbol Z, is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom. Protons, along with neutrons, constitute the atom's nucleus, while electrons orbit the nucleus in shells or energy levels. Unlike neutrons, which contribute to an atom's mass but not its charge, protons carry a positive charge. This positive charge is balanced by the negative charge of the electrons, resulting in a neutral atom. The atomic number uniquely identifies an element. No two elements share the same atomic number.
Why is Atomic Number Important?
The atomic number is arguably the most important characteristic of an atom because:
-
Element Identity: It uniquely defines each element. Hydrogen (H), with one proton, has an atomic number of 1. Helium (He), with two protons, has an atomic number of 2, and so on. The periodic table organizes elements primarily by their atomic numbers, reflecting their inherent properties.
-
Chemical Properties: The number of protons dictates the number of electrons in a neutral atom. These electrons determine how an atom interacts with other atoms, forming chemical bonds and influencing the element's chemical properties (reactivity, bonding behavior, etc.). Elements in the same column of the periodic table share similar chemical properties primarily due to having the same number of valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost shell and most involved in chemical bonding.
-
Isotopes: While the number of protons defines the element, the number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers (the sum of protons and neutrons). For example, Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon, both having an atomic number of 6 but differing in their neutron count (6 and 8, respectively).
-
Nuclear Reactions: Atomic number is crucial in understanding nuclear reactions, such as radioactive decay and nuclear fusion. These reactions often involve changes in the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, leading to the formation of different elements or isotopes.
How is Atomic Number Determined?
Determining the atomic number of an element involves various techniques, primarily focusing on analyzing the element's spectral lines and its interaction with electromagnetic radiation.
Spectroscopy: A Powerful Tool
Spectroscopy is a key method for determining the atomic number. Each element emits a unique spectrum of light when its electrons transition between energy levels. This unique spectral fingerprint is like a "barcode" for the element. By analyzing the wavelengths of light emitted, scientists can identify the element and deduce its atomic number. Different spectroscopic techniques, such as atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and atomic emission spectroscopy (AES), are used depending on the sample and required sensitivity.
Mass Spectrometry: Measuring Mass-to-Charge Ratio
Mass spectrometry is another powerful tool used to determine atomic number indirectly. While mass spectrometry primarily measures the mass-to-charge ratio of ions, by analyzing the isotopic composition and mass spectrum, the number of protons can be inferred. Knowing the mass number and the number of neutrons (determined from the isotopic abundance), one can calculate the number of protons (atomic number).
Atomic Number and the Periodic Table
The periodic table's organization is fundamentally based on the atomic number. Elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic number, revealing periodic trends in their physical and chemical properties.
Periodic Trends
The periodic table's structure reflects the periodic recurrence of similar electron configurations and resulting properties. For instance, elements within the same group (vertical column) share similar chemical properties due to having the same number of valence electrons. Moving across a period (horizontal row), the atomic number increases, and the properties gradually change, reflecting the filling of electron shells and the resulting changes in electronegativity, ionization energy, and atomic size.
Predicting Properties
The atomic number helps predict an element's properties. Knowing the atomic number, one can deduce the electron configuration, which in turn helps predict the element's reactivity, bonding preference, and other chemical properties. This predictive power is invaluable in materials science, chemical engineering, and other fields.
Atomic Number in Different Scientific Disciplines
The concept of atomic number plays a pivotal role in numerous scientific disciplines:
Chemistry
In chemistry, the atomic number is fundamental to understanding chemical bonding, reactivity, and the behavior of matter. It dictates the number of electrons available for bonding, influencing an element's oxidation state, its ability to form various types of bonds (ionic, covalent, metallic), and its overall chemical behavior.
Nuclear Physics
In nuclear physics, the atomic number is essential in understanding nuclear reactions, radioactive decay, and nuclear stability. Nuclear reactions often involve changes in the number of protons and neutrons, leading to changes in the atomic number and the formation of new elements.
Astrophysics
Atomic number is crucial in astrophysics for understanding the composition of stars and other celestial objects. The abundance of different elements in stars is determined by analyzing their spectra, which reveals their atomic composition, including the number of protons in their constituent atoms. Stellar nucleosynthesis, the process by which elements are created in stars, is deeply intertwined with changes in atomic number.
Materials Science
In materials science, atomic number plays a critical role in understanding the properties of materials. The atomic number influences the electronic structure and bonding characteristics, which determine a material's mechanical properties (strength, hardness, ductility), electrical properties (conductivity, resistivity), and thermal properties (melting point, heat capacity).
Medical Physics
In medical physics, the atomic number is crucial in radiation therapy and medical imaging. Different elements have different interaction probabilities with radiation, which is used in techniques like X-ray imaging and radiation therapy. The atomic number of the target tissue or element is a key factor in determining the effectiveness of radiation treatment.
Conclusion: The Foundation of Chemistry and Beyond
The number of protons in an atom, the atomic number, is not merely a numerical value; it's the fundamental identifier of an element and the key to understanding its behavior. This seemingly simple number unlocks a vast landscape of scientific knowledge, driving advancements in chemistry, physics, materials science, and numerous other fields. Its significance extends far beyond the textbook definition, shaping our understanding of the universe at both the macroscopic and microscopic scales. From the periodic table's organization to the intricacies of nuclear reactions and the composition of stars, the atomic number serves as an essential cornerstone of modern scientific understanding. Continued research and exploration in atomic physics and related fields promise even deeper insights into the profound implications of this fundamental atomic property.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In The Figure A Solid Cylinder Of Radius
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Percent Of 30 Is 20
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Right Angles Does A Hexagon Have
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Tail Of A Phospholipid Made Of
Mar 26, 2025
-
Independent Pairs Segregate Independently Of Each Other
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Number Of Protons In An Atom Is Called What . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
