The Electrons Present In The Outermost Shell Are Called
News Leon
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
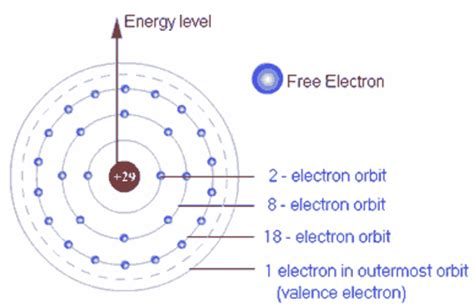
Table of Contents
The Electrons Present in the Outermost Shell Are Called Valence Electrons: A Deep Dive
The electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom are called valence electrons. These electrons are crucial in determining an element's chemical properties, reactivity, and the types of bonds it can form. Understanding valence electrons is fundamental to grasping the principles of chemical bonding, molecular structure, and the behavior of matter. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of valence electrons, their significance, and their role in various chemical phenomena.
What are Valence Electrons?
Valence electrons are the electrons located in the highest energy level or outermost shell of an atom. This outermost shell is also often referred to as the valence shell. The number of valence electrons an atom possesses dictates its reactivity and how it interacts with other atoms. Atoms strive for stability, often achieved by having a full valence shell, usually containing eight electrons (the octet rule), although this rule has exceptions, particularly for elements in the first few rows of the periodic table.
How to Determine the Number of Valence Electrons
Determining the number of valence electrons can be done in several ways:
-
Using the periodic table: The group number (vertical column) of an element in the periodic table, excluding transition metals (groups 3-12), directly indicates the number of valence electrons. For example, elements in Group 1 (alkali metals) have one valence electron, elements in Group 2 (alkaline earth metals) have two, and so on, up to Group 18 (noble gases) which generally have eight (except helium, which has two).
-
Using the electron configuration: The electron configuration shows how electrons are distributed among the different energy levels and subshells within an atom. The valence electrons are those in the highest principal energy level (n). For example, the electron configuration of oxygen is 1s²2s²2p⁴. The highest principal energy level is n=2, and the electrons in this level (2s²2p⁴) are the valence electrons, totaling six.
-
Using Lewis dot structures: Lewis dot structures are simplified diagrams that represent the valence electrons of an atom as dots surrounding the element's symbol. Each dot represents a single valence electron. This method provides a visual representation of an atom's valence electrons and is particularly useful for understanding chemical bonding.
The Significance of Valence Electrons
The significance of valence electrons cannot be overstated. They are the primary players in chemical reactions and dictate how atoms interact with one another. Their role can be summarized as follows:
-
Chemical Bonding: Valence electrons are directly involved in the formation of chemical bonds. Atoms tend to interact with each other to achieve a stable electron configuration, often a full valence shell. This interaction can occur through several types of bonds:
-
Ionic bonds: These bonds form when one atom transfers one or more valence electrons to another atom. This transfer results in the formation of ions – positively charged cations (atoms that lose electrons) and negatively charged anions (atoms that gain electrons). The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions forms the ionic bond. An example is the formation of sodium chloride (NaCl) where sodium (Na) loses one valence electron to chlorine (Cl), forming Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions.
-
Covalent bonds: These bonds form when atoms share valence electrons. This sharing allows both atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration. Covalent bonds are common in molecules composed of nonmetals. Examples include water (H₂O) and methane (CH₄).
-
Metallic bonds: These bonds occur in metals, where valence electrons are delocalized and shared among a large number of metal atoms. This creates a "sea" of electrons that holds the metal atoms together. This delocalization accounts for many properties of metals such as electrical and thermal conductivity and malleability.
-
-
Reactivity: The number of valence electrons directly influences an element's reactivity. Atoms with nearly full or nearly empty valence shells are generally more reactive than those with half-filled or completely filled shells. For instance, elements in Group 1 and Group 7 (halogens) are highly reactive because they have one and seven valence electrons respectively, and readily lose or gain an electron to achieve a stable octet. Noble gases, with their full valence shells, are largely unreactive.
-
Predicting Properties: The number of valence electrons allows us to predict certain properties of elements and compounds. For example, the boiling point and melting point of substances are often related to the type and strength of the bonds formed by valence electrons.
Valence Electrons and the Periodic Table
The periodic table is organized in a way that reflects the electron configurations of elements, and consequently, their valence electrons. This organization allows us to predict the properties of elements based on their position on the table.
Groups and Valence Electrons
Elements within the same group (vertical column) of the periodic table share the same number of valence electrons. This similarity in valence electrons leads to similar chemical properties and reactivity patterns within a group.
Periods and Energy Levels
Elements within the same period (horizontal row) have valence electrons in the same principal energy level (n). As you move across a period, the number of valence electrons increases, resulting in a gradual change in properties.
Exceptions to the Octet Rule
While the octet rule is a useful guideline, there are exceptions:
-
Incomplete octets: Some elements, particularly those in the second row (like beryllium and boron), can have fewer than eight valence electrons in their stable compounds.
-
Expanded octets: Elements in the third row and beyond can have more than eight valence electrons in their stable compounds due to the availability of d orbitals. For example, phosphorus can form compounds with ten valence electrons.
-
Odd-electron species: Some molecules have an odd number of valence electrons, making it impossible to satisfy the octet rule for all atoms.
Advanced Concepts Related to Valence Electrons
-
Formal Charge: Formal charge helps determine the most stable Lewis structure by assigning charges to atoms based on the distribution of valence electrons.
-
Resonance Structures: Some molecules have multiple valid Lewis structures, known as resonance structures, where the actual structure is a hybrid of these contributing structures. The distribution of valence electrons influences the resonance stability.
-
Oxidation States: The oxidation state of an atom represents its apparent charge based on the assumption that all bonds are purely ionic. It is based on the number of valence electrons lost or gained.
-
Hybridization: The mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals helps explain the molecular geometry and bonding in certain molecules. The number and arrangement of valence electrons play a key role in determining hybridization.
Conclusion
Valence electrons are fundamental to our understanding of chemistry. Their number and arrangement determine the chemical behavior, bonding characteristics, and properties of elements and compounds. By understanding the concepts outlined in this article, we can predict and explain a wide range of chemical phenomena, from the formation of simple molecules to the complex reactions that drive life itself. This in-depth understanding opens doors to advanced chemical concepts and lays the groundwork for further exploration in fields like materials science, biochemistry, and nanotechnology. The seemingly simple concept of valence electrons holds the key to unlocking a universe of chemical possibilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Value Of Log7 343
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Universal Start Codon
Apr 06, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of A Colloid
Apr 06, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Molecules Has The Shortest Bond Length
Apr 06, 2025
-
Carbon Dioxide Pure Substance Or Mixture
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Electrons Present In The Outermost Shell Are Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
